A) a marginal analysis.
B) a profit equation.
C) a break-even analysis.
D) price elasticity of demand.
E) a reference value.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In controversial move, Amazon.com was caught manipulating its prices. Avid DVD buyers, buying in quantity for resale, found that the online retailer was offering different customers different prices for the same DVD, and complained vociferously. Company officials admitted that the company was trying to see how much it could charge for an item before buyers balked. Amazon was caught attempting
A) horizontal price-fixing.
B) price discrimination.
C) resale price maintenance.
D) predatory pricing.
E) bait and switch pricing.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding a trade-in allowance is most accurate?
A) A trade-in allowance is a noncash exchange of one product for another of equal or lesser value.
B) A trade-in allowance is an effective way to lower the price a buyer has to pay without formally reducing the list price.
C) A trade-in allowance is a cash-back payment when a more expensive item is replaced with a less expensive one.
D) A trade-in allowance is the return of money based on proof of purchase.
E) A trade-in allowance is a cash payment to a retailer for extra in-store support or special featuring of the brand.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Companies often pursue a market share objective when
A) industry sales are flat or declining.
B) profits are increasing.
C) industry sales are beginning to rise.
D) there is a sudden increase in production costs.
E) stockholders are seeking higher dividends.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Managing for long-run profits as a pricing objective implies that a company will
A) give up immediate profit in exchange for achieving a higher market share in hopes of penetrating competitive markets.
B) maintain a given price range to ensure there is no loss of customers over time, even if the profit margin declines.
C) invest excess cash in bonds and certificates of deposit in order to counteract any inflationary economic changes in the future.
D) reinvest all profits into market research or product research rather than returned to shareholders.
E) drop all products, product lines, or divisions that cannot maintain their pricing goals.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What profit-oriented pricing method is often used because of the difficulty in establishing a benchmark of sales or investment to show how much of a firm's effort is needed to achieve the target?
A) target return-on-investment pricing
B) target return-on-sales pricing
C) standard markup pricing
D) target profit pricing
E) loss-leader pricing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mark Johnson, the manager of a discount consumer electronics store, was approached by the manufacturer's representative on behalf of a marketer of a popular and profitable line of storage racks. The manufacturer's representative implied that if Johnson didn't raise the retail prices for the storage racks to those paid by the marketer's non-discount customers, Johnson's supply of racks may be severely curtailed. The manufacturer's representative was guilty of attempting
A) horizontal price-fixing.
B) vertical price-fixing.
C) price discrimination.
D) predatory pricing.
E) bait and switch pricing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Creative Quilts Studio sells hundreds of colors and types of fabric and thread. To price its inventory, the owners add 50 percent to the cost of each bolt of fabric and every spool of thread. What is this pricing approach called?
A) target return-on-sales pricing
B) flexible pricing
C) cost-plus pricing
D) standard markup pricing
E) customary pricing
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ = (Unit price × Quantity sold) − Total cost.
A) Total revenue
B) Variable cost
C) Net present value
D) Profit
E) Break-even point
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ad campaign by Suave shampoo asked television viewers to identify the heads of hair of women who used Suave shampoo and conditioner and those that used the much more expensive salon hair-care products. The idea of the ad was that no one could tell which woman used the much cheaper Suave brand. By making price its selling point, Suave is most likely using
A) customary pricing.
B) loss-leader pricing.
C) prestige pricing.
D) skimming pricing.
E) below-market pricing.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Creative marketers engage in value-pricing, which is the practice of simultaneously increasing product and service benefits while
A) increasing costs.
B) increasing price.
C) increasing advertising.
D) decreasing costs.
E) maintaining or decreasing price.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the factors that influence demand is true?
A) As the availability of close substitutes increases, the demand for a product increases.
B) As real consumer income increases, the demand for a product increases.
C) As the price of close substitutes increases, the demand for a product declines.
D) Changing consumer tastes have little impact on the demand for a product.
E) As real consumer income decreases, the demand for a product increases.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Brazilian government wants to build a global positioning satellite (GPS) system. The satellite manufacturer will receive a mutually agreed upon profit over and above all costs associated with the project. The pricing approach the satellite manufacturer uses is called
A) standard markup pricing.
B) experience curve pricing.
C) cost-plus-percentage-of-cost pricing.
D) cost-plus-fixed-fee pricing.
E) bundle pricing.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Odd-even pricing is considered to be a ________ approach to pricing.
A) cost-oriented
B) profit-oriented
C) demand-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Loss-leader pricing refers to
A) a pricing method where the price the seller charges is below the actual cost to make the product.
B) setting a low initial price and gradually but consistently increasing that price so as not to antagonize the consumer.
C) deliberately selling a product below its customary price, not to increase sales, but to attract customers' attention in hopes that they will buy other products as well.
D) a method of pricing based on a product's tradition, standardized channel of distribution, or other competitive factors.
E) pricing a product between 8 and 10 percent lower than nationally branded competitive products.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are examples of pricing objectives except which?
A) market share
B) survival
C) unit sales
D) social responsibility
E) product obsolescence
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting one price for all buyers of a product or service is referred to as
A) customary pricing.
B) a one-price policy.
C) a dynamic pricing policy.
D) standard markup pricing.
E) uniform pricing.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some firms pursue a ________ pricing objective to generate cash to ward off bankruptcy.
A) market share
B) survival
C) sales revenue
D) single product line
E) profit
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
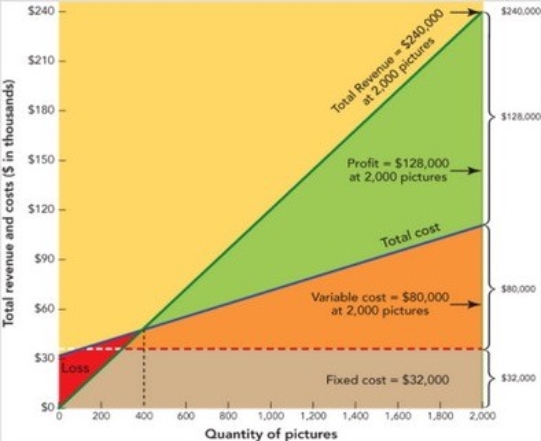 Figure 11-7
-Suppose you are the owner of a picture frame store. Assume that the average price customers are willing to pay for each picture frame is $120. Also, suppose your fixed costs (FC) total $32,000 (real estate taxes, interest on a bank loan, etc.) and unit variable cost (UVC) for a picture frame is $40 (labor, glass, frame, and matting) . According to Figure 11-7a above, how much profit will your picture frame store make if it sells 400 picture frames?
Figure 11-7
-Suppose you are the owner of a picture frame store. Assume that the average price customers are willing to pay for each picture frame is $120. Also, suppose your fixed costs (FC) total $32,000 (real estate taxes, interest on a bank loan, etc.) and unit variable cost (UVC) for a picture frame is $40 (labor, glass, frame, and matting) . According to Figure 11-7a above, how much profit will your picture frame store make if it sells 400 picture frames?
A) $48,000
B) $32,000
C) $16,000
D) $0
E) $64,000
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price is
A) the value assigned to the exchange of products and services for other products and services.
B) the value judgment made by both the buyer and seller regarding an item's worth.
C) the money or other considerations (including other products and services) exchanged for the ownership or use of a product or service.
D) the value assessed for the benefits of using a product or service.
E) the highest monetary value a customer is willing to pay for a product or service.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 372
Related Exams