A) a double-layered serous membrane that anchors some of the abdominal organs to the body wall.
B) the serous membrane that covers the lungs.
C) the serous membrane that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
D) space located between the visceral and parietal pleura.
E) the membrane that lines the pericardial sac.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the number of cells is
A) reproduction.
B) growth.
C) differentiation.
D) metabolism.
E) organization.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With regard to the validity of biomedical research in physiological studies, which statement is correct?
A) Although the general homeostatic mechanisms may be the same in some animal species, the individual variables are often very different.
B) Although the individual variables may be the same in some animal species, the general homeostatic mechanisms are often very different.
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
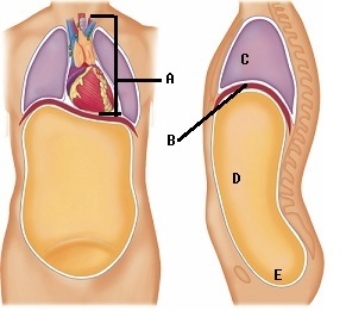 -Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other structures. What does "D" represent?
-Here is a figure showing major trunk cavities and other structures. What does "D" represent?
A) diaphragm
B) mediastinum
C) pelvic cavity
D) thoracic cavity
E) abdominal cavity
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that function together?
A) regional
B) developmental
C) systemic
D) histology
E) surface anatomy
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A vertical plane that separates the body into right and left portions is called a _____ plane.
A) sagittal
B) transverse
C) frontal
D) horizontal
E) coronal
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deep means
A) toward the middle or midline of the body.
B) away from the surface.
C) closer to the head.
D) closer than another structure to the point of attachment to the trunk.
E) toward the back of the body.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A molecular biologist discovers that if a specific drug effectively treats obesity in mice, what can researchers conclude?
A) If the drug was effective in a large number of mice, it will therefore be effective in humans.
B) If the drug was effective in a small proportion of mice, it will be effective in a small proportion of humans.
C) The mice have provided a positive control in this experiment that proves the drug is effective in humans.
D) The drug is effective in the mouse model; it must still be tested in humans.
E) The effect of the drug on mice has no bearing on the effect of the drug on humans.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The changes an organism undergoes through time is called
A) organization.
B) metabolism.
C) reproduction.
D) growth.
E) development.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Both the spleen and the urinary bladder are contained within the pelvic cavity subdivision of the abdominopelvic cavity.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Medial means
A) toward the middle or midline of the body.
B) away from the surface.
C) closer to the head.
D) closer than another structure to the point of attachment to the trunk.
E) toward the back of the body.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person lying with his/her face down is said to be in what position?
A) supine
B) prone
C) anatomical
D) reverse
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study of the body's organization by areas is
A) systemic anatomy.
B) regional anatomy.
C) molecular biology.
D) microbiology.
E) surface anatomy.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pectoral region is the
A) area in front of the elbow.
B) chest area.
C) lower back.
D) bottom of foot.
E) forearm.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
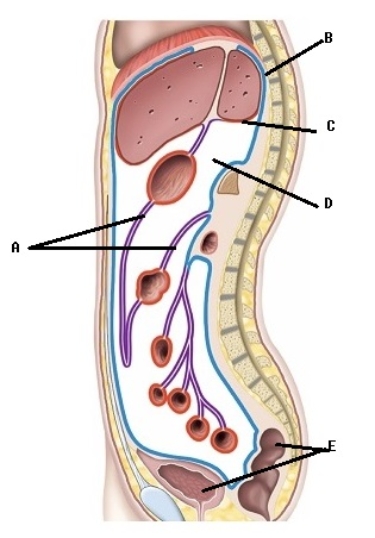 -This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity. What serous membrane does "B" represent?
-This is a sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity. What serous membrane does "B" represent?
A) visceral peritoneum (covers organs)
B) mesentery
C) parietal peritoneum (lines cavity)
D) retroperitoneal organs
E) peritoneal cavity
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study of the external form of the body and its relationship to deeper structures is
A) systemic anatomy.
B) regional anatomy.
C) molecular biology.
D) microbiology.
E) surface anatomy.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Whereas a 'plane' describes an imaginary flat surface, a 'section' describes a way to cut an organ.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In reference to the body tempaerature in living organisms, the set point can be defined as the
A) ideal normal value
B) current specific value
C) amount of change that must occur for a condition to return to ideal normal value
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What technique creates a three-dimensional dynamic image of blood vessels?
A) digital subtraction angiography
B) magnetic resonance imaging
C) dynamic spatial reconstruction
D) positron emission tomography
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure illustrates changes in blood pressure when _____ feedback mechanisms are in control. 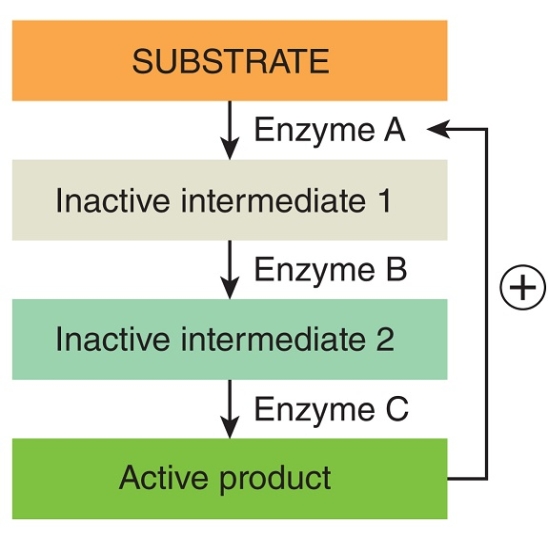
A) positive
B) negative
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 120
Related Exams