A) Bacteria
B) Plantae
C) Archaea
D) Fungi
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are properties of eukaryotes?
A) Compartmentalization
B) Multicellularity
C) Peptidoglycan in cell wall
D) Sexual reproduction
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A, B, D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What can you conclude by the observation that chloroplasts are monophyletic?
A) The same cyanobacteria were engulfed by multiple hosts that were ancestral to the red and green algae.
B) Aerobic bacteria were engulfed by eukaryotic cells forming plant cells.
C) Cyanobacteria were engulfed by all eukaryotic cells.
D) Cyanobacteria reproduced by sexual reproduction once engulfed by brown algae leading to the formation of protists.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are many features that distinguish bacteria and archaea. Which of the following is/are characteristic of bacteria, but not archaea?
A) Protein synthesis begins with formyl-methionine
B) Presence of membrane bound organelles.
C) Growth inhibited by streptomycin and chloramphenicol.
D) Peptidoglycan in cell wall.
E) Nuclear envelope.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
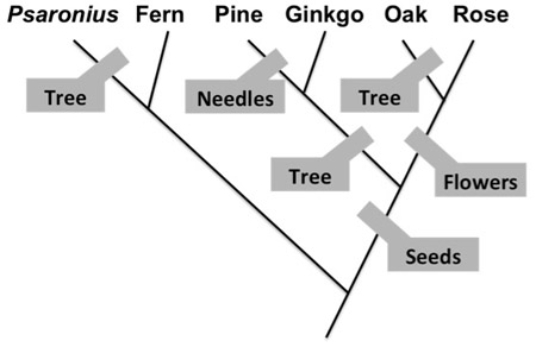 -Based on the phylogeny shown, which species is not a tree but has seeds?
-Based on the phylogeny shown, which species is not a tree but has seeds?
A) Ginkgo
B) Fern
C) Rose
D) Oak
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One day after a biology class four of your friends argue about the difference between phylogeny and systematics. Which friend is right?
A) Friend A states that systematics and phylogenies are really the same, one is more recent than the other, but basically they are the same.
B) Friend B says that systematics is the same as cladistics and cladistics is reconstructing clades, which ultimately lead to the development of phylogenies.
C) Friend C argues that systematics is the actual collecting and cataloguing of specimens into museums that can be used later by scientists to construct clades and phylogenies.
D) Friend D says that the way she remembers is that systematics is the reconstruction and study of phylogenies.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figures show alternative phylogenies of HIV strains in a victim who was infected with HIV+ blood and in potential sources of the blood (the patient) and HIV strains in members of the community. Choose the true statement(s) about the evolution of this HIV strain.
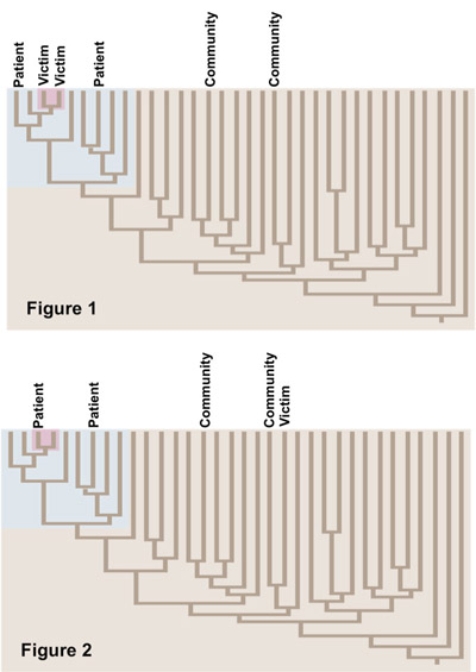
A) Figure 1 supports that the victim contracted HIV from the patient, and Figure 2 supports that the victim contracted HIV from someone in the community.
B) Figure 1 supports that the victim contracted HIV from someone in the community, and Figure 2 supports that the victim contracted HIV from the patient.
C) Figure 1 supports that the HIV strain mutated into a new strain inside the victim's body, and Figure 2 supports that HIV did not mutate into a new strain inside the victim's body.
D) Figure 1 supports that the HIV strain did not mutate into a new strain inside the victim's body, and Figure 2 supports that HIV mutated into a new strain inside the victim's body.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
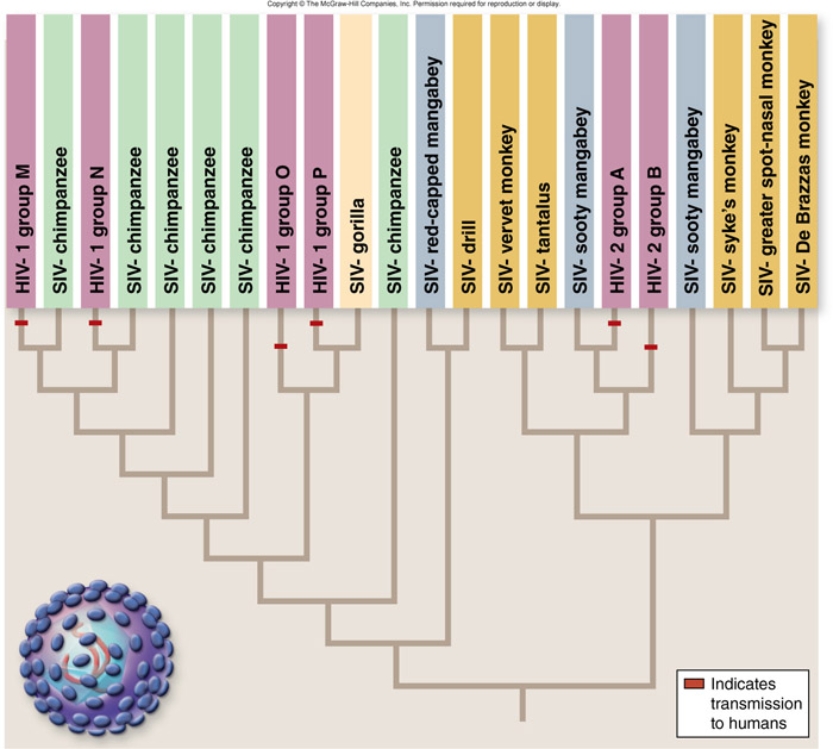 The figure shows the evolution of HIV and SIV. Choose the true statements about the evolution of HIV.
The figure shows the evolution of HIV and SIV. Choose the true statements about the evolution of HIV.
A) All strains of HIV are included within clades with SIV strains.
B) A strain of HIV is never more closely related to another strain of HIV than it is to a SIV strain.
C) Humans acquired different subtypes of HIV from different primate hosts.
D) HIV-1 group O is more closely related to SIV-chimpanzee than SIV-gorilla.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the true statement about the morphological data in the chart shown below. The "1" in the box means the trait is present and the "0" indicates that the trait is absent. 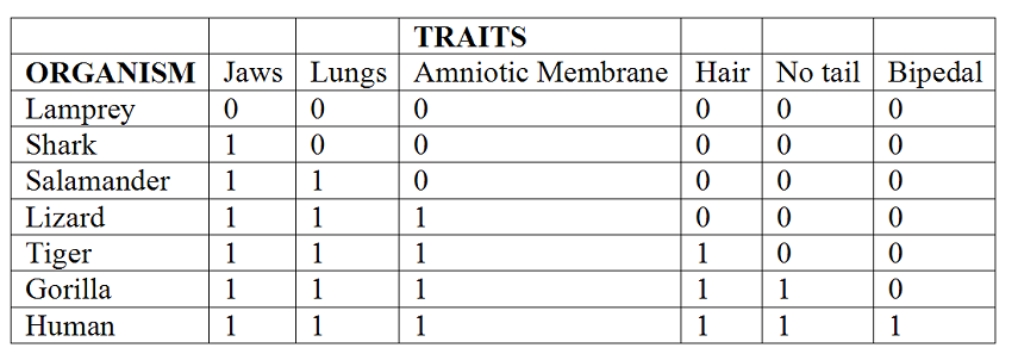
A) All organisms in this chart share all of the derived characteristics.
B) Only the gorilla and humans share all of the derived characteristics.
C) The lamprey is the only outgroup since it shares none of the derived characteristics.
D) The salamander and the tiger are outgroups because they only share two of the derived characteristics (jaws and lungs) .
E) The shark is an outgroup since it only has one of the derived characteristics (jaws) .
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
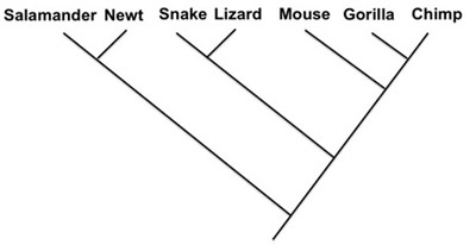 -Indicate the phylogenies that show the same relationship as the phylogeny above.
-Indicate the phylogenies that show the same relationship as the phylogeny above.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the polyphyletic group.
A) Chloroplasts
B) Eukarya
C) Bacteria
D) Protists
E) Archaea
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 11 of 11
Related Exams