B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monetarists and rational expectations theorists believe that cost-push inflation is impossible in the long run in the absence of excessive money supply growth.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which economic perspective typically views the market system as less than fully competitive, and therefore subject to macroeconomic instability?
A) monetarism
B) mainstream economics
C) real-business-cycle theory
D) rational expectations theory
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the equation of exchange, the nominal GDP is designated by
A) PQ/M.
B) MV/P.
C) PQ.
D) MV.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetarists say
A) that, because P is stable, a change in M will change Q proportionately in the opposite direction.
B) a change in the money supply will change aggregate demand and therefore nominal GDP.
C) a change in the money supply will change velocity, which in turn will change nominal GDP.
D) a change in the money supply will change the interest rate, which will change investment spending and nominal GDP.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the rational expectations view,
A) wages are flexible downward but prices are inflexible downward.
B) prices are flexible downward but wages are inflexible downward.
C) discretionary policy tends to be countercyclical.
D) discretionary policy tends to be ineffective.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A) expansionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy.
B) contractionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy.
C) expansionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy.
D) contractionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dividing nominal gross domestic product (GDP) by the money supply (M) is a way to obtain the
A) velocity of money.
B) monetary multiplier.
C) equation of exchange.
D) monetary rule.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the mainstream view, the economic instability brought about by "oil shocks" works through changes in
A) aggregate demand.
B) wage and price inflexibility.
C) money supply.
D) aggregate supply.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The "efficiency wage" is one possible explanation for rigidities in the economy that lead to economic instability.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A) increase and cause the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD
B) decrease and cause the investment demand curve to shift from AD
C) increase and cause the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD
D) decrease and cause the investment demand curve to shift from AD
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
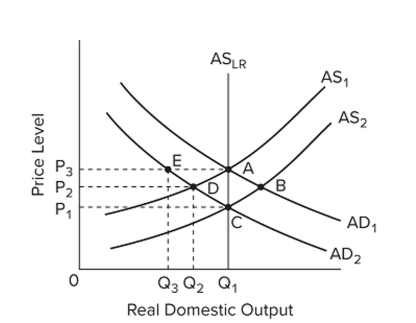 Refer to the graph. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD intersects A
. If
There is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD
, then, according to mainstream economists, if
Prices are ?exible and wages are not, this will result in an equilibrium at point
Refer to the graph. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD intersects A
. If
There is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD
, then, according to mainstream economists, if
Prices are ?exible and wages are not, this will result in an equilibrium at point
A) B.
B) C.
C) D.
D) E.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The view that inappropriate monetary policy was the main reason for the depth of the Great Depression in the United States is most closely associated with
A) monetarism.
B) the mainstream view.
C) the rational expectations theory.
D) the real-business-cycle theory.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New classical economists say that a fully anticipated increase in aggregate demand
A) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) moves the economy up along its vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) eventually results in a self-correcting decrease in aggregate demand.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the velocity of money remains unchanged and the economy is at full employment, then the equation of exchange predicts that a rise in the money supply will
A) increase prices.
B) increase interest rates.
C) increase real output.
D) decrease nominal GDP.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A)
B)
C)
D)
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crowding-out effect refers to the possibility that
A) when used simultaneously, expansionary fiscal and monetary policies are counterproductive.
B) the asset demand for money varies inversely with the interest rate.
C) deficit financing will increase the interest rate and reduce investment.
D) an increase in the supply of money will result in a decline in velocity.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the table. The e?ciency wage is
A) $10.
B) $9.
C) $8
D) $6.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An efficiency wage is
A) a wage payment necessary to compensate workers for risk of injury on the job.
B) a "wage" that contains a profit-sharing component as well as traditional hourly pay.
C) an above-market wage that minimizes a firm's labor cost per unit of output.
D) a wage that automatically rises with the national index of labor productivity.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economists today would agree with the view that "money doesn't matter" in macroeconomic theory.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 279
Related Exams