A) Memory T cells initiate the response at the site in which the allergen contacts the body.
B) Cytotoxic T cells initiate the response at the site in which the allergen contacts the body.
C) Memory T cells initiate the response at the site in which the antibodies contact the body.
D) The response can occur within a matter of seconds.
E) The response can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure that can be life-threatening.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct about the usage of a booster?
A) The booster allows the antibody concentration to rise to a level higher than the primary response.
B) The booster will raise the antibody concentration in the individual by 10%.
C) The booster will cause the antibody concentration to rise and then decrease rapidly.
D) The booster will do nothing for the individual's immune response.
E) The booster will initiate the immune response.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What could happen if T cells failed to undergo apoptosis after the defeat of an infection?
A) An HIV infection may result.
B) Leukemia or lymphoma may result.
C) Future immunity would be strengthened.
D) An autoimmune disease may result.
E) An allergy may result.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is inaccurate regarding the complement proteins?
A) They are blood plasma proteins.
B) Some form the membrane attack complex, which forms a hole in the bacterial plasma membrane.
C) They may amplify the inflammatory response by attracting phagocytes to the site of the infection.
D) They may bind to pathogens already coated with antibodies, ensuring they are phagocytized.
E) Many proteins must be independently activated in order to have a significant impact on the immune response.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is a graph of antibodies in an immunized person's blood. At point B _____ is given that enhances the immunity to the pathogen. 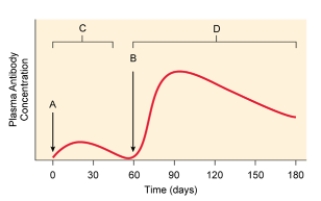
A) a booster
B) the primary exposure to the vaccine
C) a dose of antibodies
D) a live pathogen
E) histamine
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person has a genetic defect in the metabolic pathway that produces cytokines, then
A) macrophages will not be produced by the immune system.
B) B cells would not be activated to respond when cells presenting antigens are present.
C) helper T cells would take over the role of activating B cells.
D) the spleen would destroy all red blood cells.
E) histamine will not be produced by mast cells.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
AIDS is caused by
A) the human immunodeficiency virus that destroys helper T cells.
B) the human immunodeficiency virus that stimulates apoptosis of immune system cells.
C) allergens that stimulate helper T cells to produce cytokines.
D) bacteria that destroy lymphocytes in the bone marrow.
E) the human immunodeficiency virus that destroys macrophages.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What organisms are commonly used to mass-produce vaccines?
A) bacteria
B) viruses
C) cattle
D) pigs
E) humans
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
T lymphocytes
A) migrate from the thymus to the bone marrow where they mature.
B) that recognize "self-cells" leave the thymus and enter lymphatic vessels and organs.
C) must have the antigen presented to them by an antigen-presenting cell.
D) develop into plasma cells once activated.
E) are a component of the body's nonspecific immune defenses.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
T-cell receptors will bind with their specific antigens
A) immediately upon encountering them.
B) after being activated by an antigen-presenting cell.
C) after antibodies are produced for that antigen.
D) either immediately upon encountering them or when presented by an APC.
E) only in the presence of histamine.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person has type A blood. This means that
A) she has A antigens on her red blood cells and can only receive type A blood in transfusions.
B) she produces A antibodies when type A blood is used in transfusion, causing agglutination.
C) she has A antigens on her red blood cells and will produce antibodies if red blood cells with B antigens are transfused into her body.
D) she has B antigens on her red blood cells and can only receive type O blood.
E) she produces A antibodies when type B blood is used in a transfusion.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following bones contain red bone marrow in children but not in adults?
A) pelvic bones
B) sternum
C) clavicle
D) vertebrae
E) radius
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shows the function of cytotoxic T cells in the correct order?
A) perforin released - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell
B) cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - perforin released
C) apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - perforin released - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - perforin released
D) cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - perforin released - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell
E) granzymes delivered - perforin released - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way the complement system acts is by producing
A) proteins that assist phagocytes in recognizing a pathogen.
B) mast cells that attack pathogens' membranes.
C) histamines that stimulate B cell formation.
D) kinins that bind to the surface of pathogens.
E) macrophages that phagocytize bacteria.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Antibodies are _____ proteins, whileantigens that elicit an immune reaction are _____ proteins.
A) bacterial; self-produced
B) self-produced; foreign
C) self-produced; also self-produced
D) cancer; bacterial
E) viral; self-produced
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Red bone marrow in adults produces only white blood cells.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The immune system plays a significant role in fighting infections and cancer.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is a method of treatment for HIV infections?
A) chemotherapy
B) radiation treatment
C) blood transfusion
D) herbal supplements
E) drug therapy
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the body responds against its own cells as foreign antigens, this results in
A) allergies.
B) autoimmune disease.
C) passive immunity.
D) anaphylactic shock.
E) active immunity.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an inaccurate statement regarding B-cell receptors?
A) They bind with specific antigens.
B) They cause B cells to produce plasma cells and memory B cells when activated.
C) They may never encounter the antigen which binds to them.
D) They are identical to the antibodies produced by plasma cells, which they activate.
E) They may be changed by the B cell in response to whatever pathogen is present.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 52
Related Exams