A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) contractionary monetary policy.
D) expansionary monetary policy.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various economic outcomes. 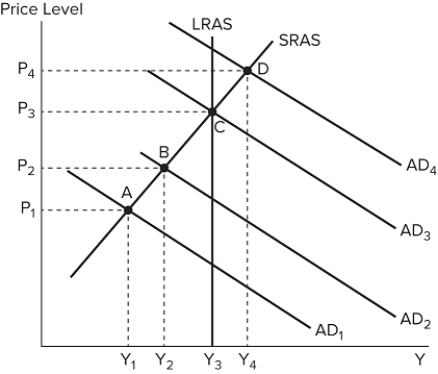 If the economy is currently at equilibrium B, and the government enacts contractionary fiscal policy, in the short run the economy will most likely:
If the economy is currently at equilibrium B, and the government enacts contractionary fiscal policy, in the short run the economy will most likely:
A) move to equilibrium A.
B) remain at equilibrium B.
C) move to equilibrium C.
D) move to equilibrium D.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After a devastating hurricane hits the Gulf Coast of Florida, Congress authorizes $50 billion in emergency spending to help families rebuild. Assuming the government already spends more than it makes in revenue, this plan will:
A) increase the debt by $50 billion.
B) increase the deficit by $50 billion.
C) increase the debt and deficit by $50 billion each.
D) increase the debt by $100 billion and the deficit by $50 billion.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The longest-term securities sold by the United States are:
A) Treasury bonds.
B) Treasury notes.
C) certificates of deposit.
D) Treasury bills.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increased government spending on unemployment insurance during a recession is an example of:
A) an automatic stabilizer.
B) discretionary fiscal policy.
C) expansionary fiscal policy.
D) contractionary fiscal policy.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy is:
A) that which the government chooses to adopt.
B) affected by taxes and government spending, without specific action from policymakers.
C) that which the government enacts only for a short period of time.
D) taxes and government spending Congress does not adopt.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A budget surplus is the:
A) amount of money a government spends beyond the net revenue it brings in.
B) amount of net revenue a government brings in beyond what it spends.
C) total amount of money that a government owes to creditors.
D) total amount of money that a government receives from a tax increase.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government increases payments to dairy farmers for their excess supply:
A) interest rates will decrease.
B) aggregate demand will increase.
C) contractionary fiscal policy will be enacted.
D) None of these are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lack of understanding regarding the current state of the economy creates a(n) _______ lag.
A) information
B) formulation
C) implementation
D) direction
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government can enact contractionary fiscal policy by:
A) reducing its spending.
B) decreasing personal income taxes.
C) decreasing corporate income taxes.
D) All of these are ways to enact contractionary fiscal policy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the country of Piedmont borrows money to start a brand-new infrastructure program. GDP is currently $400 billion. The plan will take the public debt from $250 billion to $350 billion in ten years, when GDP is projected to be $425 billion. What is the projected debt in ten years as a percentage of GDP?
A) 59 percent
B) 62.5 percent
C) 70 percent
D) 82.4 percent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays various economic outcomes. 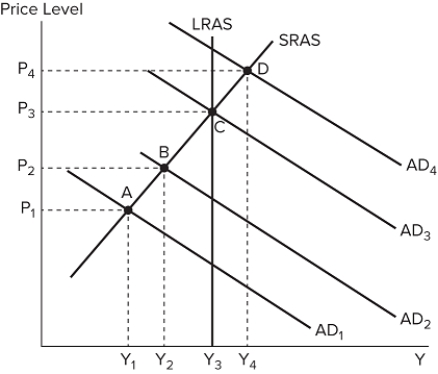 If the economy is currently at equilibrium D, and the government does nothing, then eventually:
If the economy is currently at equilibrium D, and the government does nothing, then eventually:
A) SRAS will shift to the right, and the economy will have Y 3 output with lower prices.
B) SRAS will shift to the left, and the economy will have Y 3 output at higher prices.
C) LRAS will shift to the left until equilibrium is reached.
D) AD will shift to the right, restoring long-run equilibrium.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_______ are protected against inflation.
A) Treasury bonds
B) Treasury notes.
C) TIPS
D) Treasury bills
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy that the government chooses to adopt is called:
A) an automatic stabilizer.
B) discretionary fiscal policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) contractionary policy.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government decisions about the level of taxation and public spending are called:
A) fiscal policy.
B) monetary policy.
C) congressional policy.
D) legislative budgeting policy.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The shortest-term securities sold by the U.S. are:
A) Treasury bonds.
B) Treasury notes.
C) certificates of deposit.
D) Treasury bills.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy:
A) can magnify the automatic stabilization effects of existing policies.
B) only magnifies the automatic stabilizer effects of policies that stimulate the economy.
C) often counters the effect of automatic stabilizers that already exist.
D) None of these are true.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government were to increase taxes, it would be enacting:
A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) expansionary fiscal policy.
C) contractionary monetary policy
D) expansionary monetary policy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the SRAS curve shifts to the left, the economy faces lower output and higher prices, otherwise known as stagflation. If the government then enacts expansionary fiscal policy, what will be the effect on the economy?
A) Higher output and higher prices
B) Higher output and lower prices
C) Lower output and lower prices
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government enacts fiscal policy:
A) long-run potential output is always decreased.
B) the intervention takes a long time to actually occur.
C) the economy returns to its long-run equilibrium more quickly than it can correct itself.
D) All of these are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 122
Related Exams