A) the monopolist.
B) consumers.
C) society overall.
D) government.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist is able to enjoy profits in the long run because:
A) its price is set above its marginal costs.
B) there is no threat of competition.
C) it can charge a price that is higher than its average total costs.
D) All of these are true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some economists argue the best response to a monopoly is to:
A) do whatever the public demands.
B) do nothing at all.
C) impose high taxes on its output.
D) None of these are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a government splits a natural monopoly vertically, it is breaking the monopolist up:
A) along its stages of production.
B) into smaller companies that provide the same goods and services.
C) in order to maximize its profits.
D) in order to capture all efficiencies possible.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a monopolist's outcome, total surplus is generally _______ that of a competitive market.
A) higher than that
B) lower than
C) the same as
D) Any of these is possible.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a monopolist chooses to produce at the level of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue:
A) profits are maximized.
B) price is equal to marginal revenue.
C) price is equal to average total costs.
D) total revenue is maximized.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly.  What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing price?
What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing price?
A) $3
B) $5
C) $9
D) $10
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist, the quantity effect:
A) is the increase in revenue from selling a greater quantity at a lower price.
B) is the decrease in revenue from selling a greater quantity at a lower price.
C) is always outweighed by the price effect.
D) always outweighs the price effect.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a potential barrier to entry into a monopoly market?
A) The market is a natural monopoly.
B) The incumbent firm owns a key resource.
C) The government intervenes in the market.
D) A new type of product is offered.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consequence of a publicly-owned natural monopoly is:
A) the loss of the profit motive.
B) an increase in the motivation to improve efficiency.
C) increased public pressure to reduce costs.
D) reduced likelihood to remain open longer than political terms of office.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To avoid subsidies, the government should cap the price for a natural monopoly at its:
A) marginal cost.
B) average total cost.
C) average variable cost.
D) fixed cost.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly, when marginal revenue is zero:
A) profits are maximized.
B) total revenue is maximized.
C) marginal revenue is minimized.
D) marginal costs are minimized.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolist chooses to produce:
A) where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B) at a higher quantity than the perfectly competitive firm.
C) at an efficient outcome.
D) at a cost that is equal to a competitive one.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In practice, placing a price control on a natural monopoly:
A) is easy and commonly practiced.
B) is difficult because of the lack of information.
C) always creates the same outcome as public ownership of the industry.
D) is never a good idea.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The existence of a monopoly:
A) creates market inefficiencies.
B) causes consumers to get less at a higher price.
C) causes a reduction in total surplus.
D) All of these result from the existence of a monopoly.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist, at the profit-maximizing level of output:
A) price is greater than average revenue.
B) average revenue is greater than marginal cost.
C) marginal cost is greater than price.
D) total revenue is equal to total cost.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a public policy response to a monopoly?
A) Public admonishment
B) Encouraging mergers
C) Antitrust laws
D) All of these are examples of a public policy response to a monopoly.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Antitrust activities can cause inefficiencies by:breaking up a natural monopoly.creating many small firms that cannot capture available economies of scale.reducing the profits of firms.
A) II only
B) II and III only
C) I and II only
D) III only
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. 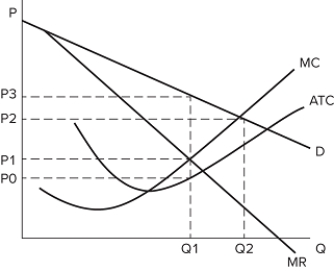 Comparing the perfectly competitive and monopoly outcomes, we can see that:
Comparing the perfectly competitive and monopoly outcomes, we can see that:
A) there is deadweight loss in the monopoly market.
B) a perfectly competitive firm would lose money in this industry.
C) a perfectly competitive firm would produce Q1 units.
D) a monopolist would charge P3 and a perfectly competitive firm would charge P1.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopoly, a negative marginal revenue implies that:
A) the price effect is larger than the quantity effect.
B) total revenues are increasing.
C) the demand is price elastic.
D) the quantity effect is larger than the price effect.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 151
Related Exams