A) requires each customer to pay exactly what they are willing to pay.
B) maximizes consumer surplus.
C) is not efficient.
D) minimizes producer surplus.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Producing any quantity of output less than the point where the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect leads to:
A) average total cost that is lower than average variable cost.
B) marginal cost that is higher than marginal revenue.
C) marginal revenue that is higher than marginal cost.
D) a loss of profits when producing the units.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown represents the revenues faced by a monopolist.
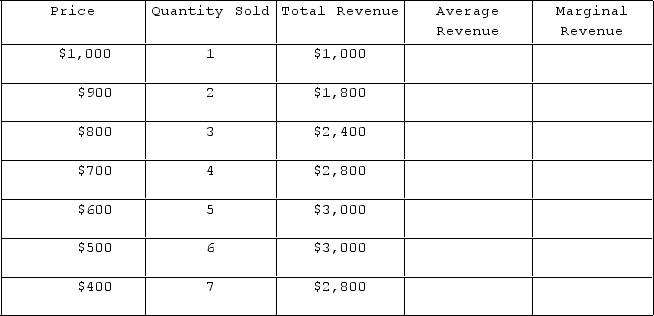 Graphing the first two columns of the table would yield which curve?
Graphing the first two columns of the table would yield which curve?
A) Marginal revenue
B) Market supply
C) Market demand
D) Total productivity
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopoly wishes to sell more output, it must:
A) find a more cost-effective way to produce its goods.
B) lower the price of its goods.
C) be experiencing economies of scale.
D) eliminate its existing competition.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the practice of price discrimination is true?
A) Firms can easily identify different groups' willingness to pay, so price discrimination is prevalent in every market.
B) Price discrimination is practiced less today than it was in the mid-1900s.
C) Perfect price discrimination is impossible.
D) Price discrimination has only been observed in markets where monopolies are present.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly, marginal revenue for all units greater than one is always _______ than price because of the _______ effect.
A) lower; price
B) greater; price
C) greater; quantity
D) lower; quantity
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In theory, placing a price control on a natural monopoly should:
A) have the same outcome as public ownership.
B) create negative economic profits for the company.
C) reduce deadweight loss to zero.
D) be implemented in conjunction with quantity controls.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown represents the revenues faced by a monopolist.
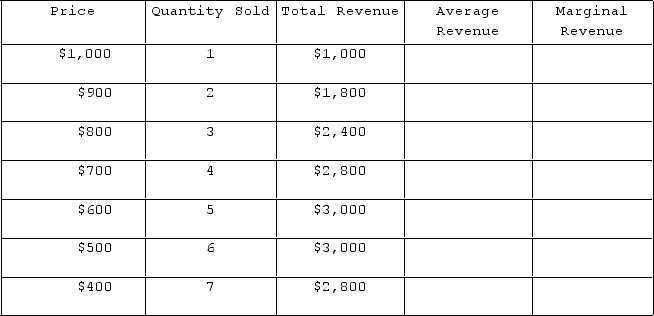 What is the firm's marginal revenue of the sixth unit?
What is the firm's marginal revenue of the sixth unit?
A) $0
B) −$200
C) $3,000
D) $500
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 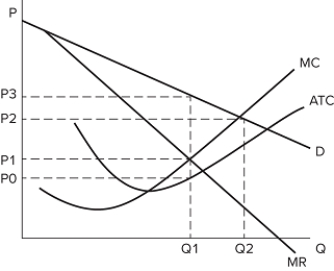 If Q2 units are being produced, the monopolist:
If Q2 units are being produced, the monopolist:
A) is not maximizing profits.
B) is producing where marginal costs are less than marginal revenue.
C) is earning negative profits.
D) should increase production.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an inefficient public monopoly cannot provide a service at a price that sufficient numbers of people are willing to pay it:
A) can remain in operation by covering its losses with revenue from taxes.
B) must shut down and leave the industry in the long run.
C) should expand operations until demand is satisfied.
D) will seek out more efficiencies.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly, for all units greater than one the marginal revenue curve:
A) lies above the demand curve.
B) lies below the average revenue curve.
C) cannot be negative.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a monopolist's outcome, producer surplus is _______ that of a competitive market.
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) the same as
D) Any of these is possible.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopoly is a market in which a single firm:
A) owns a key resource or input into the production of the good.
B) can produce the entire market quantity at a lower cost than multiple firms.
C) is protected from competition through government legislation.
D) gains market share over time through aggressive tactics.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a museum that is trying to decide what price to charge for tickets. It knows that the maximum amount students and the elderly would be willing to pay for a ticket is $10. Suppose there are 5,000 students and elderly individuals who would buy a ticket at this price. There are also 30,000 adults who would be willing to pay $25 for a ticket. If the museum cannot price discriminate, it will charge a price of _______ and earn _______ in revenue. If the museum is able to perfectly price discriminate, it will increase its revenue by _______.
A) $20; $600,000; $200,000
B) $10; $875,000; $125,000
C) $25; $750,000; $50,000
D) $25; $750,000; $125,000
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some argue that the best government response to monopolies is no response at all, because:
A) they are too powerful to be dealt with effectively.
B) no one can decide which monopolies to regulate.
C) the creation of regulation may be too difficult.
D) left unchecked all monopolies eventually shut down.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public policy responses to monopolies:
A) sometimes aim to break up existing monopolies.
B) always have more costs than benefits to society.
C) always have more benefits than costs to society.
D) never benefit society in the end.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 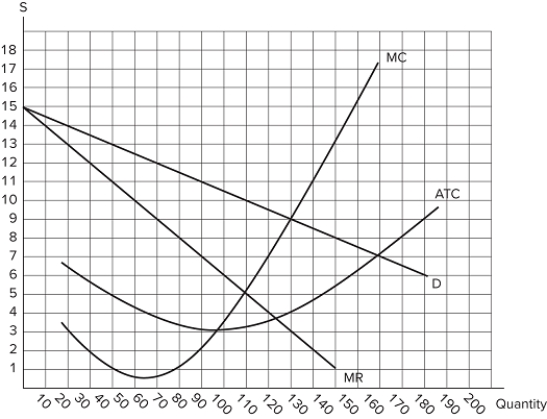 Which of the following statements is true?The profit maximizing quantity is 100.The profit maximizing price is $5.The deadweight loss at the profit maximizing price and quantity is zero.
Which of the following statements is true?The profit maximizing quantity is 100.The profit maximizing price is $5.The deadweight loss at the profit maximizing price and quantity is zero.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Perfect price discrimination:
A) eliminates all consumer surplus.
B) maximizes producer surplus.
C) creates no deadweight loss.
D) All of these are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, with a monopolist's outcome:
A) consumers lose surplus.
B) monopolies earn profit.
C) deadweight loss occurs.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a market in which one firm controls 80 percent of the market. Suppose a new firm tries to enter the market, and the firm with market power responds by temporarily cutting its prices to very low levels. This practice is known as:
A) predatory pricing.
B) monopoly pricing.
C) aggressive pricing.
D) All of these are exemplified by this practice.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 151
Related Exams