A) linkage maps.
B) pedigree charts.
C) genotype maps.
D) Punnett squares.
E) bell-shaped curves.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the ABO blood type system,there are six possible genotypes,but only two possible phenotypes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between that of the homozygotes,this is called
A) codominance.
B) independent assortment.
C) linkage.
D) incomplete dominance.
E) polygenic.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In pedigree charts,autosomal recessive disorders typically
A) appear in every generation.
B) appear only in males.
C) appear only in females.
D) may disappear in one generation and reappear in the next generation.
E) occur every third generation.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The statement that segregation of alleles for a gene on one chromosome does not influence the segregation of alleles for a gene on another chromosome during gamete formation is Mendel's law of
A) independent assortment.
B) random fertilization.
C) population dynamics.
D) crossing over.
E) segregation.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A male expresses
A) only the dominant alleles on his X chromosome.
B) both the dominant and recessive alleles on his X chromosome.
C) only the homozygous recessive alleles on his X chromosome.
D) none of the alleles on his X chromosome.
E) only the homozygous dominant alleles on his X chromosome.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A test cross is a mating of an individual with an unknown genotype and an individual that
A) is heterozygous.
B) is homozygous dominant.
C) is homozygous recessive.
D) has any known genotype.
E) is the wild type.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cross RrYy and RRyy pea plants,what fraction of the offspring will have round peas? R=round,r=wrinkled,Y=yellow,y=green
A) 50%
B) 75%
C) 100%
D) 25%
E) 0%
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In pedigree charts,autosomal dominant disorders typically
A) appear only in males.
B) appear only in females.
C) appear in every generation.
D) seem to disappear in one generation, only to reappear in the next generation.
E) occur every third generation.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In these data, the parental generation characteristics (resistant or susceptible) are shown at the top.
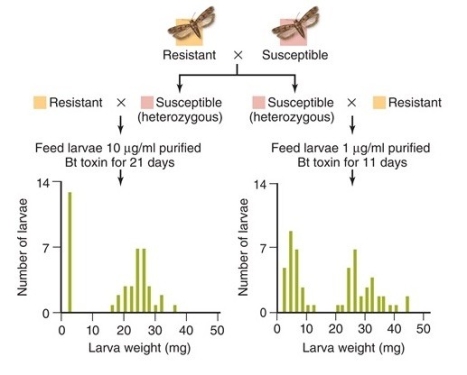 -What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in the figure?
-What did the researchers conclude from the data shown in the figure?
A) Resistance to the Bt toxin is dominant.
B) The number of larvae is dependent on treatment with the Bt toxin.
C) Resistance to the Bt toxin is recessive.
D) The size of larvae is dependent on treatment with the Bt toxin.
E) Resistance to the Bt toxin is not genetic.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To inherit an autosomal dominant disorder a person could receive the allele leading to the disease from
A) the father only, not the mother.
B) the mother only, not the father.
C) the mother or the father.
D) the parent who does not exhibit the disease.
E) All answers are correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hemophilia A is caused by
A) an X-linked recessive disorder.
B) a Y-linked recessive disorder.
C) a defective neuron response.
D) an X-linked dominant disorder.
E) a Y-linked dominant disorder.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A portion of DNA that encodes a specific protein is a
A) gene.
B) chromosome.
C) chromatid.
D) centromere.
E) kinetochore.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cross two pea plants,one with green peas and the other with yellow peas,and all of the offspring have yellow peas,you conclude
A) green is dominant over yellow.
B) yellow and green are codominant.
C) yellow is incompletely dominant over green.
D) yellow is dominant over green.
E) color is random in pea plants.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To inherit an autosomal recessive disorder requires that the person receive the allele leading to the disease from
A) the father only.
B) the mother only.
C) only the parent having the disease.
D) only one parent who is homozygous recessive for the disease.
E) both parents.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Females who are "carriers" for hemophilia
A) usually do not show symptoms of hemophilia but pass the allele for hemophilia to all of their offspring.
B) pass the allele for hemophilia to all of their sons.
C) usually show symptoms of hemophilia but do not pass the allele for hemophilia to their offspring.
D) usually show symptoms of hemophilia and pass the allele for hemophilia to all of their offspring.
E) usually do not show symptoms of hemophilia.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gene that produces a protein important in more than one biochemical pathway is
A) dominant.
B) recessive.
C) pleiotropic.
D) codominant.
E) incomplete dominant.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you cross RrYy and RRyy pea plants,what fraction of the offspring will have round yellow peas? R=round,r=wrinkled,Y=yellow,y=green
A) 100%
B) 75%
C) 25%
D) 0%
E) 50%
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Recombinant chromosomes have a mix of paternal and maternal alleles due to
A) random fertilization.
B) linkage.
C) independent assortment.
D) crossing over.
E) mutation.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mendel's law of segregation states that the two alleles of each gene are packaged into separate gametes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 94
Related Exams