A) perfectly competitive firm.
B) monopolist.
C) oligopolist.
D) monopolistically competitive firm.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium price and quantity in a monopoly market:
A) is efficient.
B) is the same as in a perfectly competitive market.
C) causes a loss of total surplus.
D) causes no welfare costs.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is one reason a firm may lose some of its monopoly power?
A) Antitrust laws
B) Vertical or horizontal splits
C) Pressure from consumers
D) All of these are reasons a firm may lose some of its monopoly power.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A government-owned monopoly is more likely to:
A) provide a greater quantity of output than a private monopoly.
B) provide output at a lower price than a private monopoly.
C) serve public interest than maximize profit.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a monopolist's outcome, consumer surplus is _______ that of a competitive market.
A) higher than
B) lower than
C) the same as
D) Any of these is possible.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 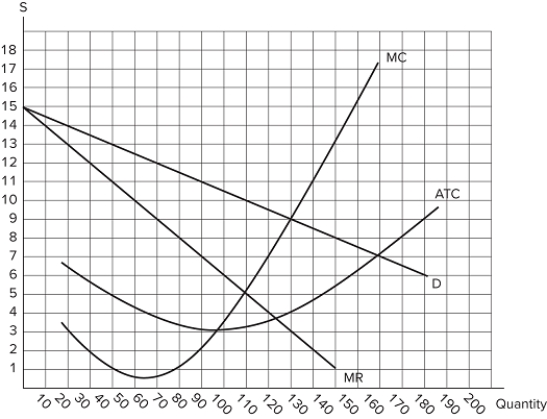 If 120 units are being produced, the monopolist:
If 120 units are being produced, the monopolist:
A) could increase profits by decreasing production.
B) is maximizing its profits.
C) is earning negative profits.
D) could increase profits by increasing production.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unregulated natural monopolies:
A) never capture the lowest costs per unit possible.
B) can capture profits by restricting output.
C) never create problems for policymakers.
D) are always protected by government policies.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopolist that sets prices equal to marginal cost will:
A) set a price that is greater than average total costs.
B) be inefficient.
C) incur losses.
D) earn zero accounting profits.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination is:
A) the practice of charging customers different prices for the same good.
B) the practice of charging customers the same price for a variety of similar goods.
C) choosing which prices to charge for certain items.
D) the process of customers choosing items based on price.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes how a monopolist's revenue curves compare to those of a perfectly competitive firm?
A) The monopolist's marginal revenue curve is downward sloping, while the perfectly competitive firm's is flat.
B) The monopolist's average revenue curve is not equal to price, as it is for a perfectly competitive firm.
C) The monopolist's marginal revenue curve is flat, while the perfectly competitive firm's is downward sloping.
D) The monopolist's total revenue curve is linear, while the perfectly competitive firm's is convex.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When government agencies become privatized:
A) they are sold to private companies.
B) stock is created and sold to the public.
C) private stock is sold to private households.
D) they are rarely regulated.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a potential barrier to entry into a monopoly market?
A) Fixed costs are large relative to variable costs.
B) Large economies of scale exist.
C) The required infrastructure for an industry is high cost.
D) All of these are potential barriers to entry.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some argue that the best government response to monopolies is no response at all. This is because:
A) the creation of regulation may be too difficult.
B) political mishandling may make the situation even worse.
C) it is difficult to manage the regulation of monopolies effectively.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists assume maximizing efficiency over other goals:
A) is a guiding principle of policy-making.
B) is always the best approach.
C) should never be done.
D) may not bring about the best outcome for society.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown represents the revenues faced by a monopolist.
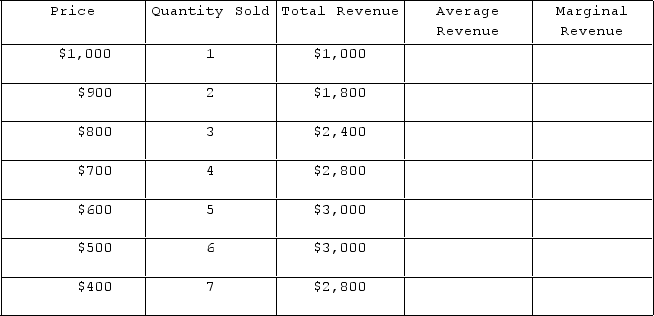 What is the firm's marginal revenue for the third unit?
What is the firm's marginal revenue for the third unit?
A) $100
B) $800
C) $600
D) $500
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Protecting intellectual property rights:
A) always benefits society.
B) never benefits society.
C) rarely affects society overall.
D) may or may not benefit society overall.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopoly power in a market allows:
A) monopolists to earn profit through higher prices.
B) consumers to gain surplus.
C) market surplus to be constant.
D) governments to ban monopolies.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government regulations:
A) always seek to increase competition.
B) sometimes protect monopoly power in certain industries.
C) never protect monopoly rights.
D) usually are ineffective.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With regard to monopolies, economists believe:
A) the government should never intervene in a natural monopoly market.
B) the reduction in efficiency can be offset by increases in equity.
C) the gains from maintaining a monopoly never outweigh the total welfare costs due to lost surplus.
D) whether or not to maintain a monopoly is a normative argument that has no right answer.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist's outcome in the long run differs from that of the perfectly competitive firm in that the monopolist:
A) earns zero profits.
B) charges a price that is higher than average total costs.
C) charges a price where marginal cost equals average revenue.
D) charges a price equal to marginal cost.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 151
Related Exams