A) Long-run supply shock
B) Short-run supply shock
C) Demand shock
D) Change in price level
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government is considering whether it should change its spending in response to a recession, it must weigh the trade-off between _______ and _______.
A) a faster recovery time; inflation
B) less output; higher prices
C) more output; lower prices
D) a faster recovery time; lower prices
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate demand curve is downward-sloping partly due to the _______ relationship between the price level and _______.
A) positive; net exports
B) negative; net exports
C) positive; government spending
D) negative; government spending
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a component of aggregate demand?
A) Net exports
B) Income
C) Government revenues
D) Interest rates
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the U.S. price level decreases, we would expect a(n) _______ the aggregate demand curve.
A) downward movement along
B) leftward shift of
C) rightward shift of
D) upward movement along
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the U.S. price level decreases relative to the rest of the world:
A) exports and net exports will increase.
B) imports and net exports will increase.
C) exports will increase and net exports will decrease.
D) exports will decrease and net exports will increase.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the economy is producing at a quantity greater than its long-run aggregate supply:
A) it is pushing some of its resources to operate beyond capacity.
B) it is experiencing greater economic growth.
C) a bubble forms in one of its major sectors.
D) it is experiencing a recession.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the dot-com bubble, consumers believed that the Internet would radically change the shopping experience and lead to higher incomes throughout the economy. How would the dot-com bubble be best represented in the AD/AS model?
A) The aggregate demand curve shifts right.
B) The aggregate demand curve shifts left.
C) Prices increase along the aggregate demand curve.
D) Prices decrease along the aggregate demand curve.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A year-long drought that destroys most of the summer's crops would be considered a:
A) short-run supply shock.
B) long-run supply shock.
C) short-run demand shock.
D) long-run demand shock.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the macroeconomic model of aggregate supply and aggregate demand, quantity is:
A) the amount traded by all individual buyers and sellers in a market.
B) only influenced by changes in aggregate demand.
C) a measure of total output.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government were to increase income taxes, we would predict:
A) a downward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
B) the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right.
C) the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left.
D) an upward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in output and an increase in prices would indicate that the economy has experienced a:
A) positive supply side shock.
B) negative supply side shock.
C) positive demand side shock.
D) negative demand side shock.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shown displays various economic outcomes. 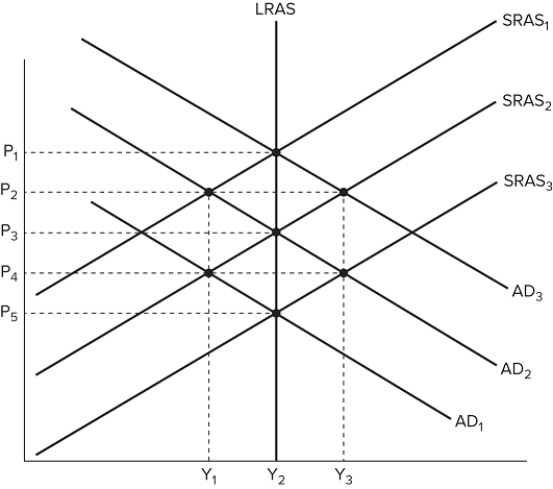 If the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2, the resulting price and output in the long run would be:
If the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2, the resulting price and output in the long run would be:
A) P 1 and Y 2.
B) P 3 and Y 1.
C) P 2 and Y 3.
D) P 2 and Y 2.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate supply and aggregate demand model is used to explain:
A) how individual markets affect other markets.
B) how entire markets operate, not just each individual seller within a market.
C) how the market price is determined by all buyers and sellers interacting in a market.
D) how output, prices, and employment are tied together in a single economic equilibrium.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price level increases, people:
A) feel less wealthy.
B) feel wealthier.
C) have the same real value of assets, regardless of the change in the price level.
D) work less.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy is in a recession, and the government increases its spending to bring the economy back to its long-run equilibrium, the long-run level of output will:
A) return, but with higher prices.
B) return, as will the original price level.
C) return, but with lower prices.
D) not return.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The introduction of the power loom during the Industrial Revolution caused the _______ aggregate supply curve to shift to the _______.
A) long-run; left
B) long-run; right
C) short-run; left
D) None of these shifts occurred when the power loom was introduced.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sudden increase in immigration would be considered a(n) :
A) short-run supply shock.
B) long-run supply shock.
C) interest-rate shock.
D) A change in immigration would not influence aggregate demand or supply.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If U.S. prices increase relative to the rest of the world, we would expect:
A) net exports to increase.
B) net exports to decrease.
C) imports to decrease.
D) imports to remain unaffected.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in stimulus provided by government spending versus tax cuts is caused by the fact that:
A) people don't respond to tax policy as greatly as they do to as spending policy.
B) the government is able to target spending in high-need areas of the economy.
C) tax cuts take longer to implement legislatively.
D) only a fraction of tax cuts are spent immediately, while the full amount of government spending immediately makes it to the economy.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 166
Related Exams