A) banks only need to keep a portion of each deposit on hand.
B) the money multiplier is equal to 1.
C) banks cannot create money in the economy.
D) lending would be curtailed to nearly zero.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which tool does the Fed use most often to change the money supply?
A) Open market operations
B) The reserve requirement
C) The discount window
D) All of these are used with equal frequency.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chair of the Federal Reserve:
A) is responsible for regulating the banking system.
B) has significant direct control over the conduct of monetary policy by the central bank.
C) is generally a partisan political appointment.
D) All of these are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A larger money multiplier means:
A) the reserve ratio must be smaller.
B) a bank can loan out less.
C) less money is created in the economy.
D) private demand for loans will be higher.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The twin responsibilities of the Federal Reserve are to:
A) maintain full employment and balance the federal budget.
B) ensure price stability and maintain full employment.
C) ensure price stability and regulate international trade.
D) print money and ensure price stability.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the money multiplier is 4, the reserve ratio is:
A) 25 percent.
B) 2.5 percent.
C) 5 percent.
D) 4 percent.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate charged for loans through the discount window is called the:
A) discount rate.
B) reserve rate.
C) federal funds rate.
D) prime rate.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assets regularly used to purchase goods and services are called:
A) money.
B) consumption income.
C) disposable income.
D) fungible goods.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays the relationship between money and the interest rate. 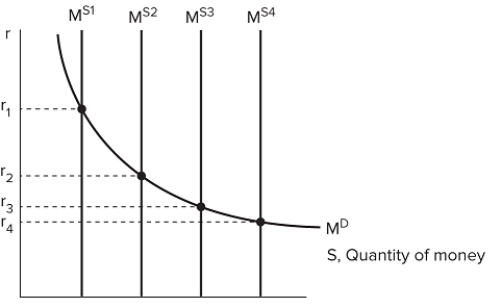 If the money supply in the economy is currently at MS3, to engage in expansionary policy the Fed would use open market operations to move the money supply to which point?
If the money supply in the economy is currently at MS3, to engage in expansionary policy the Fed would use open market operations to move the money supply to which point?
A) M S1
B) M S2
C) M S4
D) The money supply would remain at M S3.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the simple liquidity preference model, changes to the money supply will have a smaller effect on interest rates when the money demand curve:
A) is more elastic.
B) is less elastic
C) shifts to the right.
D) is perfectly inelastic.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the main roles of a central bank is:
A) managing the nation's money demand.
B) coordinating the banking system to ensure a sound economy.
C) accepting deposits from households and other private individuals.
D) funding federal government spending.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Expansionary monetary policy _______ the interest rate and _______ the price level.
A) decreases; increases
B) decreases; decreases
C) increases; increases
D) increases; decreases
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there were no fractional reserve banking:
A) the reserve ratio would be zero percent.
B) banks would not create money in the economy.
C) a very small amount of lending using deposits would occur.
D) account holders would not be able to withdraw their money in times of recession.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is providing a medium of exchange an important role of money?
A) It makes the economy much more efficient by reducing transaction costs.
B) It helps the government tax its citizens.
C) It allows consumers to more easily compare different transactions.
D) It provides a long-term place to store value.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Money is:
A) the set of all assets regularly used to purchase goods and services.
B) the amount of currency in our economy.
C) controlled by the supply and demand of goods and services.
D) anything used to buy goods and services if it is not a good itself.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a major danger of fiat money?
A) Its value may not be stable if the government prints a lot more money.
B) There is often not enough of a resource to use it for money.
C) The value of fiat currency may stay locked in place and stifle the economy.
D) It can be costly to exchange money for the commodity that backs it.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The money multiplier:
A) was relatively stable until 2008, when it dropped dramatically.
B) was relatively stable until 2008, when it rose dramatically.
C) has historically followed the business cycle.
D) runs contrary to the business cycle.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Reserve System consists of:
A) twelve regional banks and a 7-member Board of Governors.
B) a twelve-member Board of Governors and 7 regional banks.
C) twelve regional banks and 7 member banks.
D) twelve member banks and 7 regional banks.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ratio of money created by the lending activities of the banking system to the money created by the government's central bank is called the:
A) money multiplier.
B) reserve ratio.
C) federal funds.
D) demand deposits.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The discount window allows the Federal Reserve to fulfill its responsibility:
A) as a lender of last resort.
B) to keep the economy at full employment.
C) of increasing the money supply.
D) to conduct fiscal policy.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 146
Related Exams