A) Pulmonary circuit
B) Cardio circuit
C) Coronary circuit
D) Systemic circuit
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
________________ innervation increases the rate and the force of heart contraction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blood moves into and then out of a heart chamber because
A) it moves along its pressure gradient,and that gradient depends on contraction and relaxation during the cardiac cycle.
B) it is under constant pressure,but its movement is dictated by the control of valve openings and closures.
C) the veins and arteries constrict and dilate to propel and attract blood.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which heart chambers contain deoxygenated blood
A) Left atrium and right atrium
B) Left ventricle and right ventricle
C) Right atrium and right ventricle
D) Left atrium and left ventricle
E) Right atrium and left ventricle
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As blood is pumped out of the heart and into the major arteries leaving the heart,it
A) pushes against the semilunar valves and opens them.
B) pushes against the semilunar valves and closes them.
C) fills the cusps of the semilunar valves,causing them to expand and block the backflow of blood
D) pushes against the atrioventricular valves and opens them.
E) fills the cusps of the atrioventricular valve causing opening of the bicuspid and closure of the tricuspid.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The left and right coronary arteries
A) are interconnected with several high-volume anastomoses allowing for well perfused alternate blood paths.
B) are functional end arteries because the blockage of one of them leads to tissue death in the area it supplies.
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The inferior,conical end of the heart is called the _______________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Occlusion of blood vessels tends to lead to
A) increases in perfusion.
B) increases in capillary exchange.
C) inadequate blood supply and damage to body tissues.
D) defibrillation of cardic muscle cell contraction.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
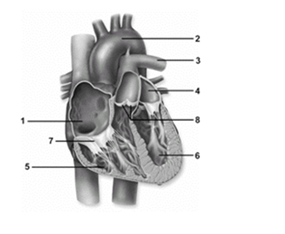 -In this figure showing an anterior view of the heart,what is depicted by number 7
-In this figure showing an anterior view of the heart,what is depicted by number 7
A) Aortic semilunar valve
B) Right atrium
C) Left ventricle
D) Right atrioventricular valve
E) Pulmonary semilunar valve
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Someone with a heart block would have
A) a long P-R interval.
B) a long T-P interval.
C) a short P-R interval.
D) a short T-P interval.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The serous fluid within the pericardial cavity works to
A) lubricate membranes of the pericardium.
B) slow the heart rate.
C) equalize the pressure in the great vessels.
D) eliminate blood pressure spikes.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The units for perfusion of blood are typically
A) grams per minute.
B) milliliters per minute per gram.
C) millimiters per hour per kilogram.
D) liters per gram.
E) beats per minute per gram.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an ECG,what does the T wave represent
A) Depolarization of the atria
B) Depolarization of the right ventricle
C) Repolarization of the ventricles
D) Closure of the AV valves
E) Depolarization of the left ventricle
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is the contraction of the atria during atrial systole that completes the filling of the ventricles while the ventricles are in diastole.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which pair is located more anteriorly in a heart in normal position
A) Left atrium and left ventricle
B) Left atrium and right ventricle
C) Right atrium and left atrium
D) Right atrium and right ventricle
E) Right atrium and left ventricle
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The papillary muscles attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves by means of the
A) pectinate muscles.
B) trabeculae carneae.
C) conus arteriosus.
D) tendinous cords.
E) tricuspid valve.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of the calcium that triggers contraction of cardiac muscle comes
A) into the cell through leakage channels in the sarcolemma.
B) into the cell through voltage-gated channels in the sarcolemma.
C) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the cell.
D) from the Golgi apparatus of the cell.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A drug that decreased calcium levels in a muscle cell and thereby lowered the number of crossbridges formed during the heart's contractions would be a
A) positive chronotropic agent.
B) negative chronotropic agent.
C) positive inotropic agent.
D) negative inotropic agent.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The term used to describe the inadequate blood flow to a structure caused by obstruction of the blood supply is _________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fossa ovalis appears just above the opening of the coronary sinus within the
A) left atrium.
B) left ventricle.
C) right atrium.
D) right ventricle.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 138
Related Exams