A) there are significant negative externalities.
B) standardized products exist.
C) there are only foreign buyers.
D) information about buyers is inadequate which allows some buyers to consequently impose high costs on the sellers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Asymmetric information in a market transaction occurs when there is unequal knowledge possessed by the
A) buyer and the government.
B) seller and the government.
C) taxpayer and the government.
D) buyer and the seller.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In dealing with market failures, the government always bases its decisions on economic analysis of marginal cost and marginal benefit.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some sellers of used cars provide warranties to buyers, with the aim of reassuring buyers that the car is of good quality. These warranties help reduce the chance of what occurring?
A) negative externalities
B) adverse selection
C) spillover benefits
D) moral hazard
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
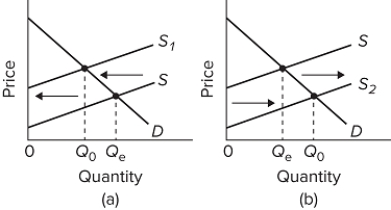 Refer to the diagrams for two separate product markets. Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q₀ and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S₁ in diagram (a) on the left and from S to S₂ in diagram (b) on the right. The shift of the supply curve from S to S₁ in diagram (a) might be caused by a per-unit
Refer to the diagrams for two separate product markets. Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q₀ and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S₁ in diagram (a) on the left and from S to S₂ in diagram (b) on the right. The shift of the supply curve from S to S₁ in diagram (a) might be caused by a per-unit
A) subsidy paid to the producers of this product.
B) tax on the producers of this product.
C) subsidy paid to the buyers of this product.
D) tax on the buyers of this product.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Upon learning that his auto transmission is about to fail, Ray sells his car to an unsuspecting buyer. This circumstance illustrates the
A) adverse selection problem.
B) free-rider problem.
C) moral hazard problem.
D) principal-agent problem.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is the custom for paper mills located alongside the Layzee River to discharge waste products into the river. As a result, operators of hydroelectric power-generating plants downstream along the river find that they must clean up the river's water before it flows through their equipment.If the government intervenes and corrects the externality in the situation described, we would expect
A) the supply of the output from the hydroelectric power plants to decrease.
B) the supply of the output from the hydroelectric power plants to increase.
C) the demand for the output from the hydroelectric power plants to decrease.
D) the demand for the output from the hydroelectric power plants to increase.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a negative externality?
A) an increase in the value of land you own when a nearby development is completed
B) the costs paid by a company to build an automated factory
C) falling property values in a neighborhood where a disreputable nightclub is operating
D) the higher price you pay when you buy a heavily advertised product
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the unit price of a product is P and buyers buy a given quantity Q, then sellers would collect total revenues equal to
A) P × Q.
B) P + Q.
C) P - Q.
D) Q - P.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a well-functioning cap-and-trade system for pollution rights, society benefits because pollution will be brought down to insignificant levels.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is the custom for paper mills located alongside the Layzee River to discharge waste products into the river. As a result, operators of hydroelectric power-generating plants downstream along the river find that they must clean up the river's water before it flows through their equipment.In the situation described above, we would expect an
A) overproduction of paper in the mills.
B) underproduction of paper in the mills.
C) external cost resulting from the production of hydroelectric power.
D) overproduction of power by the hydroelectric plants.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A market for pollution rights can be expected to
A) eliminate all pollution.
B) produce a shortage of pollution.
C) encourage potential polluters to increase emissions.
D) provide potential polluters with a monetary incentive to reduce emissions.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The socially optimal amount of pollution abatement occurs where society's marginal
A) benefit of abatement exceeds its marginal cost of abatement by the greatest amount.
B) benefit of abatement equals its marginal cost of abatement.
C) benefit of abatement is zero.
D) cost of abatement is at its maximum.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Professional buyers of antiques often have more information about the value of antique objects than do the sellers. This illustrates
A) the principal-agent problem.
B) the moral hazard problem.
C) the free-rider problem.
D) asymmetric information.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A significant amount of positive consumer surplus is the reason why sometimes a shopper regrets having bought a particular item.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consumer surplus arises in a market because
A) the quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded at the current market price.
B) the quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied at the current market price.
C) the market price is below what some consumers are willing to pay for the product.
D) the market price is higher than what some consumers are willing to pay for the product.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
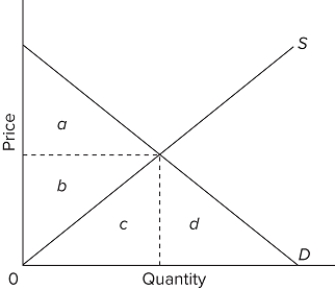 In the provided graph, the equilibrium point in the market is where the S and D curves intersect. At equilibrium, the total maximum amount that consumers would have been willing to pay for the product is represented by the area
In the provided graph, the equilibrium point in the market is where the S and D curves intersect. At equilibrium, the total maximum amount that consumers would have been willing to pay for the product is represented by the area
A) a + b.
B) a + b + c.
C) a.
D) b + c.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
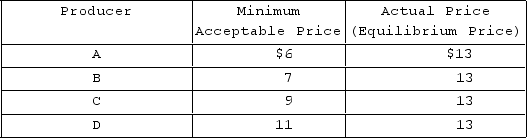 Refer to the provided table. What is the producer surplus for all producers A, B, C, and D?
Refer to the provided table. What is the producer surplus for all producers A, B, C, and D?
A) $6
B) $13
C) $19
D) $24
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person drives with less care after purchasing auto insurance, this situation would be an example of a(n)
A) reverse wealth problem.
B) negative externality problem.
C) adverse selection problem.
D) moral hazard problem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a television advertisement for AFLAC supplemental health insurance, an ice skater says to his skating partner, "Do you want to try a triple jump?" She responds, "Why not, I have AFLAC." This response illustrates the
A) principal-agent problem.
B) adverse selection problem.
C) moral hazard problem.
D) free-rider problem.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 229
Related Exams