A) physiologic dead space.
B) anatomic dead space.
C) residual volume.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Prematurely born infants sometimes experience respiratory distress due to inadequate production of surfactant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What prevents the trachea from collapsing
A) The internal air pressure within the trachea
B) The surrounding muscles
C) The internal epithelium
D) The C-shaped cartilaginous rings
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air in the alveoli and blood in the lungs is called
A) ventilation.
B) systemic respiration.
C) internal respiration.
D) external respiration.
E) cellular respiration.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has the highest partial pressure of carbon dioxide
A) The alveoli of the lungs
B) The blood circulating in systemic arteries
C) The systemic cells
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The male voice tends to be in a lower range than a female's voice because men have
A) more taut vestibular folds.
B) more air to push through the rima glottidis.
C) wider arytenoid cartilages.
D) shorter and fatter vestibular ligaments.
E) longer and thicker vocal folds.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
From moment to moment,the oxygen partial pressure gradient between systemic capillary blood and systemic cells switches: one moment it favors diffusion toward the blood and the next moment it favors diffusion toward the cells.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How long is the average trachea
A) 12-14 inches
B) 12-14 cm
C) 12-14 mm
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Breathing muscles such as the diaphragm are controlled by neurons of the _________ nervous system.
A) somatic
B) autonomic
C) enteric
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Foreign particles
A) are more likely to lodge in the right primary bronchus.
B) are more likely to lodge in the left primary bronchus.
C) lodge equally often in each of the two primary bronchi.
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The potential space between the serous membranes surrounding each lung is known as the pleural _________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the partial pressure of oxygen causes pulmonary arterioles to ________,thereby altering _______ to make gas exchange more efficient.
A) constrict;perfusion
B) dilate;perfusion
C) constrict;ventilation
D) dilate;ventilation
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure is also known as the "voice box"
A) Larynx
B) Pharynx
C) Esophagus
D) Bronchus
E) Trachea
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
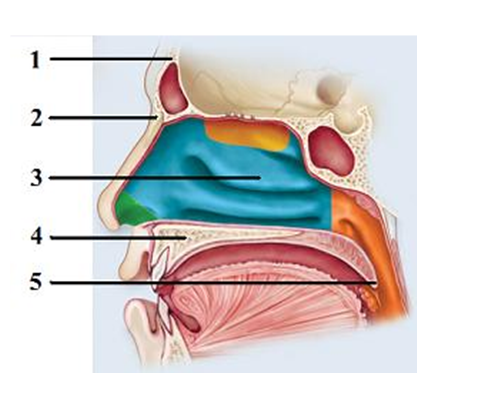 -In this sagittal section showing the upper respiratory tract,what structure does number 5 indicate
-In this sagittal section showing the upper respiratory tract,what structure does number 5 indicate
A) Uvula
B) Soft palate
C) Hard palate
D) Nasal conchae
E) Nasal bone
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most common cell making up the alveolar wall is the
A) alveolar type II cell.
B) alveolar type I cell.
C) alveolar macrophage.
D) dust cell.
E) septal cell.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When someone exercises vigorously,their breathing is described as demonstrating
A) hyperpnea,involving deeper but not faster breathing.
B) hyperventilation,involving both deeper and faster breathing.
C) bradypnea,involving deeper and slower breathing.
D) hypopnea,involving shallower but faster breathing.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Several things happen to inhaled air in a process called conditioning.Select the exception.
A) The air is cooled.
B) The air is humidified.
C) The air is cleansed.
D) The air is moistened.
E) The air becomes turbulent.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air flows out of the body during expiration because
A) intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
B) intrapleural pressure is greater than intrapulmonary pressure.
C) atmospheric pressure is greater than intrapulmonary pressure.
D) intrapleural pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nose contains a single septal cartilage.How many alar cartilages are in the nose
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The expiratory reserve volume plus the residual volume equals the
A) tidal volume.
B) functional residual capacity.
C) inspiratory reserve volume.
D) vital capacity.
E) forced expiratory volume.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 147
Related Exams