A) for a person living in a developed nation to consider to make better choices when using global food and energy resources.
B) for a person living in a developing country to see how much of the world's resources are left for him/her.
C) in converting human foods' meat biomass to plant biomass.
D) in making predictions about the global carrying capacity of humans.
E) in determining which nations produce the least amount of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
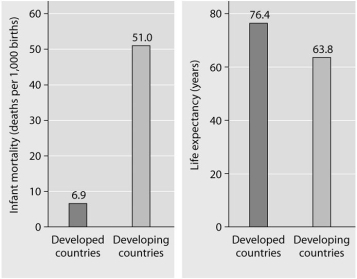 Infant mortality and life expectancy at birth in developed and developing countries (data as of 2005) .
-What is a logical conclusion that can be drawn from the graphs above?
Infant mortality and life expectancy at birth in developed and developing countries (data as of 2005) .
-What is a logical conclusion that can be drawn from the graphs above?
A) Developed countries have lower infant mortality rates and lower life expectancy than developing countries.
B) Developed countries have higher infant mortality rates and lower life expectancy than developing countries.
C) Developed countries have lower infant mortality rates and higher life expectancy than developing countries.
D) Developed countries have higher infant mortality rates and higher life expectancy than developing countries.
E) Developed countries have a life expectancy that is about 42 years more than life expectancy in developing countries.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In models of logistic population growth,
A) the population growth rate slows dramatically as N approaches K.
B) new individuals are added to the population most rapidly at the beginning of the population's growth.
C) new individuals are added to the population as N approaches K.
D) only density-dependent factors affect the rate of population growth.
E) carrying capacity is never reached.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following assumptions have to be made regarding the capture-recapture estimate of population size? I. Marked and unmarked individuals have the same probability of being trapped. II. The marked individuals have thoroughly mixed with the population after being marked. III. No individuals have entered or left the population by immigration or emigration, and no individuals have been added by birth or eliminated by death during the course of the estimate.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only
E) I, II, and III
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the description below. Theoretically, under ideal conditions, species can grow exponentially. In reality, however, species cannot maintain exponential growth indefinitely. Introducing species to habitats where conditions are optimal for that species often results in initial exponential growth. -One example of exponential growth was seen with the introduction of European rabbits into Australia. Within a short period of time the rabbit population in Australia exploded. This invasive species efficiently grazed vegetation in all habitats it colonized and before long spread throughout most of Australia. Many factors can contribute to the exponential growth rate of the rabbit population; which of the these factors would likely slow down population growth?
A) lack of predators
B) abundant food supply, fast reproductive rate
C) introducing an aggressive competitor
D) releasing a pathogen/virus (biological control) that the European rabbit had not co-evolved with
E) C and D
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Infant mortality and life expectancy at birth in developed and developing countries (data as of 2005) .
-In terms of demographics, which country is likely to experience the greatest population growth problem over the next ten years?
Infant mortality and life expectancy at birth in developed and developing countries (data as of 2005) .
-In terms of demographics, which country is likely to experience the greatest population growth problem over the next ten years?
A) Mexico, because there are fewer pre-reproductive individuals in their population.
B) China, whose population is more than a billion, but whose expected fertility rate is 1.8 children.
C) Germany, where the growth rate of the population is 0.1% per year.
D) United States (2009 population ~ 205 000 000, where 200 000 Americans are added to the population each day)
E) Afghanistan, with a 3.85 annual growth rate
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Elephants and sea turtles are both long-living vertebrates. What type of survivorship curve would you expect to see for these two species, respectively?
A) Type 1 and Type1
B) Type 1 and Type111
C) Type 1 and Type11
D) Type 11 and Type11
E) Type 111 and Type111
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carrying capacity is
A) seldom reached by marine producers and consumers because of the vast resources of the ocean.
B) the maximum population size that a particular environment can support.
C) fixed for most species over most of their range most of the time.
D) determined by density and dispersion data.
E) the term used to describe the stress a population undergoes due to limited resources.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following situations would you expect to find the largest number of K-selected individuals?
A) a recently abandoned agricultural field in Ohio
B) the sand dune communities of south Lake Michigan
C) the flora and fauna of a coral reef in the Caribbean
D) South Florida after a hurricane
E) a newly emergent volcanic island
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following could be a density-independent factor limiting human population growth?
A) social pressure for birth control
B) earthquakes
C) plagues
D) famines
E) pollution
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs of reproductive strategies is consistent with energetic trade-off and reproductive success?
A) Pioneer species of plants produce many very small, highly airborne seeds, whereas large elephants that are very good parents produce many offspring.
B) Female rabbits that suffer high predation rates may produce several litters per breeding season, and coconuts produce few fruits, but most survive when they encounter proper growing conditions.
C) Species that have to broadcast to distant habitats tend to produce seeds with heavy protective seed coats, and animals that are caring parents produce fewer offspring with lower infant mortality.
D) Free-living insects lay thousands of eggs and provide no parental care, whereas flowers take good care of their seeds until they are ready to germinate.
E) Some mammals will not reproduce when environmental resources are low so they can survive until conditions get better, and plants that produce many small seeds are likely found in stable environments.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of ground squirrels has an annual per capita birth rate of 0.06 and an annual per capita death rate of 0.02. Calculate an estimate of the number of individuals added to (or lost from) a population of 1000 individuals in one year.
A) 120 individuals added
B) 40 individuals added
C) 20 individuals added
D) 400 individuals added
E) 20 individuals lost
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the survivorship curves shown below to answer the following questions.
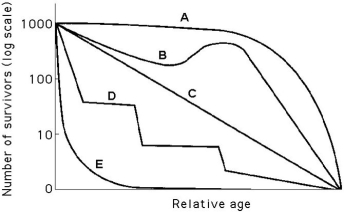 -Which curve best describes survivorship in humans who live in undeveloped nations?
-Which curve best describes survivorship in humans who live in undeveloped nations?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following groups would be most likely to exhibit uniform dispersion?
A) red squirrels, who actively defend territories
B) cattails, which grow primarily at edges of lakes and streams
C) dwarf mistletoes, which parasitize particular species of forest tree
D) moths, in a city at night
E) lake trout, which seek out cold, deep water high in dissolved oxygen
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following choices would most likely promote random distribution?
A) territorial species
B) species that secrete chemicals to attract or inhibit other individuals
C) flocking and schooling behaviours
D) spacing during the breeding season
E) homogeneous chemical and physical factors in the environment
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please read the paragraph below and review the figure to answer the following question.
Researchers in the Netherlands studied the effects of parental care given in European kestrels over five years. The researchers transferred chicks among nests to produce reduced broods (three or four chicks) , normal broods (five or six chicks) , and enlarged broods (seven or eight chicks) . They then measured the percentage of male and female parent birds that survived the following winter. (Both males and females provide care for chicks.)
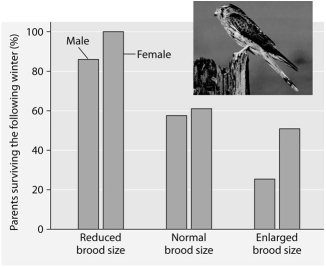 Brood size manipulations in the kestrel: Effects on offspring and parent survival.
-Which of the following is a conclusion that can be drawn from this graph?
Brood size manipulations in the kestrel: Effects on offspring and parent survival.
-Which of the following is a conclusion that can be drawn from this graph?
A) Female survivability is more negatively affected by larger brood size than is male survivability.
B) Male survivability decreased by 50% between reduced and enlarged brood treatments.
C) Both males and females had increases in daily hunting with the enlarged brood size.
D) There appears to be a negative correlation between brood enlargements and parental survival.
E) Chicks in reduced brood treatment received more food, weight gain, and reduced mortality.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about human population in industrialized countries is incorrect?
A) Life history is r-selected.
B) Average family size is relatively small.
C) The population has undergone the demographic transition.
D) The survivorship curve is Type I.
E) Age distribution is relatively uniform.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following scenarios would provide the most legitimate data on population density?
A) Count the number of nests of a particular species of songbird and multiply this by a factor that extrapolates these data to actual animals.
B) Count the number of pine trees in several randomly selected 10 m x 10 m plots and extrapolate this number to the fraction of the study area these plots represent.
C) Use the mark-and-recapture method to estimate the size of the population.
D) Calculate the difference between all of the immigrants and emigrants to see if the population is growing or shrinking.
E) Add the number of births and subtract the individuals that die to see if the population's density is increasing or decreasing.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting from a single individual, what is the size of a population of bacteria that reproduce by binary fission every 20 minutes at the end of a 2-hour time period? (Assume unlimited resources and no mortality.)
A) 6
B) 18
C) 128
D) 512
E) 1024
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do some invertebrates, such as lobsters, show a "stair-step" survivorship curve?
A) Many invertebrates mate and produce offspring on multiyear cycles.
B) Within a species of invertebrates, younger individuals have a higher survivorship than older individuals.
C) Many invertebrates moult in order to grow, and they are vulnerable to predation during their "soft shell" stage.
D) Many invertebrate species have population cycles that go up and down according to the frequency of sunspots.
E) The number of fertilized eggs that mature to become females in many species of invertebrates is based on ambient temperature.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 87
Related Exams