A) 50 more units to be sold in this market.
B) 150 more units to be sold in this market.
C) 100 fewer units to be sold in this market.
D) 50 fewer units to be sold in this market.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 A subsidy to buyers has been placed on the market in the graph shown.What is the amount of the subsidy per unit of this good?
A subsidy to buyers has been placed on the market in the graph shown.What is the amount of the subsidy per unit of this good?
A) $22
B) $16
C) $10
D) $6
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government wants to encourage the consumption of a particular good,they should enact:
A) a subsidy to buyers, since they want to affect consumption of the good.
B) a subsidy to sellers, since they want more to be produced and offered for sale.
C) a subsidy to buyers, since they deserve the benefit more than the producers.
D) a subsidy on either buyers or sellers, since they will both have the same effect on the market.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a price ceiling to have an impact on a market it:
A) must be set above the equilibrium price.
B) must be set below the equilibrium price.
C) must be set at the equilibrium price.
D) can lead more goods to be produced in a market.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
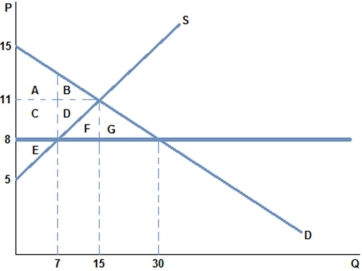 After a price ceiling of $8 is placed on the market in the graph shown,which area represents producer surplus?
After a price ceiling of $8 is placed on the market in the graph shown,which area represents producer surplus?
A) C + D + E
B) C + D + F + G
C) E
D) A + C + E
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Suppose a tax on sellers has been imposed in the graph shown.The amount of deadweight loss generated by this tax is:
Suppose a tax on sellers has been imposed in the graph shown.The amount of deadweight loss generated by this tax is:
A) $0.
B) $80.
C) $160.
D) $129.50.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in the price the buyer pays and the price the sellers keep in the presence of a tax is called:
A) a tax differential.
B) a tax wedge.
C) the tax incidence.
D) the tax burden.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tax on sellers:
A) causes equilibrium price and quantity to decrease.
B) shifts the demand curve vertically downwards by the amount of the tax, but does not affect the supply curve
C) shifts the supply curve vertically upwards by the amount of the tax, but does not affect the demand curve.
D) causes a shortage in the market.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Situations in which the assumption of efficient,competitive markets fails to hold are called:
A) market failures.
B) inelastic-response markets.
C) missing markets.
D) market interventions.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Does a subsidy to buyers affect the supply curve?
A) Yes, it shifts supply up by the amount of the subsidy.
B) Yes, it shifts supply to the right by the amount of the subsidy.
C) No, the quantity supplied will increase, but the supply curve does not move.
D) No, the quantity supplied will decrease, but the supply curve does not move.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
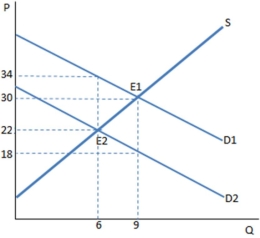 The graph shown demonstrates a tax on buyers.Who bears the greater tax incidence?
The graph shown demonstrates a tax on buyers.Who bears the greater tax incidence?
A) The seller
B) The buyer
C) The government
D) The incidence is equally shared between buyer and seller
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In evaluating policy effectiveness,economists rely on:
A) positive analysis.
B) normative analysis.
C) both normative and positive analysis.
D) Economists can never fully analyze any real-world policy effectiveness.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
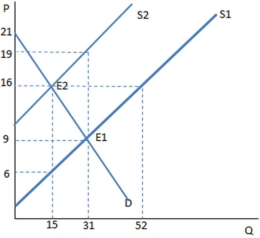
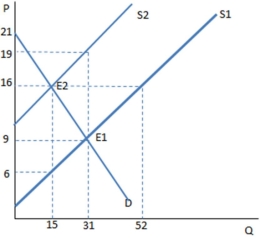 Suppose a tax on sellers has been imposed in the graph shown.Once the tax is in place,the buyers purchase ____ units and pay ____ for each one.
Suppose a tax on sellers has been imposed in the graph shown.Once the tax is in place,the buyers purchase ____ units and pay ____ for each one.
A) 15; $16
B) 15; $6
C) 31; $9
D) 31; $19
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
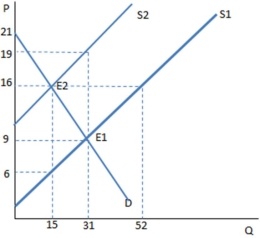 The graph shown demonstrates a tax on sellers.Which of the following can be said about the effect of this tax?
The graph shown demonstrates a tax on sellers.Which of the following can be said about the effect of this tax?
A) The tax creates a shortage, and rationing must occur.
B) The tax creates a surplus, and the government must buy the excess.
C) The tax creates a shortage, and the government must regulate the market.
D) None of these is true.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
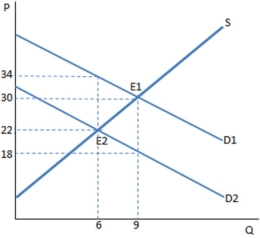 Suppose a tax on buyers has been imposed in the graph shown.Once the tax is in place,the buyers purchase ____ units and pay ____ for each one.
Suppose a tax on buyers has been imposed in the graph shown.Once the tax is in place,the buyers purchase ____ units and pay ____ for each one.
A) 6; $22
B) 6; $34
C) 9; $18
D) 9; $30
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
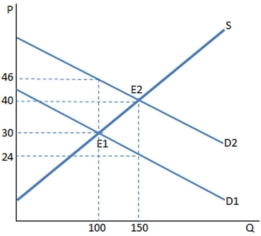 The graph shown shows a subsidy to buyers.Before the subsidy is put in place,the buyers bought _____ units and paid _____ for each of them.
The graph shown shows a subsidy to buyers.Before the subsidy is put in place,the buyers bought _____ units and paid _____ for each of them.
A) 100; $46
B) 100; $30
C) 150; $40
D) 150; $24
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A price floor that is binding:
A) must be set above the equilibrium price, and will likely cause a shortage.
B) must be set below the equilibrium price, and will likely cause a shortage.
C) must be set above the equilibrium price, and will likely cause a surplus.
D) must be set below the equilibrium price, and will likely cause a surplus.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
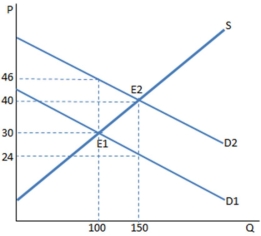 A subsidy to buyers has been placed in the market in the graph shown.The result is:
A subsidy to buyers has been placed in the market in the graph shown.The result is:
A) a higher quantity bought and sold at a higher price.
B) customers are worse off than before the subsidy.
C) producers are worse off than before the subsidy.
D) None of these is true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Does a subsidy to sellers affect the supply curve?
A) Yes, it shifts supply vertically downward by the amount of the subsidy.
B) Yes, it shifts supply to the right by the amount of the subsidy.
C) No, the quantity supplied will increase, but the supply curve does not move.
D) No, the quantity supplied will decrease, but the supply curve does not move.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Positive analysis:
A) is the best way to analyze a policy.
B) leads to the best solutions.
C) is the only way to analyze a policy.
D) examines if the policy actually accomplished its goals.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 156
Related Exams