A) adjusting the price of a product so it is "in line" with that of its largest competitor.
B) setting an annual target of a specific dollar volume of profit.
C) setting the price of a line of products at a number of different price points.
D) adding a fixed percentage to the cost of all items in a specific product class.
E) setting prices to achieve a profit that is a specified percentage of production costs.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reductions from list or quoted prices to buyers for performing some activity are referred to as
A) allowances.
B) subsidies.
C) remittances.
D) noncumulative deductions.
E) list price deductions.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Standard markup pricing refers to
A) adjusting the price of a product so it is "in line" with that of its largest competitor.
B) setting the price of a line of products at a number of different price points.
C) setting prices to achieve a profit that is a specified percentage of the sales volume.
D) increasing the price slightly to protect against undue profit losses from unforeseen environmental forces.
E) adding a fixed percentage to the cost of all items in a specific product class.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To reward wholesalers and retailers for marketing functions they will perform in the future, a manufacturer often gives ________ discounts.
A) seasonal
B) cash
C) promotional
D) trade
E) cumulative
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting prices a few dollars or cents under an even number is referred to as
A) odd-even pricing.
B) prestige pricing.
C) price lining.
D) above-, at-, or below-market pricing.
E) every day fair pricing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ratio of perceived benefits to ________ is referred to as value.
A) price
B) prestige
C) anticipated quality
D) profits
E) discounts
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Target return-on-investment (ROI) is frequently used by
A) contractors.
B) public utilities.
C) business-to-business markets.
D) supermarkets.
E) small privately owned firms.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reference value involves comparing the costs and benefits of
A) substitute items.
B) items of equal or greater value.
C) products with which a consumer is familiar and items the consumer has not seen or used before.
D) items from one particular manufacturer or distributor.
E) intangible items.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Manufacturers of private brands use which method of competition-oriented pricing?
A) penetration pricing
B) below-market pricing
C) loss-leader pricing
D) prestige pricing
E) skimming pricing
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The practice of exchanging products and services for other products and services rather than for money is referred to as
A) barter.
B) reciprocal pricing.
C) virtual pricing.
D) balance of payments.
E) value-pricing.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A demand curve is a graph that relates
A) the quantity sold and price, which shows the maximum number of units that will be sold at a given price.
B) revenues and costs, which shows the minimum number of units that must be sold to break even.
C) the quantity sold and revenues, which shows the minimum number of units that must be sold in order to make a profit.
D) total production costs to various price points in order to determine how many units must be sold in order to realize a predetermined profit.
E) primary demand to selective demand, which shows the growth of the market compared to change in market share.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To encourage retailers to pay their bills quickly, manufacturers offer them
A) quantity discounts.
B) cash discounts.
C) flexible pricing policies.
D) promotional allowances.
E) manufacturer's inducements.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Another name for a one-price policy is
A) customary pricing.
B) fixed pricing.
C) dynamic pricing.
D) standard markup pricing.
E) uniform pricing.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
VIZIO's HDTVs are sold through all of the following types of retailers except which?
A) Amazon.com
B) mass merchandisers, such as Target
C) its own brick and mortar stores
D) wholesale club stores such as Sam's Club
E) electronics stores such as Best Buy
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following statements about price are true except which?
A) Small changes in price can have big effects on both the number of units sold and company profit.
B) The price for a product or service must earn a profit for the company.
C) For most products and services, there is an agreed-upon price range set by makers.
D) The price must be right-in the sense that customers must be willing to pay it.
E) The price must generate enough sales dollars to pay for the cost of developing, producing, and marketing the product.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prestige pricing is a ________ approach to pricing.
A) demand-oriented
B) cost-oriented
C) profit-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cost-plus-percentage-of-cost pricing refers to
A) summing the total unit cost of providing a product or service and adding a specific amount to the cost to arrive at the price.
B) adding a fixed percentage to the cost of all items in a specific product class.
C) setting a price that is dictated by tradition, a standardized channel of distribution, or other competitive factors.
D) setting the price of a product or service by adding a fixed percentage to the total unit cost.
E) charging different prices to different buyers for goods of like grade and quality.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most consumers realize that the quality of diamonds varies, and most believe the higher the price of a diamond, the higher its quality. This is an example of price influencing the perception of overall quality and therefore ________ to consumers.
A) acceptable cost
B) perceptual investment
C) barter potential
D) return on investment
E) value
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
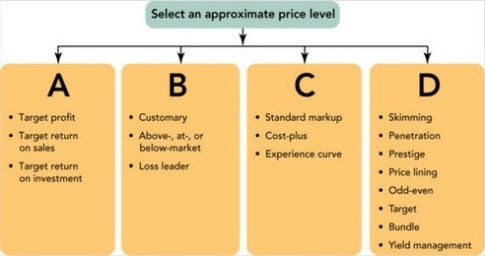 Figure 11-2
-Figure 11-2 above represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level. Box B includes standard markup and cost-plus so it represents which approach?
Figure 11-2
-Figure 11-2 above represents the four approaches to selecting an appropriate price level. Box B includes standard markup and cost-plus so it represents which approach?
A) demand-oriented approach
B) profit-oriented approach
C) competition-oriented approach
D) results-oriented approach
E) cost-oriented approach
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting the price of a product or service by adding a fixed percentage to the total unit cost is referred to as
A) cost-plus-fixed-percentage fee pricing.
B) target pricing.
C) cost-plus-percentage-of-cost pricing.
D) experience curve percentage pricing.
E) target return on investment pricing.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 372
Related Exams