A) interest rate will decline, but we cannot predict the change in the equilibrium quantity of money.
B) quantity of money and the equilibrium interest rate will both increase.
C) quantity of money will increase, but we cannot predict the change in the equilibrium interest rate.
D) quantity of money will decline, but we cannot predict the change in the equilibrium interest rate.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a difference between "quantitative easing" and ordinary open-market operations?
A) There is no difference between the two policy tools.
B) Open-market operations are done to lower interest rates; quantitative easing is done to increase the quantity of bank reserves.
C) Quantitative easing is done in order to lower interest rates; open-market operations are merely intended to increase bank reserves.
D) Open-market operations involve forward commitment; quantitative easing is intentionally vague to maintain flexibility.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The collateral used for repos and reverse repos is (are)
A) corporate securities.
B) autos.
C) homes.
D) government bonds.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Reserve System regulates the money supply primarily by
A) controlling the production of coins at the U.S. mint.
B) altering the reserve requirements of commercial banks and thereby the ability of banks to make loans.
C) altering the reserves of commercial banks, largely through sales and purchases of government bonds.
D) restricting the issuance of Federal Reserve Notes because paper money is the largest portion of the money supply.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A commercial bank can add to its actual reserves by
A) lending money to bank customers.
B) buying government securities from the public.
C) buying government securities from a Federal Reserve Bank.
D) borrowing from a Federal Reserve Bank.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does it mean when economists say that the Fed has attempted to "normalize" monetary policy after the Great Recession?
A) The Fed has tried to use monetary policy to restore the unemployment rate to its normal full employment rate of around 5 percent.
B) The Fed has tried to use monetary policy to raise excess reserves back up to normal prerecession levels.
C) The Fed has tried to make all of the monetary policy actions used during the financial crisis a normal part of the monetary policy tool kit.
D) The Fed has tried to use monetary policy to bring interest rates back to their historically normal levels.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer holds money to meet spending needs. This would be an example of the
A) use of money as a measure of value.
B) use of money as legal tender.
C) transactions demand for money.
D) asset demand for money.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price of a bond having no expiration date is originally $8,000 and has a fixed annual interest payment of $800. A fall in the price of the bond by $3,000 will provide a new buyer of the bond an interest rate of
A) 10 percent.
B) 12 percent.
C) 14 percent.
D) 16 percent.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the transactions demand for money is equal to 20 percent of the nominal GDP, the supply of money is $800 billion, and the asset demand for money is that shown in the table. If the nominal GDP is $2,000 billion, the equilibrium interest rate is
A) 4 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 6 percent.
D) 7 percent.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Taylor rule, if the target rate of inflation for the Fed is 2 percent and inflation rises to 3 percent at full unemployment, then the Fed should
A) raise the real federal funds rate by one percentage point.
B) lower the real federal funds rate by one percentage point.
C) raise their targeted interest rate by half of a percentage point.
D) lower their targeted interest rate by half of a percentage point.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed wants to maintain current interest rates, it would be buying government bonds in the open market when
A) the demand for money decreases.
B) the demand for money increases.
C) investment demand decreases.
D) the discount rate increases.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interest paid on excess reserves held at the Fed
A) is available to the general public, but not to commercial banks.
B) will incentivize financial institutions to hold more reserves and reduce risky lending.
C) is determined by the federal funds rate.
D) totaled over $1 trillion in 2018.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about quantitative easing is most accurate?
A) Quantitative easing refers to the Fed's use of open-market operations to buy trillions of dollars' worth of medium- and longer-maturity financial assets.
B) Quantitative easing has become one of the permanently recognized tools of monetary policy.
C) Quantitative easing significantly lowered interest rates in the aftermath of the financial crisis.
D) Quantitative easing is the new official name for open-market operations.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
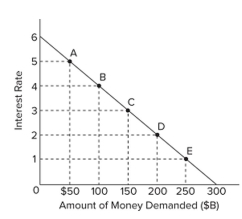 Refer to the graph. If the interest rate rises from 2 percent to 3 percent, the supply of money must have
Refer to the graph. If the interest rate rises from 2 percent to 3 percent, the supply of money must have
A) decreased by $50 billion.
B) decreased by $100 billion.
C) decreased by $150 billion.
D) increased by $50 billion.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A wealthy executive is holding money, waiting for a good time to invest in the stock market. This action would be an example of the
A) transactions demand for money.
B) asset demand for money.
C) creation of fiat money.
D) use of money as a medium of exchange.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U.S. Treasury deposits at the Federal Reserve Banks are
A) a liability of the Federal Reserve Banks and the U.S. Treasury.
B) an asset of the Federal Reserve Banks and the U.S. Treasury.
C) a liability of the Federal Reserve Banks and an asset for the U.S. Treasury.
D) an asset of the Federal Reserve Banks and a liability for the U.S. Treasury.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in nominal GDP increases the demand for money because
A) interest rates will rise.
B) more money is needed to finance a larger volume of transactions.
C) bond prices will fall.
D) the opportunity cost of holding money will decline.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
There is an asset demand for money because households and business firms use money as a store of value.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The purpose of an expansionary monetary policy is to shift the
A) aggregate demand curve leftward.
B) aggregate demand curve rightward.
C) aggregate supply curve leftward.
D) investment demand curve leftward.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, an increase in input prices will
A) reduce aggregate supply and reduce real output.
B) increase the interest rate and lower the international value of the dollar.
C) increase aggregate supply and increase the price level.
D) increase net exports, increase investment, and reduce aggregate demand.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 405
Related Exams