A) II and III only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) I only
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Payoffs are:
A) the rewards that come from particular actions.
B) always monetary.
C) things that are only enjoyed by the winner.
D) bribes made to gain some advantage unfairly during a game.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
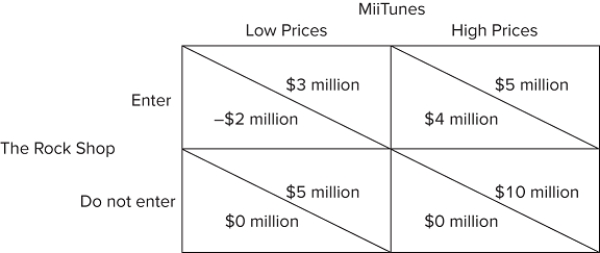 The figure shown represents the choices and payoffs (company profits) of two music shops-MiiTunes and The Rock Shop. MiiTunes is an established business in the area deciding whether to charge its usual high prices or to charge very low prices, in the hopes that a new business will not be able to compete at these prices. The Rock Shop is trying to decide whether or not it should enter the market.According to the figure, if The Rock Shop enters the market, MiiTunes will:
The figure shown represents the choices and payoffs (company profits) of two music shops-MiiTunes and The Rock Shop. MiiTunes is an established business in the area deciding whether to charge its usual high prices or to charge very low prices, in the hopes that a new business will not be able to compete at these prices. The Rock Shop is trying to decide whether or not it should enter the market.According to the figure, if The Rock Shop enters the market, MiiTunes will:
A) charge high prices.
B) charge low prices.
C) leave the market.
D) threaten to charge low prices.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In sequential games, an especially important part of strategic behavior is:
A) using the final-mover advantage.
B) analyzing a problem in reverse.
C) attempting to minimize the other players' payoffs.
D) making threats.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
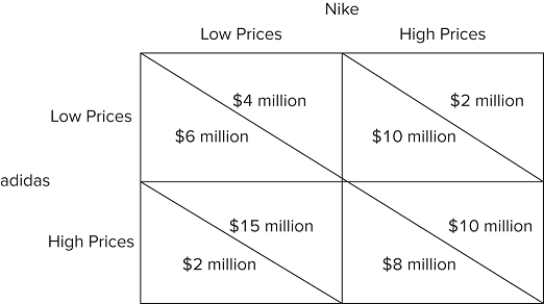 The figure shown portrays a game using a:
The figure shown portrays a game using a:
A) decision tree.
B) decision matrix.
C) flowchart.
D) graph.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
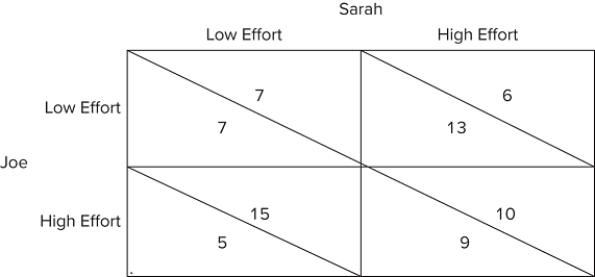 The figure shown represents the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.The game in the figure is a version of:
The figure shown represents the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.The game in the figure is a version of:
A) the prisoners' dilemma.
B) the first-mover advantage.
C) a sequential game.
D) a repeated game.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a prisoners' dilemma,
A) the ideal outcome could be reached if communication between players was allowed.
B) the outcome is less than ideal for at least one player.
C) the ideal outcome could be reached if players behaved rationally.
D) the outcome is less than ideal for all players.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All games involve which of the following?Multiple playersStrategiesPayoffs
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, and III
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In game theory, _______ would be considered a payoff.
A) being the first mover in a game
B) sharing information only with a select few
C) monetary gains made by a player
D) giving an advantage to only one player
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a game of bargaining, the player who is willing to _______ has more bargaining power and thus receives a _______ payoff.
A) be cooperative; worse
B) hold out longer; worse
C) hold out longer; better
D) make the first move; better
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the tit-for-tat strategy in repeated games is true?
A) A player takes the same action that an opponent did in the preceding round.
B) Both players explicitly agree to compete in the first round; if one player cooperates, the other will defect.
C) This type of strategy is not effective in repeated play of prisoner's dilemma-type games.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Games:
A) only have one possible stable outcome.
B) may have noncooperative equilibriums that are positive-positive outcomes.
C) can only reach equilibrium if there is a dominant strategy present.
D) None of these are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Games with a negative-negative outcome must have a noncooperative equilibrium.
B) A negative-negative outcome is not necessarily the best one for the players involved.
C) When players act in their own self-interest, a negative-negative outcome results.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the use of a commitment strategy is true?
A) It can alter the payoffs in a simultaneous game, but not in a sequential game.
B) It can alter payoffs in a sequential game, but not in a simultaneous game.
C) It has little impact on payoffs in both simultaneous and sequential games.
D) It can alter the payoffs in both simultaneous and sequential games.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a winning strategy in a game of bargaining?
A) First-mover advantage
B) Patience
C) Cooperation
D) Self-interested behavior
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists call a game that is played more than once:
A) a repeated game.
B) collusion.
C) a commitment strategy.
D) cooperative price play.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
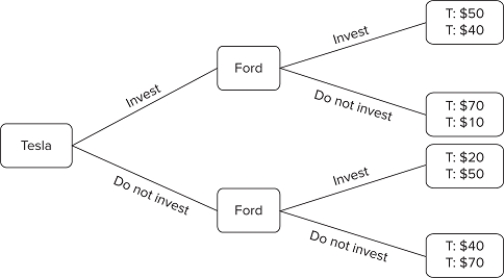 The figure shown displays the choices that could be made by two firms in an industry: Tesla and Ford. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to invest in research and development. Tesla will make a decision first, and then Ford will make a decision after observing Tesla's choice. The payoffs are the profits (in millions) these companies will earn as a result of their choices.If these players act in their own self-interest, then Ford will earn:
The figure shown displays the choices that could be made by two firms in an industry: Tesla and Ford. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to invest in research and development. Tesla will make a decision first, and then Ford will make a decision after observing Tesla's choice. The payoffs are the profits (in millions) these companies will earn as a result of their choices.If these players act in their own self-interest, then Ford will earn:
A) $40 million.
B) $10 million.
C) $50 million.
D) $70 million.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Behaving strategically:
A) means recognizing that the actions of others will affect the trade-offs you face and acting accordingly.
B) is an essential part of game theory.
C) involves rational decision-making.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
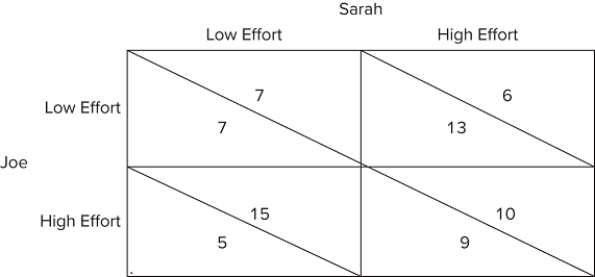 The figure shown represents the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.Assume that Joe and Sarah, in addition to working together on the school project, are also dating. Joe is madly in love with Sarah, who is an excellent student. Sarah tells Joe that she will break up with him if he does not put forth high effort on this project. This future punishment by Sarah is an example of:
The figure shown represents the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.Assume that Joe and Sarah, in addition to working together on the school project, are also dating. Joe is madly in love with Sarah, who is an excellent student. Sarah tells Joe that she will break up with him if he does not put forth high effort on this project. This future punishment by Sarah is an example of:
A) a commitment strategy.
B) an effort optimization strategy.
C) an ultimatum.
D) a bargaining strategy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the prisoner's dilemma, players:
A) will always choose to cooperate if they can communicate in advance.
B) may or may not choose to cooperate, even if they can communicate in advance.
C) will always choose to cooperate, with or without advance communication.
D) will only choose to cooperate if they are honest and trustworthy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 155
Related Exams