A) Thailand
B) China
C) Togo
D) United States
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What was the largest U.S. fishery, in dollar terms, in 2016?
A) Pacific halibut
B) sea scallop
C) walleye pollock
D) lobster
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In time-value of money analysis, an increase in interest rates
A) raises the present value of a future amount.
B) lowers the present value of a future amount.
C) lowers the future value of a present amount.
D) has no effect on present or future amount.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The real cost of buying a market basket of 25 important commodities in 2019 compared to the cost in the 1845-1850 base period in The Economist's Commodity Price Index is
A) higher by about 100 percent.
B) about the same or equal.
C) lower by about 60 percent.
D) higher by about 50 percent.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The key to optimally managing renewable and nonrenewable resources is to design incentive structures that
A) reduce the costs of production to the lowest possible level.
B) increase the benefits from production to the highest possible level.
C) weigh the net benefits of current use with the net benefits of future use.
D) add the net benefits of current use to the net benefits of future use.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Renewable natural resources can never be exhausted.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the United States in 2017, one million BTUs of energy yielded _______ worth of goods and services (in 2009 dollars) .
A) $57.90
B) $63.09
C) $162.07
D) $184.55
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sue fishes for cod at a cost of $2 per ton, while Dave fishes at a cost of $4 per ton. Both have one 1,000-ton ITQ and the current market price is $5 per ton. If Dave offered to sell his ITQ to Sue for $2,000, he and Sue would
A) make the sale because they're both better off.
B) not make the sale, because Sue is better off and Dave is not.
C) not make the sale, because Dave is better of and Sue is not.
D) not make the sale, because neither is better off.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the world runs out of oil, it will also run out of energy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alex and Belle are both loggers wanting to harvest timber from the same forest. Alex prefers to harvest and replant at a sustainable rate; Belle wants to harvest as many trees as possible to maximize short-run profit and then move on. They face the same production costs. If property rights are well-defined and enforced,
A) Alex could buy Belle's part of the land and harvest and replant in a sustainable manner.
B) Belle could buy Alex's part of the land and harvest all the timber as quickly as possible.
C) Incentives to harvest and replant in a sustainable manner are greater than with no property rights.
D) Any of the results described in the other possible answers could occur in this situation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary focus of natural resource economics is to develop policies for harvesting or extracting natural resources that
A) minimize the net costs from doing so.
B) maximize the net benefits from doing so.
C) minimize the negative externalities of doing so.
D) maximize the positive externalities of doing so.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Renewable resources
A) can never be exhausted permanently.
B) can be exhausted if harvest rates exceed replenishment rates for an extended period.
C) can be exhausted if replenishment rates exceed harvest rates for an extended period.
D) will tend to be overharvested when they are private property.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
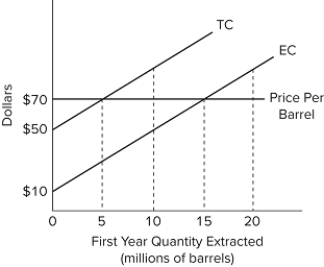 Refer to the diagram, representing Slippery Slope Oil Company. A $10 increase in the user cost would shift
Refer to the diagram, representing Slippery Slope Oil Company. A $10 increase in the user cost would shift
A) up the extraction cost curve only and reduce the amount of oil extracted in the present.
B) up both the extraction cost and total cost curves and reduce the amount of oil extracted in the present.
C) up the total cost curve only and reduce the amount of oil extracted in the present.
D) down the total cost curve and increase the amount of oil extracted in the future.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
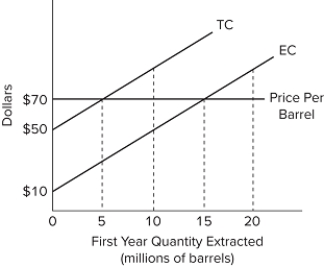 Refer to the diagram, representing Slippery Slope Oil Company. What price of oil would make 15 million barrels the optimal quantity to extract and sell this year?
Refer to the diagram, representing Slippery Slope Oil Company. What price of oil would make 15 million barrels the optimal quantity to extract and sell this year?
A) 50
B) 110
C) 70
D) 90
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because of Environmental Protection Agency pollution credits to biodiesel producers, biodiesel becomes economically viable (as or less costly than using oil) when oil prices reach _____ or more per barrel.
A) $110
B) $55
C) $80
D) $127
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Melanie and Oli are competing Pacific halibut fishers. Both have been allocated ITQs that limit their catch to 1,000 tons of Pacific halibut each. Melanie's cost per ton is $20; Oli's cost per ton is $28. If the market price of Pacific halibut is $40 per ton, what is the minimum amount per ton that Melanie would have to offer Oli to convince him to sell Melanie his ITQs?
A) $8.
B) $10.
C) $12.
D) $20.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
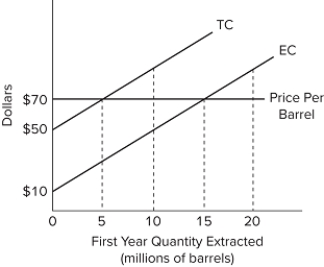 Refer to the diagram, representing Slippery Slope Oil Company. A $5 decrease in the user cost would
Refer to the diagram, representing Slippery Slope Oil Company. A $5 decrease in the user cost would
A) decrease the optimal quantity extracted in the present.
B) increase the optimal quantity extracted in the present.
C) not affect the optimal quantity extracted in the present.
D) reduce extraction costs in the present.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is generally easier to prevent deforestation than fishery collapse because
A) it is easier to establish and enforce property rights on national lands than in international waters.
B) there is greater incentive to have sustainable forests than sustainable fisheries.
C) the demand for wood products has dropped significantly, while the demand for fish has grown significantly.
D) All of the other possible answers are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Individual transferable quotas (ITQs)
A) promote efficiency and limit catches.
B) promote efficiency in production but still lead to overfishing.
C) limit catches but encourage production cost increases that are inefficient.
D) have failed to limit catches or promote efficiency.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Productive inputs capable of replacing themselves if harvested at moderate rates are known as
A) renewable natural resources.
B) natural capital.
C) nonrenewable natural resources.
D) fossil fuels.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 281 - 300 of 337
Related Exams