A) the mere presence of monopoly violated the Sherman Act, irrespective of Microsoft's behavior.
B) Microsoft was a "bad monopoly."
C) Microsoft was generally a "good monopoly" but that its tying contracts involving Internet Explorer violated the Clayton Act.
D) the case was similar to the U.S. Steel case of 1920.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Alcoa case
A) was based on an approach to antitrust based on monopoly structure.
B) struck down the treble damages provision of the antitrust laws.
C) called for federal regulation of any industry with a four-firm concentration ratio in excess of 50 percent.
D) decision was consistent with an approach focusing on monopoly behavior.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The legislation that prohibited acquisition of stock of another company if this would significantly lessen competition is the
A) Federal Trade Commission Act.
B) Clayton Act.
C) Celler-Kefauver Act.
D) Wheeler-Lea Act.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The antitrust laws are based on the
A) creative destruction view of competition.
B) idea that competition leads to greater economic efficiency than does a monopoly.
C) view that nonprice competition should be strictly regulated by government.
D) view that all negative externalities should be eliminated by government action.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The argument that an industry that is highly concentrated will act like an anticompetitive monopolist would support the case that the application of antitrust laws should be based on industry
A) mergers.
B) structure.
C) regulation.
D) behavior.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conglomerate mergers are combinations of
A) many small firms.
B) firms producing the same product.
C) firms producing unrelated products.
D) firms operating at different stages in a given production process.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a per se violation?
A) price discrimination
B) price-fixing
C) extremely high Herfindahl index
D) horizontal merger
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
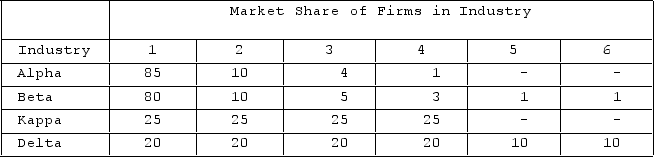 The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. The industry with the least market power as measured by the Herfindahl index is
The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. The industry with the least market power as measured by the Herfindahl index is
A) Delta.
B) Beta.
C) Alpha.
D) Kappa.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A conglomerate merger
A) can extend the line of products sold, extend the territories in which products are sold, or combine totally unrelated products.
B) is defined as a merger involving two firms that previously had a buyer-seller relationship.
C) is defined as a merger involving two firms producing the same or similar products and selling them in the same geographical market.
D) is illegal, per se.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following results will not occur in a monopolistic market?
A) The monopolist will maximize profits by setting a price that's higher than marginal cost.
B) The price will be higher than what would prevail in a competitive market.
C) In monopoly pricing, income is, in effect, transferred from consumers to the monopolist.
D) The output level will be higher than in a competitive market.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
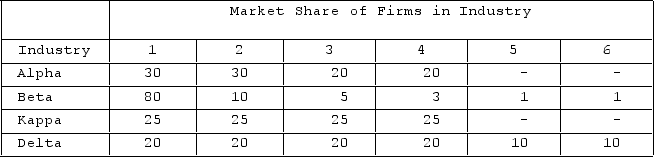 The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. The government would be most likely to challenge a merger between
The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. The government would be most likely to challenge a merger between
A) Firm 1 in Alpha and Firm 6 in Delta.
B) Firms 3 and 4 in Beta.
C) Firms 1 and 2 in Kappa.
D) Firm 4 in Alpha and Firm 3 in Kappa.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following gave the Federal Trade Commission responsibility to protect the public against false and misleading advertising?
A) Celler-Kefauver Act of 1950
B) Wheeler-Lea Act of 1938
C) Clayton Act of 1914
D) Sherman Act of 1890
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A merger that is neither horizontal nor vertical is called a
A) tying merger.
B) conglomerate merger.
C) Herfindahl merger.
D) natural merger.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Herfindahl index measures the
A) size of the market share of the four largest firms in an industry.
B) sum of the squared values of market shares of firms in an industry.
C) increase in economic concentration resulting from a conglomerate merger.
D) effect of per se violation in antitrust cases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generally speaking, if a firm faces decreasing average total costs of production throughout its entire range of output, then
A) more firms will enter the market.
B) it will be unable to remain in business.
C) the firm is a natural monopoly.
D) the firm is able to earn only a normal profit.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following U.S. Supreme Court cases ruled that only monopolies that "unreasonably restrain trade" are violating antitrust laws?
A) DuPont cellophane case of 1956
B) U.S. Steel case of 1920
C) Alcoa case of 1945
D) AT&T case of 1982
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Slow Ketchup requires that, as a condition of purchase, all restaurants using its product must buy and make available its new sales product. This arrangement is an example of
A) price-fixing.
B) an interlocking directive.
C) a tying contract.
D) price discrimination.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
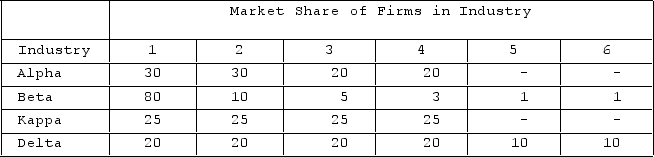 The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. The Herfindahl index for Kappa is
The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. The Herfindahl index for Kappa is
A) 2,500.
B) 100.
C) 100,000.
D) 5,000.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The agency responsible for investigating instances of fraudulent or misleading advertising is the
A) Federal Trade Commission.
B) Interstate Commerce Commission.
C) Federal Communications Commission.
D) Uniform Business Practices Commission.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The active antitrust perspective believes that competitive market forces will automatically and actively reduce a firm's monopoly power in the long run.
B) The active antitrust perspective believes that the government should play the role of officials and umpires and enforce the rules of the competitive game.
C) The laissez-faire perspective views firms as players in a competitive game who will sometimes violate the rules in order to gain a huge advantage over others.
D) The laissez-faire perspective believes that an active enforcement of antitrust policy is the only way to reduce the monopoly power of giant firms.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 264
Related Exams