A) responds in an all-or-none fashion.
B) depolarizes when both sodium and calcium ions diffuse into the cell.
C) has fast waves of depolarization.
D) has fast waves of repolarization.
E) has a resting membrane potential that is more negative than skeletal muscle fibers.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Concentric contractions occur when
A) the muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
B) the tension and length of the muscle remain constant during a contraction.
C) tension in a muscle is maintained while the muscle increases in length.
D) the muscle produces tension while the length of the muscle increases.
E) isometric contractions occur.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sarcomere extends from
A) one Z disk to an adjacent Z disk.
B) one T tubule to the next T tubule.
C) the middle of the I band to the middle of the A band.
D) the H zone to the I band.
E) the M line to the next M line.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following helps explain the increased tension seen in multiple wave summation?
A) increased motor unit recruitment
B) increased concentration of calcium ions around the myofibrils
C) exposure of more active sites on myosin myofilaments
D) the breakdown of elastic elements in the cell
E) decreased stimulus frequency
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of muscle tissue causes peristalsis?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Callie is a world class marathon runner. Which of the descriptions about her dominant type of skeletal muscle is FALSE?
A) They split ATP slowly.
B) They have large deposits of myoglobin.
C) They are well adapted to anaerobic activity.
D) They have a well developed blood supply.
E) They have low glycogen stores.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) The greater the overlap of actin and myosin, the stronger the contraction.
B) Overstretching a muscle will increase its tension.
C) Optimal actin and myosin overlap will produce maximal contraction.
D) The greatest amount of tension is achieved when actin and myosin do not overlap.
E) Tension is great when actin and myosin overlap as much as they can.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events occurs on the postsynaptic membrane?
A) acetylcholine production
B) rapid degradation of acetylcholine
C) release of neurotransmitter
D) neurotransmitter combines with a receptor molecule
E) release of calcium ions
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the statement concerning general functional characteristics of muscle that is true.
A) Muscle tissue shortens forcefully but lengthens passively.
B) Muscle tissue shortens passively but lengthens forcefully.
C) Muscle tissue can get shorter, but can not get longer.
D) Muscle tissue can get longer, but can not get shorter.
E) None of these statements are true.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete tetanus
A) is the time during which the tissue cannot respond again.
B) results in complete and incomplete tetanus.
C) is the condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions.
D) is the condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations.
E) is the constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following situations does a resting membrane potential exist?
A) a relaxed muscle fiber
B) a conducting neuron
C) a stimulated sensory receptor in the skin
D) a contracting cardiac muscle cell
E) the eye seeing an image
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One ATP molecule is required for
A) formation of the cross-bridge.
B) movement of the cross-bridge.
C) release of the cross-bridge.
D) formation of the cross-bridge and for movement of the cross-bridge.
E) formation of the cross-bridge, for movement of the cross-bridge, and for release of the cross-bridge.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue has spindle-shaped cells?
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
D) both skeletal and cardiac muscle
E) both cardiac and smooth muscle
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plasma membrane of an excitable cell is more permeable to potassium ions because
A) of its positive electrical charge.
B) there are more leak ion channels for K+ than Na+.
C) protein molecules cannot exit through the cell membrane.
D) calcium ions block Na+ and Cl- channels.
E) there are more gated channels for K+.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
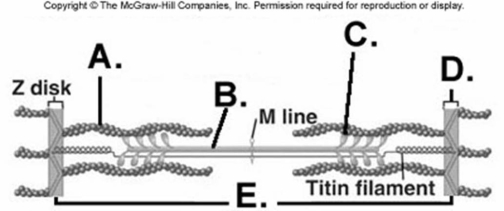 -What does "A" represent on the diagram?
-What does "A" represent on the diagram?
A) myosin myofilament
B) actin myofilament
C) sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) cross-bridge
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a known effect of illegal use of anabolic steroids in large dosages?
A) increased muscle size
B) kidney damage
C) diminished testosterone secretion
D) increased cardiovascular fitness
E) sterility
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will respond to a threshold stimulus with an all-or-none contraction?
A) a single muscle fiber
B) a single motor unit
C) a whole muscle
D) a single muscle fiber and a single motor unit
E) a single muscle fiber, a single motor unit, and a whole muscle
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Troponin
A) has two subunits.
B) is part of the myosin myofilament.
C) is a long, flexible protein.
D) has a calcium-binding site.
E) binds to ATP.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
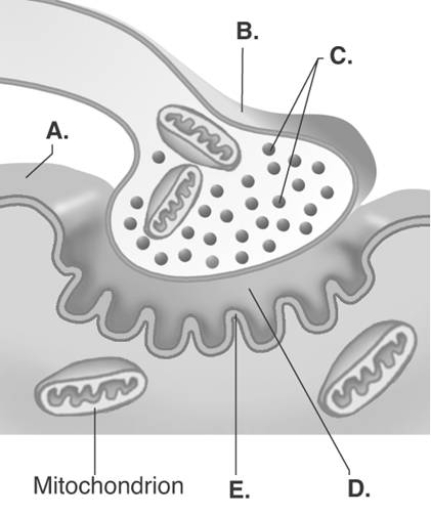 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "B" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "B" represent?
A) synaptic vesicles
B) synaptic cleft
C) sarcolemma
D) presynaptic terminal
E) postsynaptic membrane
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Randy is participating in a strong man competition and is required to pull a yacht as far as he can. Which type of chemical process will his skeletal muscles rely on during this competition?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) aerobic respiration
C) both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 200
Related Exams