B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Essential" water is cheaper than "nonessential" diamonds because
A) new industrial uses for diamonds have been discovered.
B) the supply of water is great relative to demand and the supply of diamonds is small relative to demand.
C) although the total utility of diamonds is greater, their marginal utility is small.
D) the supply of diamonds is great relative to demand and the supply of water is small relative to demand.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The law of diminishing marginal utility implies that in order to induce a buyer to buy more of a product, the seller must lower its price.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows the marginal-utility schedules for goods A and B for a hypothetical consumer. The price of good A is $1, and the price of good B is $2. The income of the consumer is $8. 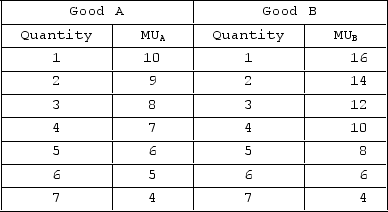 If the consumer spends the given budget and gets maximum utility out of it, then she is receiving how much satisfaction from each dollar spent on the final unit of good B consumed?
If the consumer spends the given budget and gets maximum utility out of it, then she is receiving how much satisfaction from each dollar spent on the final unit of good B consumed?
A) 14 utils per dollar
B) 7 utils per dollar
C) 9 utils per dollar
D) 2 utils per dollar
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The limited money income of consumers results in a so-called budget constraint.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A product has utility if it
A) takes more and more resources to produce successive units of it.
B) violates the law of demand.
C) satisfies consumer wants.
D) is useful.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
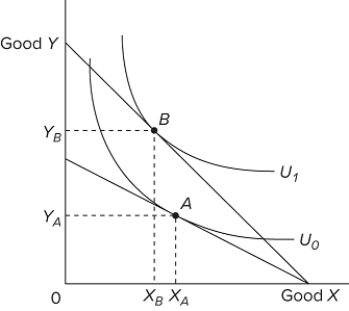 Refer to the diagram. Suppose the budget line shifts so that the consumer's equilibrium changes from point A to point B. This means that the
Refer to the diagram. Suppose the budget line shifts so that the consumer's equilibrium changes from point A to point B. This means that the
A) price of Y has increased.
B) price of Y has decreased.
C) price of X has increased.
D) consumer's money income has increased.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
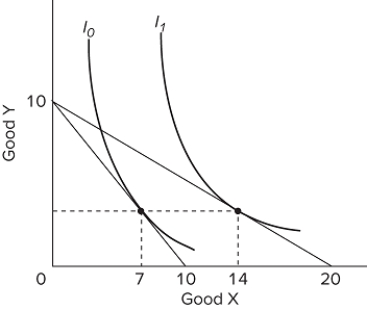 Given the indifference curves for an individual as shown above, if the price of good Y = $1, it can be determined that two points on his or her demand curve for good X are
Given the indifference curves for an individual as shown above, if the price of good Y = $1, it can be determined that two points on his or her demand curve for good X are
A) ( Pₓ = $1, Qdₓ = 10) ; ( Pₓ = $2, Qdₓ = 14) .
B) ( Pₓ = $1, Qdₓ = 7) ; ( Pₓ = $0.50, Qdₓ = 14) .
C) ( Pₓ = $0.50, Qdₓ = 7) ; ( Pₓ = $1, Qdₓ = 10) .
D) ( Pₓ = $2, Qdₓ = 20) ; ( Pₓ = $1, Qdₓ = 10) .
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
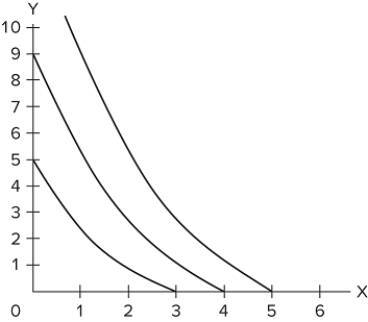 Refer to the graph. Suppose you had tastes as described by the indifference curves above. If your income was $90, Pₓ = 30, and Pᵧ = 10, which combination of X and Y would maximize your utility?
Refer to the graph. Suppose you had tastes as described by the indifference curves above. If your income was $90, Pₓ = 30, and Pᵧ = 10, which combination of X and Y would maximize your utility?
A) 3X and 0Y
B) 0X and 9Y
C) 3X and 9Y
D) 1X and 6Y
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is possible for a consumer's indifference curves to intersect.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In moving northeasterly from the origin, we encounter indifference curves that reflect higher and higher levels of total utility.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A child is given $5.20 of pocket money to be spent on either hard candies or chocolates. Chocolates cost 40 cents and hard candies 80 cents each. The marginal utilities derived from each product are as shown in the following table. 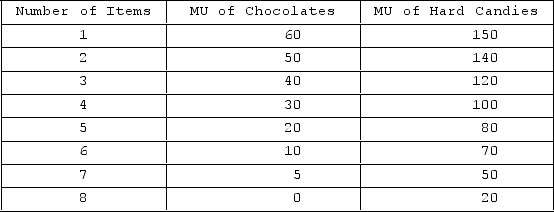 Which combination would give the child the maximum utility out of spending $5.20?
Which combination would give the child the maximum utility out of spending $5.20?
A) 8 chocolates and 2 hard candies
B) 5 chocolates and 4 hard candies
C) 3 chocolates and 5 hard candies
D) 2 chocolates and 4 hard candies
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
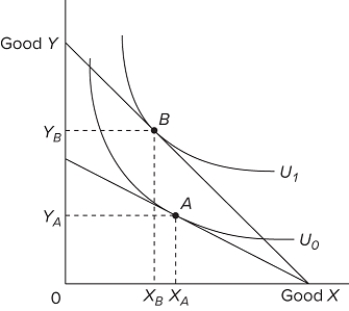 Refer to the diagram. The budget line shift that moves the consumer's equilibrium position from point A to point B suggests
Refer to the diagram. The budget line shift that moves the consumer's equilibrium position from point A to point B suggests
A) an increase in the quantity of Y demanded.
B) a decrease in the quantity of Y demanded.
C) a leftward shift in the demand curve for Y.
D) a rightward shift in the demand curve for Y.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A change in the relative prices for two goods can be shown as a parallel shift in a consumer's budget line.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
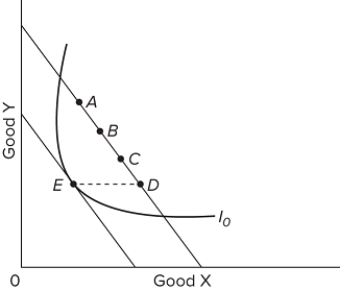 Consider the diagram, where E is the consumer's original equilibrium position. We know good Y is not a normal good if, as income increases, the consumer's new equilibrium position is at point
Consider the diagram, where E is the consumer's original equilibrium position. We know good Y is not a normal good if, as income increases, the consumer's new equilibrium position is at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that football tickets at your university are given away for free and that there are still empty seats for all games. Ignoring all other costs of going to the games, you should continue attending until your
A) total utility stops increasing.
B) marginal utility begins to diminish.
C) marginal utility stops increasing.
D) total utility reaches zero.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
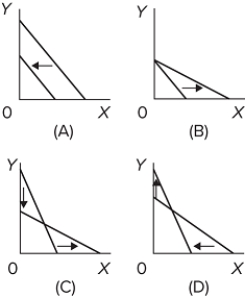 Which of the graphs shows a change in the buyer's income, but no changes in the prices of X and Y?
Which of the graphs shows a change in the buyer's income, but no changes in the prices of X and Y?
A) graph A
B) graph B
C) graph C
D) graph D
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Understanding the water and diamond paradox is valuable because it explains why
A) diamonds have many substitutes.
B) water is more important than diamonds.
C) the prices of products are not necessarily measures of the products' usefulness.
D) consumer spending on diamonds has increased, while spending on water has decreased.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows an indifference schedule for several combinations of X and Y. 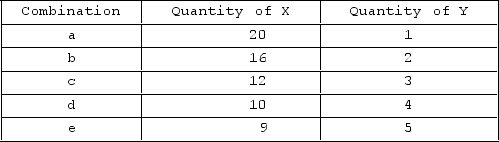 Approximately how much of Y is the consumer willing to give up to obtain the tenth unit of X?
Approximately how much of Y is the consumer willing to give up to obtain the tenth unit of X?
A) 5
B) 1
C) 4
D) 1/4
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diamond-water paradox arises because
A) essential goods may be cheap, while nonessential goods may be expensive.
B) the marginal utility of certain products increases, rather than diminishes.
C) essential goods are always higher priced than nonessential goods.
D) we sometimes fail to use money as a standard of value.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 358
Related Exams