A) large decrease in farm prices and total revenue for farmers.
B) small increase in farm prices and total revenue for farmers.
C) small decrease in farm prices and a relatively large increase in total revenue for farmers.
D) large increase in farm prices and a relatively small decrease in total revenue for farmers.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Import quotas on sugar may cost consumers $2 billion per year. But this quota goes unchallenged because the $10 average annual cost per person is so small that probably not one voter in 200 knows the quota exists. This statement describes
A) the voting paradox.
B) the special-interest effect.
C) the median-voter model.
D) free-rider problem.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Increases in incomes usually result in more than proportionate increases in the demand for agricultural products in a growing economy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has been an effect of the U.S. government's ethanol program?
A) Prices for crops such as soybeans and sorghum have fallen dramatically.
B) Prices for beef, pork, and chicken have risen.
C) Water use has declined, as corn is a less water-intensive crop.
D) All of these effects have resulted from the ethanol program.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
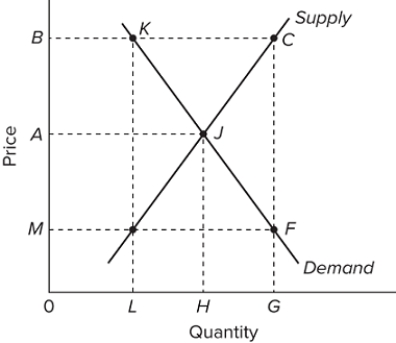 Refer to the diagram for the corn market. As a consequence of a price support of B, consumers will
Refer to the diagram for the corn market. As a consequence of a price support of B, consumers will
A) increase their purchases of the product.
B) pay a lower price, M rather than A, for the product.
C) pay a higher price, B rather than A, for the product.
D) pay a higher price, A rather than M, for the product.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major feature of the "Freedom to Farm" Act of 1996 was the
A) elimination of price supports and acreage allotments for many agricultural crops.
B) expansion of government price supports for many agricultural crops.
C) bolstering of the foreign demand for U.S. agricultural products.
D) increased support for research on farm productivity to help expand the supply of farm products.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in the quantity of soybeans produced could result from
A) elimination of farm subsidies to soybean producers.
B) a decrease in the price of another farm crop that could be grown.
C) a decrease in the cost of soybean production.
D) an increase in consumer incomes.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Historically, many aspects of U.S. farm policies had their origins in the
A) Agricultural Extension Service Act.
B) Agricultural Adjustment Act.
C) Homestead Act.
D) Land Grant Act.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The increasing relative importance of agricultural exports has increased the instability of the demand for U.S. farm products.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The parity ratio initially stood at 0.5. Then after several years, the prices received by farmers doubled while the prices they paid tripled. This will bring the parity ratio to
A) 0.25.
B) 0.33.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.80.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price parity concept, which is a cornerstone of U.S. agricultural policy, was established by the
A) Agricultural Income Act of 1914.
B) Agricultural Adjustment Act of 1933.
C) Obama administration.
D) Reagan administration.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over time, technological change has
A) reduced both the price elasticity and income elasticity of the demand for farm products.
B) reduced the minimum efficient scale of production in agriculture and increased the prices of farm products.
C) increased both price elasticity and income elasticity of the demand for farm products.
D) increased the minimum efficient scale of production in agriculture and reduced the prices of farm products.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2017, farm employment constituted about
A) 15.8 percent of total employment.
B) 1.2 percent of total employment.
C) 1.6 percent of total employment.
D) 2.6 percent of total employment.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The growing importance of export demand for American agriculture has
A) reduced the international value of the dollar.
B) had no significant effect on the stability of the demand for farm products.
C) destabilized the total demand for farm products.
D) stabilized the total demand for farm products.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As applied to agriculture, the special-interest effect suggests that
A) urban legislators support farm legislation in exchange for rural legislators supporting urban-oriented legislation.
B) a relatively small number of farmers receive large benefits at the expense of a much larger group of taxpayers who individually suffer small losses.
C) politicians support farm subsidies because most of the associated costs are hidden rather than explicit.
D) the size of farm subsidies should vary directly with a farmer's earned income.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is correct?
A) Farmers fared considerably better than most other economic groups during the Great Depression.
B) Farmers typically sell their products in highly competitive markets and buy in imperfectly competitive markets.
C) The principal beneficiaries of government farm subsidies have been the very-low-income farmers.
D) The use of price supports has accelerated the exodus of resources from agriculture.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S. Agriculture Act of 2014 did the following, except
A) ending the so-called countercyclical payments to farmers.
B) extending the direct payments to farmers, which were independent of their crop production.
C) creating an insurance program, called price loss coverage, which pays farmers if the price of their crop falls below a specified level.
D) introducing a countywide insurance program called agricultural risk coverage.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major criticism of agricultural subsidies is that
A) they restrict agricultural output but reduce farm incomes when demand is inelastic.
B) the principal beneficiaries of these subsidies have been foreign farmers and not domestic farmers.
C) they duplicate other economic policies that are designed to increase the prices for agricultural products.
D) they do not address the misallocation of resources between agriculture and the rest of the economy.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Farm groups spend considerable amounts of money to maintain and enlarge political support for farm subsidies. This illustrates
A) coalitions.
B) rent-seeking activity.
C) the special-interest effect.
D) the voting paradox.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An extraordinarily small crop of farm products due to drought causes
A) a large increase in the price of farm products because the demand for farm products is price inelastic.
B) only a slight increase in the price of farm products because the demand for farm products is income elastic.
C) only a slight increase in the price of farm products because the demand for farm products is income inelastic.
D) a large increase in the price of farm products because the demand for farm products is price elastic.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 265
Related Exams