A) S represents an individual worker's supply of labor at each wage.
B) S represents the firm's supply of jobs at each wage.
C) P* represents the equilibrium wage.
D) Q* represents the equilibrium wage.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, economists place all factors of production into which three categories?
A) Land, labor, and capital
B) Technology, land, and capital
C) Land, labor, and technology
D) Technology, labor, and capital
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply of labor is determined by the:
A) number of workers.
B) opportunity cost of hiring labor.
C) marginal product of labor.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A profit-seeking firm will choose the combination of inputs that maximizes profit, based on the:
A) ratio of one factor of production to another.
B) substitutability of each factor of production.
C) price of each factor of production.
D) total productivity of each factor of production.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm adopts a labor-augmenting piece of technology, the:
A) marginal product of labor will increase.
B) marginal product of labor will decrease.
C) marginal supply of labor will increase.
D) marginal supply of labor will decrease.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the current wage is below the market equilibrium level in a competitive labor market:
A) firms will demand more labor than workers are willing to supply.
B) firms will be able to offer lower wages and still fill all the jobs they have.
C) unemployment will persist until the wage increases.
D) All of these are true.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the capital market, the rental price is what a:
A) producer pays to use a factor of production for a certain period or task.
B) producer pays to gain permanent ownership of a factor of production.
C) consumer pays to use labor or land services for a certain period or task.
D) consumer pays to gain permanent ownership of a factor of production.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays the production schedule for a bakery in a competitive market that sells cookies for $2 each.
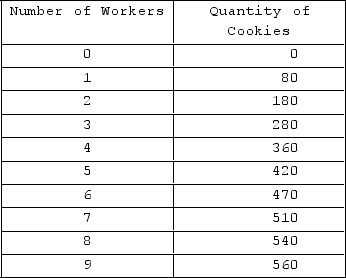 What is the value of the marginal product of labor for the sixth worker?
What is the value of the marginal product of labor for the sixth worker?
A) $50
B) $100
C) $470
D) $390
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the market for labor, the monopsonist is the sole _______ and can push wages _______ the competitive wage.
A) seller; below
B) buyer; above
C) buyer; below
D) seller; above
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The set of skills, knowledge, experience, and talent that determine the productivity of workers is called:
A) human capital.
B) physical capital.
C) capital per worker.
D) workers per capita.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the demand for hand-sewn leather shoes increases, the demand for leather will likely:
A) also increase.
B) decrease slightly.
C) stay the same.
D) drop significantly, and producers will use another material.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By comparing the value of marginal product with the cost of each input, a firm can find the _______ quantity of inputs to use.
A) cost-maximizing
B) profit-maximizing
C) revenue-maximizing
D) output-maximizing
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Any event that increases the value of the marginal product of labor will:
A) increase labor demand.
B) decrease labor demand.
C) increase labor supply.
D) decrease labor supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Farming in poor countries is considered to be _______ intensive because _______.
A) labor; labor is relatively cheaper than machinery in poor countries
B) capital; the labor used is concentrated and shared across a lot of capital
C) labor; the tools in poor countries are more plentiful than the people
D) capital; the tools in poor countries are relatively cheaper than the cost of hiring labor
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor supply curve will be downward sloping if the _______ effect outweighs the _______ effect.
A) income; price
B) price; income
C) substitution; income
D) price; substitution
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Safiya works at a factory for $15 an hour and typically works 40 hours a week. Safiya receives a pay raise and now earns $20 an hour. She decides to work 45 hours a week at her new wage. Which of the following statements is true about her decision to increase her hours worked upon receiving a wage increase?
A) The price effect outweighed the income effect of her pay raise.
B) Her labor supply curve is upward sloping.
C) This type of outcome is typically observed.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The factors of production are the:
A) ingredients that go into making any good or service.
B) outputs that society as a whole has chosen to produce.
C) costs and benefits of a given production process.
D) inputs required for a given durable good.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the demand for spinach will cause an increase in the price for spinach and will affect the labor market for spinach farm workers. We would expect to see a(n) _______ in labor demand, resulting in _______ wages.
A) decrease; higher
B) increase; higher
C) increase; lower
D) decrease; lower
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the labor market worked efficiently, then an effective minimum wage law would:
A) cause unemployment.
B) hold wages higher than the equilibrium price.
C) help those who were employed at that price.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the competitive firm's value of the marginal product of labor intersects the market-wage level, the firm:
A) can increase its profits by hiring any amount less than this point.
B) can increase its profits by hiring any amount greater than this point.
C) should consider shutting down because it is not earning profit.
D) has found the profit-maximizing quantity of labor to hire.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 176
Related Exams