A) downward sloping; vertical
B) downward sloping; horizontal
C) upward sloping; vertical
D) upward sloping; horizontal
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various price and output levels in an economy. 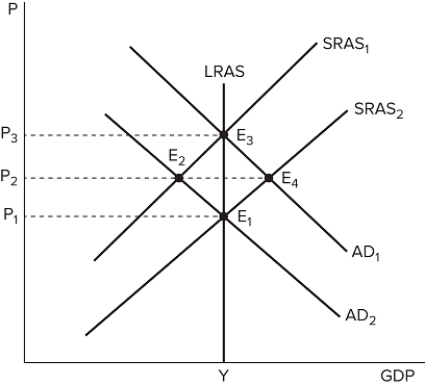 If the economy is currently at point E1, it must be in:
If the economy is currently at point E1, it must be in:
A) long-run equilibrium.
B) a recession.
C) an economic boom.
D) an economic recovery.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation:
A) reduces the level of aggregate demand in the economy.
B) increases the level of aggregate demand in the economy.
C) does not affect the level of aggregate demand in the economy.
D) reduces the level of aggregate supply in the economy.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neutrality of money is the idea that:
A) changes in aggregate price levels do not affect real outcomes in the economy.
B) monetary policy conducted by the Fed has no real impact on the economy.
C) it makes no difference who is spending each dollar in real terms.
D) there is no difference between fiscal and monetary policy as long as the same amount of money is injected into the economy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economists agree that stable economies generate inflation of around:
A) ten percent.
B) two to three percent.
C) five to six percent.
D) seven percent.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Headline inflation is:
A) core inflation plus the prices of food and energy.
B) core inflation seasonally adjusted.
C) the change in prices of inputs used by Fortune 500 companies.
D) core inflation minus the price of inputs.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the real value of your savings decreases over time:
A) the real rate of interest is positive.
B) inflation is zero.
C) the real rate of interest is negative.
D) the real rate of interest is zero.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the quantity equation?
A) M × V = P × Y
B) M × P = Y × V
C) P × V = M × Y
D) M × Y = P × V
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A temporary change in the price level caused by changes in the business cycle is known as:
A) demand-pull inflation.
B) cost-push inflation.
C) demand-push inflation.
D) cost-pull inflation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Core inflation:
A) excludes goods with historically volatile price changes.
B) is the overall rise in prices in the economy.
C) excludes durable goods.
D) is not regularly tracked by the BLS.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the nominal interest rate is the same as the real interest rate, then inflation must be:
A) zero.
B) higher than the nominal rate of interest.
C) lower than the nominal rate of interest.
D) negative.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The money, time, and opportunity used to change prices to keep pace with inflation are called:
A) menu costs.
B) shoe-leather costs.
C) tax distortions.
D) the velocity of inflation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If unemployment is below the NAIRU, inflation generally:
A) accelerates.
B) decelerates.
C) becomes negative.
D) gets caught in a downward spiral.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brian is paid monthly via a direct deposit into an interest-bearing checking account. He withdraws $500 of this pay in cash at the beginning of the month to spend throughout it. However, due to recent inflation, Brian decides to instead withdraw $125 from the bank every week, so that his money can earn interest for as long as possible. The time and energy Brian spends visiting the bank more often would be classified as a:
A) shoe-leather cost.
B) menu cost.
C) transactions cost.
D) tax distortion.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown provides CPI values for various years. 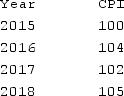 What was the inflation rate in 2016?
What was the inflation rate in 2016?
A) 2.9 percent
B) −1.9 percent
C) 1.9 percent
D) 4 percent
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which measure of inflation best reflects changing prices for the average consumer?
A) Headline inflation
B) Core inflation
C) The Producer Price Index
D) The GDP deflator
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various price and output levels in an economy. 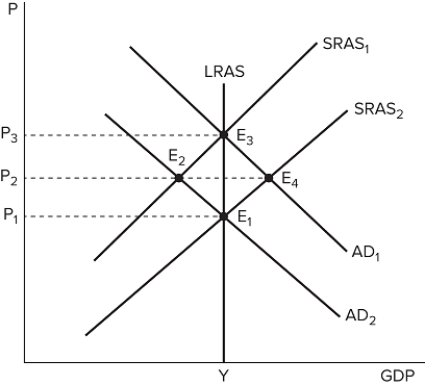 If the economy is currently at point E3, it must be in:
If the economy is currently at point E3, it must be in:
A) long-run equilibrium.
B) a recession.
C) an economic expansion.
D) an economic recovery.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various price and output levels in an economy.  What does the "P" on the y-axis stand for?
What does the "P" on the y-axis stand for?
A) Average price level
B) Inflation rate
C) Price of GDP
D) Price of Y
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation is:
A) a sustained rise in the aggregate price level.
B) negative inflation.
C) as common as inflation.
D) a decline in inflation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces 1,000 units of output when the price level is $5 and the money supply is $1,000, what is the velocity of money?
A) 5
B) 200
C) 50
D) 2
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 151
Related Exams