A) metaphase
B) anaphase
C) synthesis
D) MPF
E) G₀
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decline of MPF activity at the end of mitosis is due to
A) the destruction of the protein kinase Cdk.
B) decreased synthesis of Cdk.
C) the degradation of cyclin.
D) the accumulation of cyclin.
E) synthesis of DNA.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plant-derived protein known as colchicine can be used to poison cells by blocking the formation of the spindle.Which of the following would result if colchicine is added to a sample of cells in G₂?
A) The cells would immediately die.
B) The cells would be unable to begin M and stay in G₂.
C) The chromosomes would coil and shorten but have no spindle to attach to.
D) The chromosomes would segregate but in a disorderly pattern.
E) Each resultant daughter cell would also be unable to form a spindle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions.
The data were obtained from a study of the length of time spent in each phase of the cell cycle by cells of three eukaryotic organisms designated beta,delta,and gamma.
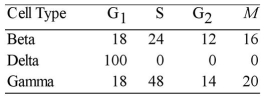 Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
-Of the following,the best conclusion concerning the difference between the S phases for beta and gamma is that
Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
-Of the following,the best conclusion concerning the difference between the S phases for beta and gamma is that
A) gamma contains more DNA than beta.
B) beta and gamma contain the same amount of DNA.
C) beta cells reproduce asexually.
D) gamma contains 48 times more DNA and RNA than beta.
E) beta is a plant cell and gamma is an animal cell.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the M phase checkpoint,the complex allows for what to occur?
A) Separase enzyme cleaves cohesins and allows chromatids to separate.
B) Cohesins alter separase to allow chromatids to separate.
C) Kinetochores are able to bind to spindle microtubules.
D) All microtubules are made to bind to kinetochores.
E) Daughter cells are allowed to pass into G₁.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine,a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus,at which stage will mitosis be arrested?
A) anaphase
B) prophase
C) telophase
D) metaphase
E) interphase
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase,how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40
E) 80
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The MPF protein complex turns itself off by
A) activating a process that destroys cyclin components.
B) activating an enzyme that stimulates cyclin.
C) binding to chromatin.
D) exiting the cell.
E) activating the anaphase-promoting complex.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells?
A) They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
B) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle.
C) They are not subject to cell cycle controls.
D) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle, and they are not subject to cell cycle controls.
E) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle; they are not subject to cell cycle controls; and they do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when grown in culture.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You observe cells under the microscope and notice that,while in telophase,small vesicles line up along the middle of the cell. -Through a microscope,you can see a cell plate beginning to develop across the middle of a cell and nuclei forming on either side of the cell plate.This cell is most likely
A) an animal cell in the process of cytokinesis.
B) a plant cell in the process of cytokinesis.
C) an animal cell in the S phase of the cell cycle.
D) a bacterial cell dividing.
E) a plant cell in metaphase.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nucleotides can be radiolabelled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation.In a set of experiments,a student-faculty research team used labelled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times. -Which of the following questions might be answered by such a method?
A) How many cells are produced by the culture per hour?
B) What is the length of the S phase of the cell cycle?
C) When is the S chromosome synthesized?
D) How many picograms of DNA are made per cell cycle?
E) When do spindle fibres attach to chromosomes?
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The M-phase checkpoint ensures that all chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle.If this does not happen,when would cells most likely be arrested?
A) telophase
B) prophase
C) prometaphase
D) metaphase
E) anaphase
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the mitotic spindle involved in?
A) cytokinesis
B) triggering the compaction and condensation of chromosomes
C) dissolving the nuclear membrane
D) separation of sister chromatids
E) replication of DNA
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes how chromosomes move toward the poles of the spindle during mitosis?
A) The chromosomes are "reeled in" by the contraction of spindle microtubules.
B) Motor proteins of the kinetochores move the chromosomes along the spindle microtubules.
C) Nonkinetochore spindle fibres serve to push chromosomes in the direction of the poles.
D) The chromosomes are "reeled in" by the contraction of spindle microtubules, and motor proteins of the kinetochores move the chromosomes along the spindle microtubules.
E) The chromosomes are "reeled in" by the contraction of spindle microtubules, motor proteins of the kinetochores move the chromosomes along the spindle microtubules, and nonkinetochore spindle fibres serve to push chromosomes in the direction of the poles.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cyclin component of MPF is destroyed toward the end of which phase?
A) G₀
B) G₁
C) S
D) G₂
E) M
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
The lettered circle in the figure below shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes.There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes,one long and the other short.One haploid set is symbolized as black and the other haploid set is grey.The chromosomes in the unlettered circle have not yet replicated.Choose the correct chromosomal conditions for the following stages.
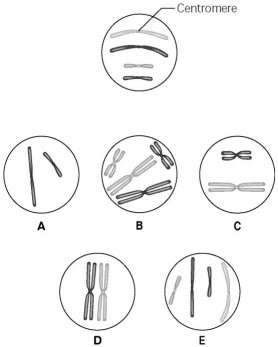 -What is the correct chromosomal condition at the prometaphase of mitosis?
-What is the correct chromosomal condition at the prometaphase of mitosis?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using which of the following techniques would enable your lab group to distinguish between a cell in G₂ and a cell from the same organism in G₁?
A) fluorescence microscopy
B) electron microscopy
C) spectrophotometry
D) radioactive-labelled nucleotides
E) labelled kinetochore proteins
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens if MPF (mitosis-promoting factor) is introduced into immature frog oocytes that are arrested in G₂?
A) Nothing happens.
B) The cells undergo meiosis.
C) The cells enter mitosis.
D) Cell differentiation is triggered.
E) The cells enter S phase.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You observe cells under the microscope and notice that,while in telophase,small vesicles line up along the middle of the cell. -You conclude that these cells are
A) animal cells.
B) plant cells.
C) bacteria.
D) diatoms.
E) tumour cells.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Density-dependent inhibition is explained by which of the following?
A) As cells become more numerous, they begin to squeeze against each other, restricting their size and ability to produce control factors.
B) As cells become more numerous, the cell surface proteins of one cell contact the adjoining cells and they stop dividing.
C) As cells become more numerous, the protein kinases they produce begin to compete with each other, such that the proteins produced by one cell essentially cancel those produced by its neighbour.
D) As cells become more numerous, more and more of them enter the S phase of the cell cycle.
E) As cells become more numerous, the level of waste products increases, eventually slowing down metabolism.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 98
Related Exams