A) association.
B) behavior modification.
C) habituation.
D) learning.
E) sensitization.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are examples of animal behavioral responses to environmental cues except
A) the feeding frenzy.
B) the mating ritual.
C) bee waggle-dance.
D) resistance to infection.
E) migration.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements comparing the naked mole rat social system with social insect societies is false?
A) As with social insect societies,colony members are kin.
B) As with social insect societies,it is based on haplodiploidy.
C) Unlike social insect societies,all colony members are diploid.
D) As with social insect societies,there is one queen and several reproductive males per colony.
E) As with social insect societies,there is a division of labor within the colony.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alarm calling seems to be an example of ________,that is,it favors relatives.
A) sociology
B) demography
C) aggression
D) kin selection
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genetic basis of behavior is supported by all of the following except
A) hybridization studies.
B) studies on the behavior of twins.
C) artificial selection.
D) studies of supernormal stimuli.
E) imprinting.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The degree of parental investment required often results in the non-random mating behavior called ___________.
A) sexual selection
B) fidelity
C) mate choice
D) preferability
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A behavior that has evolved to aid relatives,although at personal risk,and thus increases the chance of your genes being passed on to the next generation is known as
A) altricial behavior.
B) instinctive behavior.
C) kin selection.
D) operant conditioning.
E) adaptive behavior.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Artificial selection and hybridization can demonstrate the __________ basis of behavior.
A) cognitive
B) instinctive
C) genetic
D) associational
E) endogenous
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pea fowl (peacocks and peahens) show sexual dimorphism.Which statement best describes the graphed data? 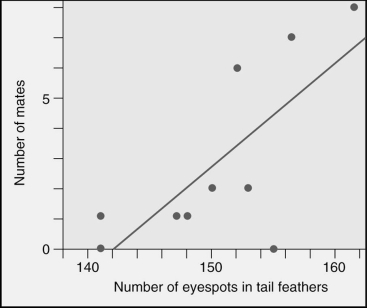
A) There are no peacocks with less than 140 eyespots.
B) The fewer eyespots that a peacock has in his tail,the more mates he attracts.
C) Actually eyespots have very little to do with mate-attracting activities.
D) The more eyespots that a peacock has in his tail,the more mates he attracts.
E) There are no peacocks with more than 165 eyespots.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Konrad Lorenz demonstrated that newly hatched birds would direct their social behavior toward him if they saw him first after they hatched from their eggs.This is referred to as
A) cross-fostering behavior.
B) operant conditioning.
C) fixed action patterning.
D) habituation behavior.
E) imprinting behavior.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In species where the young are precocial,meaning requiring little parental care,males may be more likely to be
A) monogamous.
B) polygynous.
C) polyandrous.
D) polygamous.
E) altricial.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Young birds see objects flying overhead and respond by crouching down into the nest and remaining still.Over time some objects become familiar and the young birds do not crouch down.This type of learning is referred to as
A) sensitization.
B) associative learning.
C) operant conditioning.
D) habituation.
E) Pavlovian conditioning.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an appropriate interpretation for these graphs? 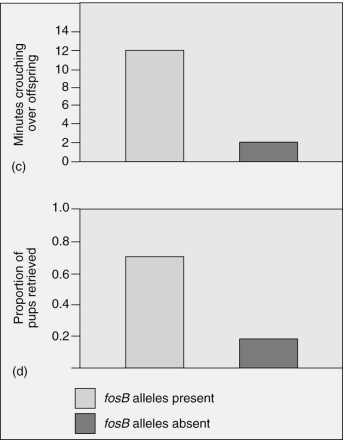 Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
A) less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
B) greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
C) the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
D) less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele;however,the graphs depict only minor differences,which are most likely not significant.
E) not possible to determine from the data.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The area over which an animal moves in the course of daily activity,but which it does not necessarily defend against other animals,is its
A) family home.
B) foraging space.
C) home range.
D) nesting site.
E) territory.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the letter of the best match from the following: -A form of communication in honeybees.
A) cognition
B) waggle dance
C) navigation
D) filial imprinting
E) fixed action pattern
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following examples describes a communication mode that would be best for signaling over the greatest distance in a dark,densely forested environment?
A) display of plumage of a male bird to attract females
B) waggle dance of a honeybee in a colony within the forest
C) pheromones released by a female moth
D) territorial song of a male bird to repel other males
E) flashing of a male firefly to attract conspecific females
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the letter of the best match from the following: -Innate motor program.
A) cognition
B) waggle dance
C) navigation
D) filial imprinting
E) fixed action pattern
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical signals that mediate interactions between two or more members of a given species are called ________________.
A) pheromones
B) alarm signals
C) hormones
D) competitive exclusions
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the letter of the best match from the following: -Move long distances using sun and stars.
A) cognition
B) waggle dance
C) navigation
D) filial imprinting
E) fixed action pattern
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You place an empty dog-food dish across the room from a puppy that then goes over to investigate the dish.You pick the dish up and ten minutes later you place it in a different part of the room,and you keep repeating this pattern.After the fifth time the puppy no longer goes over to the empty dish.Which of the following terms best describes this form of learning?
A) trial and error learning
B) habituation
C) classical conditioning
D) operant conditioning
E) imprinting
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 76
Related Exams