A) the tundrA.
B) savannas.
C) deserts.
D) partially treed grasslands.
E) partial shrublands.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tropical climates are warmer than temperate climates because
A) temperate climates have more mountains and thus more snow causing the landmasses to warm slower.
B) tropical climates have more vegetation and thus can absorb more heat.
C) temperate climates are closer to the poles and the polar surfaces cause a reduction in heat gain.
D) tropical climates receive the sun's rays at an almost perpendicular angle;since Earth is a sphere,the temperate climates receive the sun's rays at a much steeper incidence thus spreading the radiation over a broader area.
E) tropical climates receive the sun's rays at a much steeper incidence thus spreading the radiation over a broader area and causing the tropic to be warmer while the temperate climates receive the sun's rays at an almost perpendicular angle,which causes some areas to be warm and other areas to be cold.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the most serious and rapidly accelerating of all global environmental problems is the loss of
A) carbon dioxide in the tropical forests.
B) ground water in the tropical forests.
C) cloud cover in the tropical forests.
D) nutrients in the tropical forests.
E) biodiversity in the tropical forests.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chlorinated hydrocarbons cause
A) "Biological magnification."
B) air pollution.
C) ozone hole.
D) greenhouse effect.
E) acid precipitation.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following gases is most associated with global warming?
A) oxygen
B) ozone
C) nitrous oxides
D) carbon dioxide
E) chlorofluorocarbons
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following choices best describes the relationship that exists between moisture and air temperature?
A) The moisture-holding capacity of air decreases when it is warm and increases when it is cool.
B) The moisture-holding capacity of air remains the same (warm or cool) and is not related to its temperature.
C) The moisture-holding capacity of air increases when it is warm and decreases when it is cool.
D) The moisture-holding capacity of air increases as the higher altitude winds of the polar regions descend onto the continents.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements about the causes and effects of global warming is false?
A) Global warming will not be uniform in different regions of the world.
B) In addition to carbon dioxide,other greenhouse gases include methane and nitrous oxide.
C) Melting of the Artic permafrost will speed the process of global warming because of its release of methane.
D) The effects of global warming can be measured today.
E) Carbon dioxide absorbs short wavelength radiant energy better than long wavelength radiant energy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements about acid precipitation is false?
A) Acid rain is intermediate between point-source and diffuse pollution.
B) Mercury is a pollutant that often accompanies acid precipitation.
C) Acid precipitation is a severe problem in areas with soils having high buffering capacity.
D) Acid precipitation can affect aquatic ecosystems.
E) Acid precipitation can affect forests,weakening the trees and making them more susceptible to diseasE.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The orbit of Earth's revolution around the sun is inclined at an angle of 23.5 ,and this causes seasonal variation in the amount of solar energy reaching a given region.Which of the following does not differ for the tropics and polar regions?
A) angle of incidence
B) total hours of possible sunlight per year
C) mean annual air temperature
D) solar energy input during the month of July
E) annual variation in day length
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The eastern sides of the Sierra Nevada mountains are much drier than the western sides,and the vegetation is often different;this phenomenon is called the
A) solar effect.
B) precipitation effect.
C) latitude effect.
D) rain shadow effect.
E) cloud shadow effect.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the letter of the best match from the following: -Very high solar energy input;temperature and moisture not limiting;high biomass,high total productivity;many species.
A) desert
B) savanna
C) taiga
D) temperate grassland
E) tropical rain forest
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equatorial region of rising warm,moist air of low pressure causes
A) equatorial rains.
B) westerlies.
C) rain shadows.
D) microclimate.
E) El Niño.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biomes are broad regional areas with defined flora and fauna.Which one of the following choices correctly identifies the biomes shown plotted in the included graph of precipitation versus temperature? 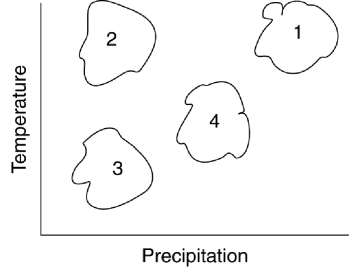
A) Tropical Rain forest = 1;Desert = 2;Tundra = 3;Grassland = 4
B) Tropical Rain forest = 2;Desert = 3;Tundra = 4;Grassland = 1
C) Tropical Rain forest = 3;Desert = 4;Tundra = 1;Grassland = 2
D) Tropical Rain forest = 4;Desert = 1;Tundra = 2;Grassland = 3
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
About 40% of the world's photosynthetic productivity occurs in _________floating in the oceans.
A) seaweeds
B) phytoplankton
C) macroalgae
D) zooplankton
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Microscopic plant-like organisms are collectively called
A) zooplankton.
B) phytoplankton.
C) pelagic organisms.
D) benthic organisms.
E) heterotrophs.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A layer of ozone in the upper atmosphere shields Earth from most
A) acid rain.
B) bacterial diseases.
C) greenhouse effects.
D) solar ultraviolet radiation.
E) water pollution.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements about ozone depletion is false?
A) Concentrations of ozone-depleting chemicals continue to rise in the atmosphere.
B) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are the major cause of ozone depletion.
C) Free chlorine in the upper atmosphere catalyzes the conversion of O3 into O2.
D) Weather conditions also influence the size of the ozone hole in the stratosphere.
E) CFCs are acted on by conditions in the stratosphere to form diatomic chlorine (Cl2) .
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A friend asks you about what has caused global warming.You explain
A) as carbon dioxide and other gases have increased in the atmosphere,the global temperature has increased due to trapped solar radiation.
B) as carbon dioxide and other gases have increased in the atmosphere,the global temperature has increased due to ozone depletion.
C) as carbon dioxide and other gases have increased in the atmosphere,the global temperature has increased due to acid precipitation changing the pH of the atmosphere.
D) that there really is no evidence for global warming and these are mere scare tactics being used by environmentalists to reduce oil consumption.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biomagnification is a significant problem in aquatic communities.The amounts of chemicals magnify (increase or accumulate) at each new link in a food chain.Use the following information to calculate the level of chemical X in the large-mouth bass.One small plant can accumulate 1 unit of chemical X.A microscopic animal eats 15 small plants.A minnow consumes 10 microscopic animals,a large-mouth bass consumes 20 minnows.
A) 15 units of chemical X
B) 30 units of chemical X
C) 150 units of chemical X
D) 300 units of chemical X
E) 3,000 units of chemical X
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the letter of the best match from the following: -Spruce,fir;moose;deep snow,brief summer;vast sameness;marshes,lakes,and ponds.
A) desert
B) savanna
C) taiga
D) temperate grassland
E) tropical rain forest
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 79
Related Exams