A) No, because any inhibitory signals will cancel out the excitatory signals.
B) Yes, but the action potential will be much smaller than if only excitatory signals were received.
C) It depends; if more excitatory than inhibitory signals are received, then an action potential may result.
D) Yes, because excitatory signals always stimulate an action potential.
E) It depends; if more inhibitory than excitatory signals are received, then the neuron will be free to produce an action potential.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which two anterior pituitary hormones do not target other endocrine glands?
A) prolactin (PRL) and growth hormone (GH)
B) oxytocin and prolactin (PRL)
C) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and growth hormone (GH)
D) luteinizing hormone (LH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
E) antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dendrites
A) are usually the longest nerve fibers.
B) are covered with a myelin sheath.
C) receive signals from sensory receptors or other neurons.
D) generate nerve impulses.
E) are longer and less numerous than axons.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
A) is associated with "fight or flight."
B) uses the neurotransmitter norepinephrine.
C) arises from parts of the spinal cord.
D) inhibits digestion.
E) opposes the effects of the sympathetic division.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The arrow shows the direction of the nerve impulse in a neuron. Part X would represent a(n) 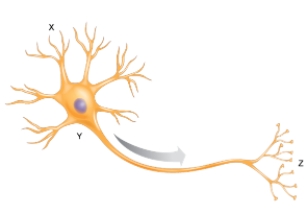
A) axon.
B) dendrite.
C) cell body.
D) myelin sheath.
E) axon terminal.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ inhibits osteoclasts, while _____ stimulates them.
A) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) ; calcitonin
B) Growth hormone (GH) ; calcitonin
C) Epinephrine; norepinephrine
D) Calcitonin; parathyroid hormone (PTH)
E) Glucagon; growth hormone (GH)
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you do not obtain enough iodine in your diet, you will likely develop
A) pituitary gigantism.
B) simple goiter.
C) exophthalmos.
D) diabetes mellitus.
E) tetany.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Only the glands of the endocrine system
A) use chemical signals to bring about changes in target organs.
B) work to regulate the activities of other body systems.
C) use the bloodstream to convey signals throughout the body.
D) help to maintain homeostasis.
E) bring about rapid responses by target organs.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _____ conveys sensory information to the central nervous system and motor commands away from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles.
A) parasympathetic division
B) autonomic nervous system
C) somatic system
D) sympathetic division
E) brain stem
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gigantism can result from excessive secretion from the
A) posterior pituitary.
B) anterior pituitary.
C) adrenal medulla.
D) adrenal cortex.
E) pancreas.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are relaxing, having a snack and watching TV, when suddenly the entire house begins to shake violently. The activity of your _____ quickly decreases, while that of your _____ increases.
A) somatic nervous system; autonomic nervous system
B) autonomic nervous system; somatic nervous system
C) sympathetic division; parasympathetic division
D) sympathetic division; somatic nervous system
E) parasympathetic division; sympathetic division
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which part of a neuron could be covered with a myelin sheath?
A) nucleus
B) axon
C) dendrite
D) cell body
E) terminal
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Weight gain, diabetes mellitus, and a moon-shaped face may indicate
A) Addison disease.
B) Graves disease.
C) simple goiter.
D) pituitary dwarfism.
E) Cushing syndrome.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nerve impulse travels down a myelinated axon by
A) repolarization.
B) saltatory conduction.
C) simple diffusion.
D) integration.
E) summation.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is activated, its effects can be prolonged by secretions of the
A) adrenal cortex.
B) thyroid gland.
C) parathyroid glands.
D) adrenal medulla.
E) posterior pituitary.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spinal cord's gray matter is located
A) on the outside, surrounding a central core of white matter.
B) on the inside, surrounding the central canal.
C) on both the inside and the outside.
D) neither inside nor outside-the spinal cord is entirely white matter.
E) scattered among a collection of ganglia.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People who are under constant stress have a tendency to gain weight, especially in the midsection, even if they do not overeat. This is because the hypothalamus responds to the stress by stimulating the
A) posterior pituitary.
B) adrenal cortex.
C) thyroid.
D) adrenal medulla.
E) pancreas.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Someone who is good at memorizing other people's phone numbers has an excellent _____ memory.
A) episodic
B) skill
C) semantic
D) short-term
E) sensory
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you eat a jelly donut, your pancreatic islets will respond by secreting
A) growth hormone.
B) glucagon.
C) epinephrine.
D) insulin.
E) oxytocin.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transmission across the synaptic cleft is accomplished by chemical signals called
A) hormones.
B) exocrine secretions.
C) enzymes.
D) stimulants.
E) neurotransmitters.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 54
Related Exams