A) worth or value today of future expected returns or costs.
B) worth in the future of a current flow of returns or costs.
C) current worth of a financial asset purchased in the past.
D) expected future value of a financial asset purchased today.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Meb owns stock in two similar, large, financially sound corporations. Company A consistently earns rates of return of 12 percent per year, while company B regularly generates rates of return of 8 Percent per year. If Meb is attempting to arbitrage, he will
A) sell his stock in company B and buy more stock in company A.
B) sell his stock in company A and buy more stock in company B.
C) keep his portfolio balanced with an equal or nearly equal number of shares of each stock.
D) buy stock in other companies in an effort to diversify and minimize risk.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The maximum amount of money that company shareholders can lose on their investment in the corporation is
A) whatever percentage of their wealth equals their percentage of ownership.
B) whatever they paid for the shares in the company.
C) whatever the corporation loses each year times the percentage of ownership in the company.
D) zero.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
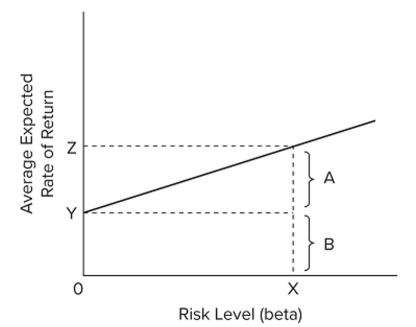 In the accompanying graph, point Y represents the
In the accompanying graph, point Y represents the
A) rate of return for the market portfolio.
B) rate of return for the risk-free asset.
C) risk premium for the market portfolio.
D) compensation for time preference for a given asset.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A change in investors' feelings about risk will change the intercept (and therefore shift) the Security Market Line.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do stocks represent?
A) shares of ownership in a corporation and a guaranteed stream of profits
B) shares of ownership in a corporation and an entitlement to its future profits
C) debt contracts with a corporation and regular interest payments on the loan
D) debt contracts with a corporation and variable interest payments on the loan
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Index funds
A) are passively managed.
B) are actively managed.
C) may be either passively or actively managed.
D) are neither passively nor actively managed.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic investment refers to
A) buying a financial asset for a gain.
B) selling a financial asset for a gain.
C) postponing purchases of goods and services.
D) making new additions to a firm's stock of capital.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economic investment refers to the buying or selling of any asset in expectation of a financial gain.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that money has "time value" refers to the fact that
A) people prefer to receive a given sum of money in the future rather than in the present.
B) money can be used to purchase the services of labor, as measured in hourly units.
C) a specific amount of money is more valuable to a person the sooner it is received.
D) compound interest converts future dollars into a greater amount of current dollars.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an investor owns a well-diversified portfolio, then
A) his portfolio does not involve any risk.
B) the idiosyncratic risk in his portfolio is minimized.
C) the systemic risk in his portfolio is minimized.
D) his portfolio will have the highest expected return.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One fundamental concept in financial economics is that an investment's rate of return is
A) positively related to the price paid for it.
B) inversely related to the price paid for it.
C) inversely related to the riskiness of the investment.
D) inversely related to the maturity of the investment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
After 4 years, a $5,000 investment earning a 6 percent annual interest rate will be worth more than a $6,000 investment earning 1 percent annual interest.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
$800 invested at an annually compounded interest rate of 6 percent will be worth how much at the end of 10 years?
A) $1,280
B) $1,433
C) $1,417
D) $1,369
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a difference between stocks and bonds?
A) Stocks are issued for a fixed period; bonds are not.
B) Stocks pay interest; bonds pay dividends.
C) Bond payouts are more predictable than payouts from stocks.
D) Bonds represent ownership; stocks represent debt.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
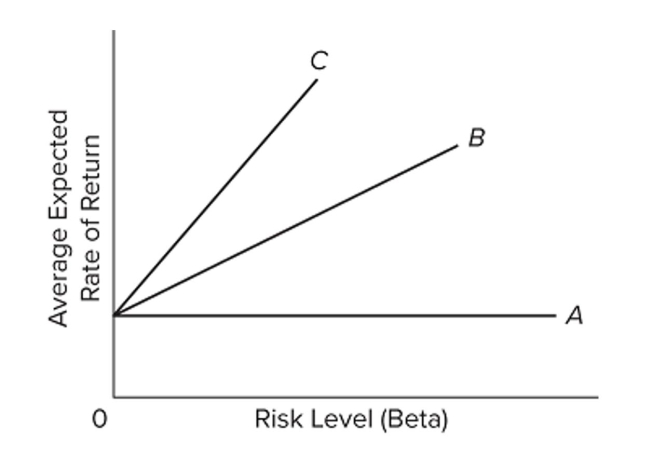 Refer to the graph. An increase in investor concern about risk would be shown by
Refer to the graph. An increase in investor concern about risk would be shown by
A) an increase in the intercept.
B) a shift from line C to line B.
C) a shift from line A to line B.
D) a decrease in the risk-free interest rate.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The market portfolio would have a beta of
A) 0.
B) 1.0.
C) 100.
D) any value.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lottery winners who take the lump-sum payouts instead of payments spread out over many years
A) believe the rate of return they could find in other financial assets is less than that implied in the extended payout.
B) sacrifice free money and are making an economically irrational decision.
C) prefer immediate to delayed returns.
D) are only making a rational economic decision if there is rapid inflation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is considered to be the best measure of the risk-free interest rate?
A) the rate of return on a corporate bond index fund
B) the rate of return on a corporate stock index fund
C) the rate of return on the Standard & Poor's 500
D) the rate of return on short-term U.S. government bonds
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between risk and the average expected return of investments?
A) Less risky assets will have similar average expected rates of return to more risky assets.
B) Less risky assets will have higher average expected rates of return than more risky assets.
C) More risky assets will have higher average expected rates of return than less risky assets.
D) More risky assets will have lower average expected rates of return than less risky assets.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 356
Related Exams