A) Notes Payable.
B) Accounts Receivable.
C) Notes Receivable.
D) Unearned Revenue.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts on January 1 equals $10,000 and during the year $11,000 of specific customers' accounts were written off,then its Allowance for Doubtful Accounts will have an unadjusted balance of:
A) $1,000 credit.
B) $1,000 debit.
C) $10,000 credit.
D) $9,000 debit.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The receivables turnover ratio is calculated as: Average net receivables ÷ Net sales.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Norwood Co.reported a receivables turnover ratio of 8.0.Cost of goods sold was $700,000 and net sales revenue was $960,000.The average net receivables must have been
A) $90,000.
B) $240,000.
C) $120,000.
D) $180,000.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Extending credit to customers will introduce all of the following additional costs except:
A) increased wage costs will be incurred to hire people to evaluate whether each customer is creditworthy,track how much each customer owes,and follow up to collect the receivable from each customer.
B) bad debt costs will result when amounts cannot be collected from customers.
C) delayed receipt of cash may result in requiring the company to take out short-term loans and incur interest costs.
D) decreased gross profit from reduced sales.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about receivables turnover analysis is correct?
A) The receivables turnover ratio indicates how many times,on average,the process of selling to and collecting from customers occurs during the accounting period.
B) Companies of similar size in different industries tend to have similar receivables turnover ratios.
C) A high turnover ratio may suggest the company is allowing too much time for customers to pay.
D) The days to collect ratio is found by dividing the receivables turnover ratio by 365 days.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Companies A and B both report net income growth of 12% per year.Company A has a receivables turnover ratio of 5.6,which is lower than last year.Company B has a receivables turnover ratio of 11.3,which is higher than last year.All other things being equal:
A) Company A is more effectively managing its receivables.
B) Company B is more effectively managing its receivables.
C) Company A's days to collect is lower than Company B's in both years.
D) Company B's days to collect increased.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Foothill Construction uses the allowance method for bad debts.If management is overly pessimistic about its ability to collect customer accounts,the company will overstate Bad Debt Expense and:
A) understate net income and days to collect will increase.
B) understate net income but days to collect will decline.
C) overstate net income and days to collect will increase.
D) overstate net income and days to collect will decline.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A contra-asset account,such as Allowance for Doubtful Accounts or Accumulated Depreciation,has a normal balance of a ________ and causes total assets to:
A) credit;decrease.
B) debit;increase.
C) debit;decrease.
D) credit;increase.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a note receivable that was created on November 1,2018 and is due for repayment on October 31,2019,what is the time fraction needed to compute interest revenue for the year ended December 31,2018?
A) 2/12
B) 2/10
C) 12/12
D) 22/12
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is correct?
A) The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is credited when a specific write-off is recorded.
B) Under the aging of accounts receivable method,Bad Debt Expense is calculated and then added to the beginning balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
C) The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is a contra-revenue account.
D) The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a normal credit balance.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things being equal,a company is better off when its receivable turnover ratio:
A) and its days-to-collect measure are both low.
B) is high and its days-to-collect measure is low.
C) and its days-to-collect measure are both high.
D) is low and its days-to-collect measure is high.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Total doubtful accounts at the end of the year are estimated to be $12,500 based on an aging of accounts receivable.If the balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is a $3,500 debit before adjustment,what is current year's Bad Debt Expense?
A) $3,500
B) $9,000
C) $12,500
D) $16,000
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the direct write-off method is used,the entry to write-off a specific account would:
A) increase net income.
B) have no effect on net income.
C) increase Accounts Receivable and increase net income.
D) decrease Accounts Receivable and decrease net income.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
The Dubious Company operates in an industry where all sales are made on account.The company has experienced bad debt losses of 1% of credit sales in prior periods.
Presented below is the company's forecast of sales and expenses over the next three years.
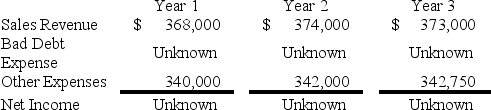 Required:
a.Calculate Bad Debt Expense and net income for each of the three years,assuming uncollectible accounts are estimated as 1.0% of sales.
b.Assume that the company changes its estimate of uncollectible credit sales to 1.0% in Year 1,2.0% in Year 2 and 1.5% in Year 3.Calculate the Bad Debt Expense and net income for each of the three years under this alternative scenario.
Required:
a.Calculate Bad Debt Expense and net income for each of the three years,assuming uncollectible accounts are estimated as 1.0% of sales.
b.Assume that the company changes its estimate of uncollectible credit sales to 1.0% in Year 1,2.0% in Year 2 and 1.5% in Year 3.Calculate the Bad Debt Expense and net income for each of the three years under this alternative scenario.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A scenario under which a company's credit sales are increasing and its accounts receivable turnover is decreasing might suggest:
A) channel stuffing.
B) cookie jar accounting.
C) an investment opportunity.
D) improved receivables monitoring.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Charleston,Inc.has Accounts Receivable of $320,000 and an Allowance for Doubtful Accounts of $16,000.If it writes-off a customer account balance of $1,600,what is the amount of its net accounts receivable?
A) $318,400
B) $320,000
C) $304,000
D) $302,400
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Perry Company reported Accounts Receivable,Net of $66,600 at the beginning of the year and $72,600 at the end of the year.If the company's net sales revenue during the fourth year was $876,000,what are the days to collect during year? (Round all calculations to 1 decimal place. )
A) 12.6
B) 29.0
C) 8.0
D) 34.0
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term and its definition.There are more definitions than terms. -Net Realizable Value
A) The process of removing specific customers' accounts deemed uncollectible.
B) When a company increases the amount of accounts receivable by adding the interest earned as accounts age without being collected.
C) How much money you can expect to earn over a period of time selling your goods.
D) Selling accounts receivable to another company for immediate cash.
E) Credit that a company receives when one good is exchanged for another.
F) Also known as net accounts receivable.
G) The length of the credit period and any discounts offered for prompt payment.
H) The amount of money lent.
I) A method of estimating uncollectible debts by forecasting the probability of not collecting late accounts.
J) The interest earned by money over a period of time.
K) A method of estimating uncollectible debts by looking at the historical average of credit sales not collected.
L) The account in which the estimated amount of accounts receivable expected to be uncollectible is recorded.
N) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Failing to record bad debt expense in the same period as the related revenue violates which principle?
A) Expense recognition principle ("matching")
B) Revenue recognition principle
C) Lower-of-cost-or-market value principle
D) Cost principle
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 240
Related Exams