A) 60 units
B) 120 units
C) 180 units
D) cannot be determined
E) none of the choices
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to this product tree: 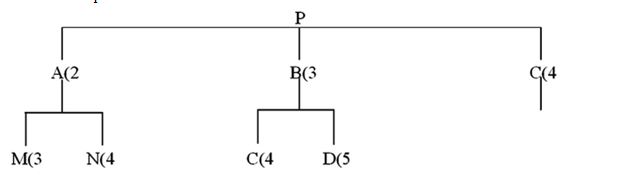 If 17 Ps are needed, and on-hand inventory consists of 10 As, 15 Bs, 20 Cs, 12 Ms, and 5 Ns, how many Cs are needed?
If 17 Ps are needed, and on-hand inventory consists of 10 As, 15 Bs, 20 Cs, 12 Ms, and 5 Ns, how many Cs are needed?
A) 48
B) 144
C) 192
D) 212
E) 272
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The MRP input stating which end items are to be produced, when they are needed, and what quantities are needed, is the:
A) master schedulE.
B) bill of materials.
C) inventory records.
D) assembly time chart.
E) net requirements chart.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to this product tree: 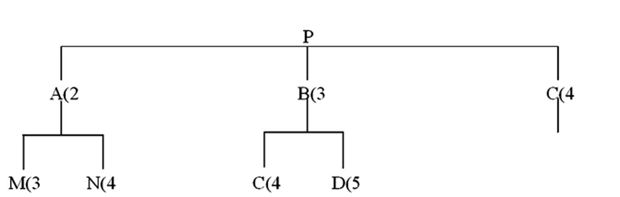 If 17 Ps are needed, and no on-hand inventory exists for any items, how many Cs will be needed?
If 17 Ps are needed, and no on-hand inventory exists for any items, how many Cs will be needed?
A) 8
B) 16
C) 136
D) 204
E) 272
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A visual depiction of the subassemblies and components that are needed to produce and/or assemble a product is called a(n) :
A) assembly time chart.
B) product structure treE.
C) MRP II.
D) pegging.
E) Gantt chart.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The master schedule needs to be for a period long enough to cover the stacked or cumulative lead time necessary to produce the end items.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a master schedule, the planning horizon is often separated into a series of time periods called:
A) pegging.
B) lead times.
C) stacked lead times.
D) time buckets.
E) firm, fixed, and frozen.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Lot-for-lot ordering in MRP provides coverage for some predetermined number of periods (such as two or three) that extend beyond the orders already received for those periods.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capacity requirements planning helps managers reconcile __________ with __________.
A) what is needed; what has been done
B) what is needed; what is possible
C) what has been done; who will be doing it
D) what needs to be done; where it will be done
E) what has been done; how much what needs to be done will cost
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _________ of ERP makes it valuable as a strategic planning tool.
A) Internet base
B) rapid batch capability
C) employee focus
D) real-time aspect
E) database structure
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The MRP input listing the assemblies, subassemblies, parts, and raw materials needed to produce one unit of finished product is the:
A) master production schedule.
B) bill of materials.
C) inventory records.
D) assembly time chart.
E) net requirements chart.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
MRP output reports are divided into two main groups, daily and weekly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An assembly-time chart indicates gross and net requirements taking into account the current available inventory.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following most closely describes the MRP approach that is used for components or subassemblies to compensate for variations in lead time?
A) pegging
B) safety stock
C) increased order sizes
D) safety time
E) low-level coding
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
MRP works best if the inventory items have dependent demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In MRP, the gross requirements of a given component part are calculated directly from:
A) net requirements + projected on-hand inventory.
B) gross requirements of the immediate parent.
C) planned order releases of the end item.
D) net requirements of the end item.
E) planned order releases of the immediate parent.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents an attempt to balance the benefits of stability in the production plan against the benefits of responding quickly to new orders?
A) safety stock
B) safety time
C) bills of material
D) time fences
E) fixed-period lot sizing
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these items would be most likely to have dependent demand?
A) computer chips
B) potato chips
C) poker chips
D) chocolate chip cookies
E) wood chippers
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The output of MRP is:
A) gross requirements.
B) net requirements.
C) a schedule of planned orders for all parts and end items.
D) inventory reorder points.
E) economic order quantities and reorder points.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Safety time is sometimes used in MRP rather than safety stock quantities.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 81
Related Exams