A) synthesize organic compounds they obtain from decaying heterotrophs.
B) synthesize inorganic compounds from organic compounds.
C) use light energy to synthesize organic compounds.
D) use chemical energy to synthesize organic compounds.
E) convert light energy into matter.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nitrogen is available to plants only in the form of
A) N₂ in the atmosphere.
B) nitrite ions in the soil.
C) uric acid from animal excretions.
D) amino acids from decomposing plant and animal proteins.
E) nitrate ions in the soil.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As big as it is,the ocean is nutrient-limited.If you wanted to investigate this,one reasonable approach would be to
A) follow whale migrations in order to determine where most nutrients are located.
B) observe Antarctic Ocean productivity from year to year to see if it changes.
C) experimentally enrich some areas of the ocean and compare their productivity to that of untreated areas.
D) compare nutrient concentrations between the photic zone and the benthic zone in various marine locations.
E) contrast nutrient uptake by autotrophs in marine locations that are different temperatures.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organisms is incorrectly paired with its trophic level?
A) some prokaryotes - detritivores
B) rabbits - primary consumers
C) zooplankton - primary consumers
D) phytoplankton - primary producers
E) great white shark - secondary consumer
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following food web to answer the questions below.
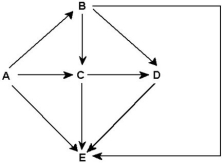 Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem (arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species)
-Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem.Which species is autotrophic?
Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem (arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species)
-Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem.Which species is autotrophic?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
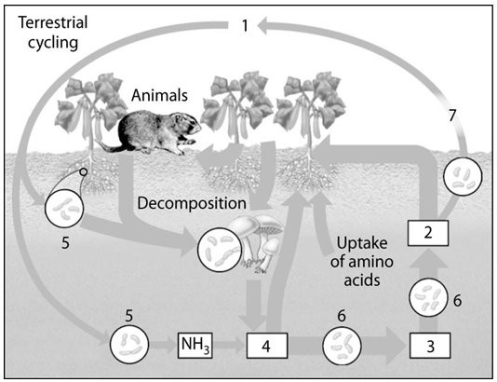 -On the diagram of the nitrogen cycle,which number represents nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
-On the diagram of the nitrogen cycle,which number represents nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
A) 5
B) 6
C) 7
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which trophic level is most vulnerable to extinction?
A) producer level
B) primary consumer level
C) secondary consumer level
D) tertiary consumer level
E) decomposer level
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do the Taylor Glacier bacteria produce their energy?
A) photosynthesis
B) heterotrophism
C) chemoautotrophism
D) thermophobism
E) chemosynthesis
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following ecosystems would likely have a larger net primary productivity/hectare and why?
A) open ocean because of the total biomass of photosynthetic autotrophs
B) grassland because of the small standing crop biomass that results from consumption by herbivores and rapid decomposition
C) tropical rain forest because of the massive standing crop biomass and species diversity
D) cave due to the lack of photosynthetic autotrophs
E) tundra because of the incredibly rapid period of growth during the summer season
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct about biogeochemical cycling?
A) The phosphorus cycle involves the recycling of atmospheric phosphorus.
B) The phosphorus cycle involves the weathering of rocks.
C) The carbon cycle is a localized cycle that primarily involves the burning of fossil fuels.
D) The carbon cycle has maintained a constant atmospheric concentration of CO₂ for the past million years.
E) The nitrogen cycle involves movement of diatomic nitrogen between the biotic and abiotic components of the ecosystem.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of detrivores?
A) They recycle chemical elements directly back to primary consumers.
B) They synthesize organic molecules that are used by primary producers.
C) They convert organic materials from all trophic levels to inorganic compounds usable by primary producers.
D) They secrete enzymes that convert the organic molecules of detritus into CO₂ and H₂O.
E) Some species are autotrophic, while others are heterotrophic.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of nutrient cycling,why does timber harvesting in a temperate forest cause less ecological devastation than timber harvesting in tropical rain forests?
A) Trees are generally less numerous in temperate forests, so fewer nutrients will be removed from the temperate forest ecosystem during a harvest.
B) Temperate forest tree species require fewer nutrients to survive than their tropical counterpart species, so a harvest removes fewer nutrients from the temperate ecosystem.
C) The warmer temperatures in the tropics influence rain forest species to assimilate nutrients more slowly, so tropical nutrient absorption is much slower than in temperate forests.
D) There are far fewer decomposers in tropical rain forests, so turning organic matter into usable nutrients is a slower process than in temperate forest ecosystems.
E) Typical harvests remove up to 75% of the nutrients in the woody trunks of tropical rain forest trees, leaving nutrient-impoverished soils behind.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does a vegetarian leave a smaller ecological footprint than an omnivore?
A) Fewer animals are slaughtered for human consumption.
B) There is an excess of plant biomass in all terrestrial ecosystems.
C) Vegetarians need to ingest less chemical energy than omnivores.
D) Vegetarians require less protein than do omnivores.
E) Eating meat is an inefficient way of acquiring photosynthetic productivity.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following food web to answer the questions below.
 Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem (arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species)
-Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem.Which species is most likely a decomposer on this food web?
Food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem (arrows represent energy flow and letters represent species)
-Examine this food web for a particular terrestrial ecosystem.Which species is most likely a decomposer on this food web?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a true statement regarding mineral nutrients in soils and their implication for primary productivity?
A) Globally, phosphorous availability is most limiting to primary productivity.
B) Adding a nonlimiting nutrient will stimulate primary productivity.
C) Adding more of a limiting nutrient will increase primary productivity, indefinitely.
D) Phosphorous is sometimes unavailable to producers due to leaching.
E) Alkaline soils are more productive than acidic soils.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do logged tropical rain forest soils typically have nutrient-poor soils?
A) Tropical bedrock contains little phosphorous.
B) Logging results in soil temperatures that are lethal to nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
C) Most of the nutrients in the ecosystem are removed in the harvested timber.
D) The cation exchange capacity of the soil is reversed as a result of logging.
E) Nutrients evaporate easily into the atmosphere in the post-logged forest.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cow's herbivorous diet indicates that it is a(n)
A) primary consumer.
B) secondary consumer.
C) decomposer.
D) autotroph.
E) producer.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Owls eat rats,mice,shrews,and small birds.Assume that,over a period of time,an owl consumes 5000 J of animal material.The owl loses 2300 J in feces and owl pellets and uses 2500 J for cellular respiration.What is the primary efficiency of this owl?
A) 0) 02%
B) 1%
C) 4%
D) 10%
E) 40%
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trophic efficiency is
A) the ratio of net secondary production to assimilation of primary production.
B) the percentage of production transferred from one trophic level to the next.
C) a measure of how nutrients are cycled from one trophic level to the next.
D) usually greater than production efficiencies.
E) about 90% in most ecosystems.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does phosphorus normally enter ecosystems?
A) cellular respiration
B) photosynthesis
C) rock weathering
D) vulcanism
E) atmospheric phosphorous gas
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 98
Related Exams