A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 1, 3, 4, 2
C) 1, 3, 2, 4
D) 2, 4, 3, 1
E) 1, 4, 3, 2
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brain waves associated with information processing or problem solving are ____ waves.
A) alpha
B) beta
C) delta
D) theta
E) kappa
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
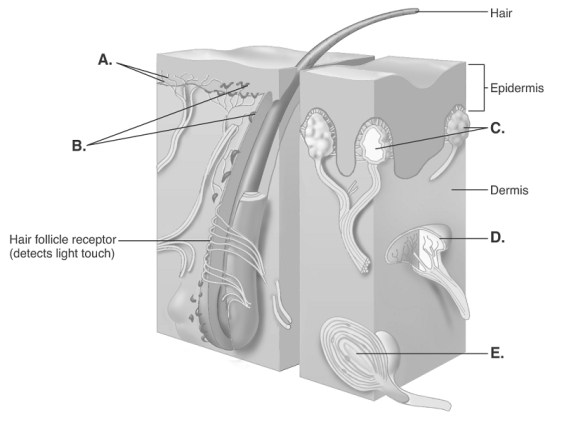 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "E" represent?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What structure does "E" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
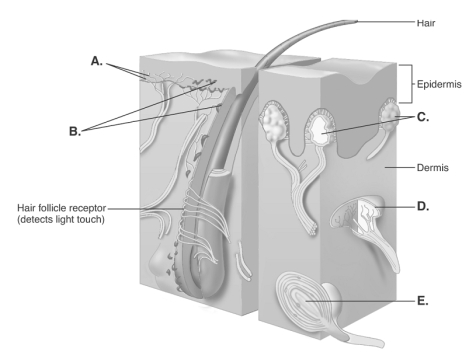 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "D"?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "D"?
A) detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) responds to painful stimuli
C) responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) detects continuous touch or pressure
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) corticospinal tract - movements, especially the hands
B) corticobulbar tract - movements in the head and face
C) rubrospinal tract - two-point discrimination
D) vestibulospinal tract - maintains upright posture
E) reticulospinal - posture adjustments and walking
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vision is dependent upon
A) chemoreceptors.
B) photoreceptors.
C) thermoreceptors.
D) mechanoreceptors.
E) nociceptors.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following functions is most likely to be performed by the visual association area?
A) "recognizes" the face of a close friend
B) "sees" the shape of the visual image
C) "senses" pain impulses
D) "moves" the eyes
E) "sees" color
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The auditory cortex is located in the
A) insula.
B) temporal lobe.
C) parietal lobe.
D) frontal lobe.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "C"?
-The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin. What is the function of "C"?
A) detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) responds to painful stimuli
C) responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) detects continuous touch or pressure
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in the blood concentration of glucose, oxygen and hydrogen are detected by
A) baroreceptors.
B) chemoreceptors.
C) nociceptors.
D) proprioceptors.
E) thermoreceptors.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In short-term memory,
A) information is retained for less than a second.
B) the frontal lobe plays the most important role.
C) current information is lost when new information is presented.
D) there is increased synaptic activity by long-term potentiation.
E) there is consolidation of information.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person suffering a stroke in the right parietal lobe may lose the ability to recognize faces. This is called
A) aphasia.
B) aprexia.
C) athetosis.
D) amorphosynthesis.
E) incoherency.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to Wernicke area would result in
A) facial paralysis.
B) facial tics.
C) aphasia.
D) "seeing stars".
E) apraxia.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
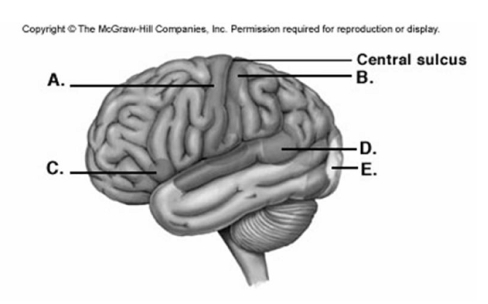 -Label area "D" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "D" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca area)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person decided to jump over a chair, which of the following areas organizes the motor functions needed to carry out this action.
A) visual cortex
B) premotor area
C) prefrontal area
D) auditory association area
E) visual association area
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wernicke area is necessary for
A) motivation.
B) understanding and formulating coherent speech.
C) initiating the muscular movements of speech.
D) processing visual images.
E) smiling.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus would help us
A) perceive pain.
B) tell if an object is rough or smooth.
C) sense temperature.
D) move our arms and legs.
E) write a sentence.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) visceroreceptors - associated with organs
B) adaptation - decreased sensitivity to continued stimulus
C) projection - sensation is perceived at the site of the stimulus
D) proprioceptors - information about body position
E) cutaneous receptors - associated with the viscera
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gate control theory of pain says that pain impulses traveling through the lateral spinothalamic tract can be suppressed by increased activity of the
A) anterior spinothalamic tract.
B) tertiary neurons.
C) extrapyramidal tracts.
D) dorsal column/medial lemniscal system.
E) spinocerebellar tracts.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The conscious awareness of stimuli received by sensory receptors is called perception.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 142
Related Exams