A) how much the quantity demanded of one good changes in response to a change in the price of a different good.
B) how much the quantity demanded of one good changes in response to a change in its price.
C) the magnitude of the shift in demand for a good in response to a change in its price.
D) how much the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in consumers' incomes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Total revenue is the amount a firm:
A) receives from the sale of goods and services.
B) keeps after all expenses are paid.
C) reinvests in itself from sales.
D) receives from dividends.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Elasticity along a demand curve:
A) is constant if the demand curve is linear.
B) changes only when the demand curve is bowed out.
C) changes when the demand curve is linear.
D) changes only when the demand curve is bowed in.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Bob was employed, he would see a movie at the theater once a month. However, Bob got laid off six months ago, and since then he has only gone to the movie theater twice. This type of behavior can be measured using:
A) price elasticity of demand.
B) price elasticity of supply.
C) income elasticity of demand.
D) cross-price elasticity of demand.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the price of a good increases from $9 to $11. Using the mid-point formula, what is the percentage change in price?
A) −20 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 20 percent
D) 2 percent
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whether a cross-price elasticity of demand is positive or negative indicates whether the:
A) goods are substitutes or complements.
B) elasticities are reported in absolute value.
C) demands are elastic or inelastic.
D) goods are a luxury or a necessity.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demand for a good is inelastic if:
A) total revenue decreases when price increases.
B) the quantity effect outweighs the price effect of a price increase.
C) the absolute value of price elasticity is greater than 1.
D) total revenue increases when price increases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand for ice cream is _____ price elastic than the demand for frozen treats overall because _____.
A) less; ice cream has fewer substitutes than frozen treats.
B) more; ice cream has fewer substitutes than frozen treats.
C) less; the scope of the market for ice cream is less broadly defined
D) more; the scope of the market for ice cream is less broadly defined
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If supply and demand analysis is a measure of how, then elasticity is a measure of:
A) how much.
B) when.
C) why.
D) how quickly.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists typically use the mid-point method of calculating elasticity because:
A) it is easier to calculate.
B) it is universally understood by all economists.
C) the negative sign can then be ignored.
D) the elasticity between two points is the same, regardless of the direction of the movement.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good with an income elasticity of 2.3 is:
A) a luxury.
B) inferior.
C) a necessity.
D) a complement.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in price:
A) causes a decrease in total revenue due to the quantity effect.
B) causes an increase in total revenue due to the price effect.
C) does not cause a quantity effect when demand is perfectly inelastic.
D) does not change quantity demanded if demand is elastic.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of a DVD decreases by 50 percent and the quantity of DVDs demanded increases by 75 percent, the price elasticity of demand is _____ and is _____.
A) −1.5; inelastic
B) −1.5; elastic
C) −0.67; elastic
D) −0.67; inelastic
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose price decreases from $27.00 to $13.00. Using the mid-point formula, what is the percentage change in price?
A) −0.35 = −35 percent
B) −0.7 = −70 percent
C) 0.7 = 70 percent
D) 0.14 = 14 percent.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand for a specific brand of corn flakes cereal is likely to be:
A) very price elastic, because there are many close substitutes available.
B) less price elastic, because there are many close substitutes available.
C) very price elastic, because the cost of cornflakes relative to income is low.
D) less price elastic, because cornflakes are an inferior good for many consumers.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A baker of chocolate chip cookies is likely to have a _____ price elasticity of supply than the seller of rare baseball cards due to _____.
A) more elastic; the availability of inputs
B) less elastic; the availability of inputs
C) less elastic; a shorter adjustment time
D) less elastic; a more flexible production process
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Measurements of elasticity include:
A) income elasticity of demand and income elasticity of supply.
B) price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply.
C) cross-price elasticity of demand and income elasticity of supply.
D) preference elasticity of demand and cross-price elasticity of supply.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
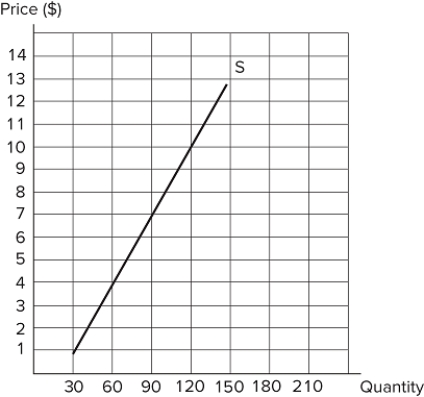 Consider the market in the graph shown. Using the mid-point method, what is the price elasticity of supply when the price increases from $4 to $7?
Consider the market in the graph shown. Using the mid-point method, what is the price elasticity of supply when the price increases from $4 to $7?
A) 1.13
B) 0.4
C) 0.45
D) 0.89
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose when the price of pineapples goes from $5 to $3 per pineapple, production decreases from 3,500 pineapples to 2,000 pineapples per year. Using the mid-point method, what is the percentage change in price?
A) −0.5 percent
B) −50 percent
C) −33 percent
D) −40 percent
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cross-price elasticity of demand between peanut butter and jelly is likely:
A) a positive number.
B) a very high positive number.
C) a negative number.
D) less than one.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 159
Related Exams