A) Buyers and sellers have no control over the market price.
B) Sellers are selling unique products.
C) Buyers have complete control over the market price and sellers have none.
D) Sellers have complete control over the market price and buyers have none.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown represents the cost and revenue curves of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. 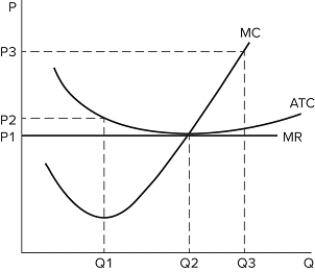 The long run output decision for this firm is:
The long run output decision for this firm is:
A) Q1, P1.
B) Q1, P2.
C) Q2, P1.
D) Q3, P3.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market is producing at a level of output where marginal costs are equal to marginal revenue, it:
A) should cut back production to increase profits.
B) should increase production to increase profits.
C) is producing a profit-maximizing quantity.
D) may or may not need to change production, but this cannot be known without more information.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the market price falls below the minimum of the firm's average total cost curve:
A) there is no level of output at which the firm can make a profit.
B) the firm is earning profits.
C) the market price must be lower than the firm's average variable cost.
D) total revenue must be higher than total cost.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market facing a market price of $5 decides to produce 400 units, what will the firm's total revenue be?
A) $5
B) $400
C) $2,000
D) $405
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short run in a perfectly competitive market:
A) the number of firms is fixed.
B) the total quantity supplied is fixed.
C) the price is fixed.
D) All of these are true in the short run.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An essential characteristic of a perfectly competitive market is that buyers and sellers have:
A) no competition and must set the market price on their own.
B) so much competition that they must work together perfectly to set a market price.
C) so much competition that they have no ability to set their own prices.
D) no control over the price they set because it is determined by government.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown displays the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
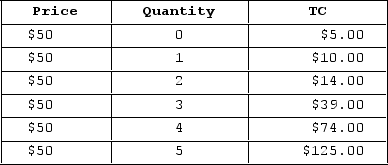 This firm's marginal costs:
This firm's marginal costs:
A) are constant.
B) increase as output increases.
C) decrease up through the second unit, then increase.
D) increase up through the fourth unit, then decrease.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because firms in perfectly competitive markets can sell any quantity without driving down prices, they should:
A) produce as much as possible to maximize profits.
B) produce at the lowest cost per unit to maximize profits.
C) try to flood the market.
D) increase quantity until the additional profit earned on the last unit sold is zero.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market is producing at a level of output where marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, it:
A) should cut back production to increase profits.
B) should increase production to increase profits.
C) is producing a profit-maximizing quantity.
D) may or may not be maximizing profits.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Firms are more likely to collude:
A) when there are barriers to market entry.
B) in perfectly competitive markets.
C) when they can easily enter the market.
D) when the market has no transactions costs.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a standardized good?
A) Grain
B) Granola cereal
C) Hamburgers
D) Digital cameras
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Standardized goods and services:
A) are interchangeable.
B) have close substitutes.
C) are unique.
D) are regulated by government.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, a price decrease:
A) raises the profit-maximizing quantity.
B) lowers the profit-maximizing quantity.
C) does not affect the profit-maximizing quantity.
D) signifies that the firm should leave the market.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market facing a market price of $2 decides to increase its production from 2,000 units to 4,000 units, the firm's marginal revenue:
A) will increase from $4,000 to $8,000.
B) will decrease from $8,000 to $4,000.
C) will stay the same.
D) None of these are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
<p><b><b><span style="font-size:20pt;"><span style="color:#FF0000;"> 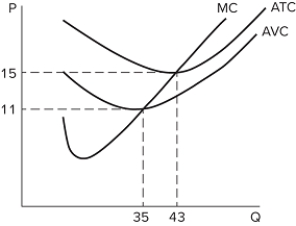 </span></span> </b> If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and produces at the profit-maximizing level of output, which of the following is true?
</span></span> </b> If a firm in a perfectly competitive market faces the cost curves in the graph shown and produces at the profit-maximizing level of output, which of the following is true?
A) The firm will plan to exit the industry in the long run if the price falls below $15.
B) The firm will continue to operate in the short run as long as the price is below $11.
C) The firm will earn positive profits any time the price is greater than $11.
D) The firm will earn maximum profits at a quantity of 35.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allowing firms to freely enter and exit a market can: drive business profits up. increase demand for a product. encourage innovation. reduce prices for consumers.
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) II and IV
D) I, II, and III
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In theory, which of the following characterizes the long run supply curve for firms in a perfectly competitive market that are identical to each other?
A) Perfectly elastic
B) Perfectly inelastic
C) Upward sloping
D) Downward sloping
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market facing a market price of $4 decides to produce 700 units of a good, what will the firm's average revenue be?
A) $4
B) $2,800
C) $175
D) $700
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When demand increases in a perfectly competitive market, _______ in the short run, and in the long run _______.
A) prices increase; supply increases
B) prices increase; prices stay permanently higher
C) quantity supplied increases; prices increase
D) quantity supplied decreases; prices decrease
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 166
Related Exams