A) inflation.
B) deflation.
C) the consumer price index.
D) the producer price index.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nominal output is the _______ of goods and services produced and real output is the _______ of goods and services produced.
A) dollar value; actual amount
B) actual amount; dollar value
C) actual amount; dollar value with inflation
D) dollar value with inflation; dollar value without inflation
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed conducts expansionary monetary policy, it _______ in the short run, but _______ in the long run.
A) boosts demand; causes inflation
B) causes inflation; boosts output
C) causes inflation; boosts economic growth
D) boosts demand; boosts supply
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the annual nominal interest rate is 4 percent and the inflation rate is 5 percent. If you deposit $1,000, at the end of the year:
A) you will have earned a real rate of return of 1 percent.
B) your purchasing power will have increased.
C) your savings will have a nominal increase of $40.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between the money supply, output, and the overall price level is illustrated by the:
A) classical theory of inflation.
B) neutrality of money.
C) aggregate price level.
D) measure of real output.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity equation implies that any decrease in the money supply will lead directly to:
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in the price level.
C) an increase in real output.
D) a decrease in real output.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economy experiences deflation, consumption decreases because:
A) people will wait for prices to drop before spending.
B) shoe-leather costs increase.
C) savings accounts lose value.
D) the prices of imports increase.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation is a:
A) sustained fall in the aggregate price level.
B) sustained increase in the aggregate price level.
C) steady, unchanging aggregate price level.
D) steady fall in the exchange rate.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Menu costs refer to:
A) the money, time, and opportunity used to change prices to keep pace with inflation.
B) the time, money, and effort one has to spend managing cash in the face of inflation.
C) the higher taxes one must pay when earning a greater dollar amount, even though real purchasing power hasn't changed.
D) the labor costs associated with inflation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation _______consumption and investment, which _______.
A) decreases; decreases aggregate demand
B) decreases; maintains aggregate demand
C) increases; maintains aggregate demand
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When interest rates are already at zero during a recession, a central bank would:
A) have little leeway to further reduce interest rates in order to stimulate the economy.
B) not be able to engage in any type of policy to stimulate the economy.
C) need to spend more money in order to stimulate the economy.
D) likely work with Congress to stimulate the economy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a central bank uses contractionary monetary policy, _______ is most likely to occur.
A) disinflation
B) inflation
C) deflation
D) stagflation
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various price and output levels in an economy. 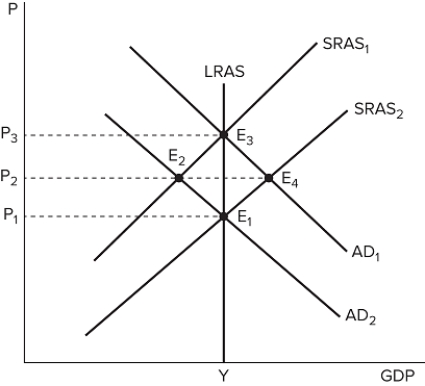 If the economy is currently at point E3, what could be said about its unemployment?
If the economy is currently at point E3, what could be said about its unemployment?
A) There is higher unemployment than the natural rate.
B) There is lower unemployment than the natural rate.
C) The unemployment rate is near the natural rate.
D) The unemployment rate is zero.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various price and output levels in an economy. 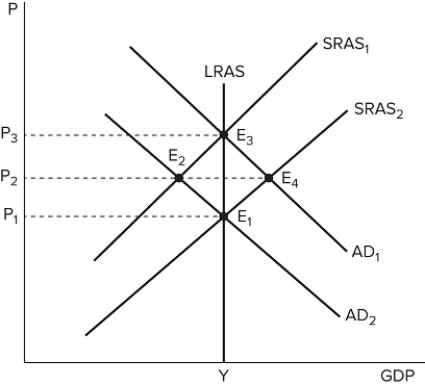 Which point on the graph shown would represent an economic expansion?
Which point on the graph shown would represent an economic expansion?
A) E 1
B) E 2
C) E 3
D) E 4
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual quantity of goods or services sold is measured in:
A) nominal values.
B) real values.
C) aggregated values.
D) intermediate values.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _______ price level is a measure of the average price level for GDP.
A) aggregate
B) national
C) economy
D) total
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the real rate of return is 2 percent and the inflation rate is 2 percent, the nominal interest rate is:
A) 4 percent.
B) 2 percent.
C) −2 percent.
D) −4 percent.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed were to push unemployment below the NAIRU:
A) inflation would likely increase.
B) deflation would likely send the economy into a deflationary spiral.
C) the dual mandate will have been met.
D) the economy would be operating efficiently.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Subtracting the inflation rate from the nominal rate of interest gives us the:
A) nominal rate of return.
B) real interest rate.
C) real rate of inflation.
D) price level of the economy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The inability to conduct expansionary monetary policy at the zero lower bound is also known as:
A) stagflation.
B) a liquidity trap.
C) crowding out.
D) Ricardian equivalence.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 151
Related Exams