A) are preferences found more in American teenagers than in most other cultures around the world.
B) actually begin at age 10, but begin to decline significantly as students enter high school.
C) ironically are found more frequently among teenagers who cannot afford to make those purchases than for those who can.
D) are preferences of teenagers around the world regardless of where they live.
E) are often established early among European teens and they typically linger well into adulthood.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The practice of shielding one or more sectors of a country's economy from foreign competition through the use of tariffs or quotas is referred to as
A) domestic imperialism.
B) protectionism.
C) blocked competition.
D) import taxation.
E) trade restriction.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since global marketing is affected by economic considerations, a scan of the global marketplace should include which of the following factors?
A) an analysis of cultural diversity within the country under consideration
B) regulatory constraints regarding contracts, mergers, and partnerships
C) an assessment of the economic infrastructure in different countries
D) an assessment of language differences including dialect variation
E) political and ideological differences between the countries involved
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are advantages of licensing except which?
A) the foreign country gains employment by having the product manufactured locally
B) the licensee gains information that allows it to start with a competitive advantage
C) the lower risk to the company granting the license compared to direct investment
D) the licensor's ability to protect its brand name from harm
E) the capital-free entry into a foreign country
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lever Europe, a division of Unilever, markets Snuggle fabric softener. But in 10 European countries, it uses seven brand names, including Kuschelweich in German, Coccolino in Italy, and Mimosin in France. These products also have different packages, different advertising programs, and occasionally different formulas. From this information, we can assume that Lever Europe uses ________ marketing strategy.
A) an ethnocentric
B) a transnational
C) a global
D) an international
E) a multidomestic
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A global marketing strategy refers to
A) the strategy used by multinational firms that have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business.
B) the strategy of transnational firms not to employ adaptive marketing techniques when there are cultural differences, but to redirect their marketing resources toward customer education.
C) the strategy of transnational firms that employ the practice of standardizing marketing activities when there are cultural similarities and adapting them when cultures differ.
D) the global strategy of seeking out already established firms in other nations and selling them the rights to manufacture and distribute the firm's products through a host nation's local businesses.
E) the strategy currently used by most U.S. domestic firms that when entering a new international market, these firms offer only those products that require the least amount of product adaptation.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generally, as the proportion of middle-income households in a country increases, the nation's purchasing power
A) levels off.
B) decreases.
C) increases.
D) becomes less of an economic priority.
E) becomes progressively unstable.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the distribution channels through which a product manufactured in one country must travel to reach its destination in another country. The distribution channels can be considered to have been successful when the product reaches the
A) seller.
B) channels between nations.
C) seller's international marketing headquarters.
D) final consumer.
E) channels within foreign nations.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
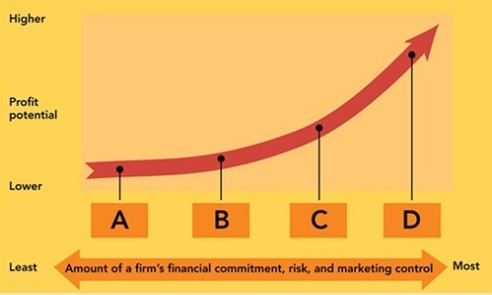 Figure 6-4
-According to Figure 6-4, point D would most likely represent what option for entering the global marketplace?
Figure 6-4
-According to Figure 6-4, point D would most likely represent what option for entering the global marketplace?
A) exporting
B) joint venture
C) direct investment
D) franchising
E) licensing
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study of similarities and differences among consumers in two or more nations or societies is referred to as
A) market synthesis.
B) cross-cultural analysis.
C) international sociographics.
D) transnational anthropology.
E) multicultural ethnocentrism.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Personally or socially preferable modes of conduct or states of existence that tend to persist over time are referred to as
A) customs.
B) ethics.
C) values.
D) culture.
E) beliefs.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is the tendency to believe that it is inappropriate, indeed immoral, to purchase foreign-made products.
A) Country partisanship
B) Cultural ethnocentrism
C) Xenophobia
D) Consumer ethnocentrism
E) Nationalism
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Global competition exists when
A) a firm produces and markets its products domestically rather than internationally.
B) firms originate, produce, and market their products and services worldwide.
C) two firms from two different countries compete for market share in a single domestic market.
D) two or more firms from different nations combine their resources to market products in a single domestic market.
E) the firm from one nation dominates the market for its product in every nation.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Once a company has decided to enter the global marketplace, it must select a means of market entry. One of the four general options is
A) licensing.
B) accreditation.
C) countertrading.
D) cooperative.
E) internationalization.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U.S. citizens pay $5 billion more annually for shoes and Japanese citizens pay $6 billion more for rice than the actual cost of the products because
A) both countries have suffered major financial crises due to a severe trade imbalance.
B) both countries have imposed tariffs on imported goods to protect their domestic markets.
C) both countries have imposed limits on the quantity of these goods that can leave their respective domestic markets.
D) both products are considered essentials and as a result are more heavily taxed.
E) these products were purchased at a lower price from nations that currently are under governmental sanctions.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starbucks and Tata Global Beverage have together formed Tata Starbucks Private Limited in order to bring Starbucks to India. The global market entry strategy is known as
A) franchising.
B) a joint venture.
C) licensing.
D) direct investment.
E) exporting.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about global brands is most accurate?
A) A global brand has centrally coordinated marketing programs.
B) A global brand is marketed under different names but uses identical ads for all markets.
C) A global brand alters the product formulation or service for each geographical region.
D) A global brand delivers multiple benefits based on the GDP of each country.
E) A global brand is a collaborative effort among several different national firms.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A joint venture entails
A) offering the right to a trademark, patent, trade secret, or similarly valued items of intellectual property in return for a royalty or fee.
B) contracting with a foreign firm to manufacture products according to certain specifications.
C) a foreign company and a local firm investing together to create a local business.
D) having a company handle its own exports directly, but using intermediaries for importing.
E) exporting through an intermediary, which often has the knowledge and means to succeed in selling a firm's products abroad.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In international trade, dumping refers to
A) illegally disposing of unusable or damaged goods to avoid paying removal fees and/or taxes.
B) a firm selling damaged or unsalable goods below their original production cost.
C) a firm selling quality goods at significantly lower prices for the primary purpose of reducing inventory to make room for seasonal goods.
D) a firm selling quality goods at significantly lower prices for the primary purpose of reducing inventory to make room for newer or more expensive models.
E) a firm selling a product in a foreign country below its domestic price or below its actual cost.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Even though there are about 100 official languages in the world, the three major ones used in global diplomacy and commerce are
A) English, Japanese, and Chinese.
B) English, French, and Spanish.
C) Japanese, Spanish, and French.
D) Japanese, Spanish, and English.
E) Spanish, English, and Chinese.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 250
Related Exams