B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One of the primary output reports of MRP concerns changes to planned orders.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Lot-for-lot ordering in MRP eliminates the holding costs for parts that are carried over to other periods.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Independent demand tends to be more "lumpy" than dependent demand, meaning that we need large quantities followed by periods of no demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an MRP master schedule, the planning horizon is often separated into a series of time periods called:
A) pegging.
B) lead times.
C) stacked lead times.
D) time buckets.
E) firm, fixed, and frozen.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Given the following data, construct a material requirements plan which will result in 100 units of Parent 1 (P1) at the beginning of week 6, and 200 units of Parent 2 (P2) at the beginning of week 8: 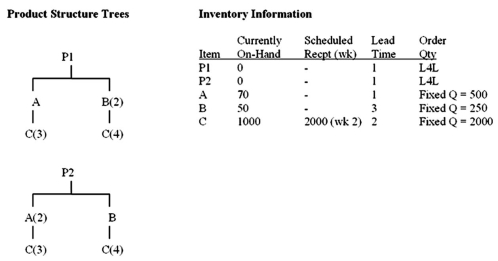
Correct Answer

verified
Item A has an on-hand balance ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
When MRP II systems include feedback, they are known as:
A) MRP III.
B) enterprise resource planning.
C) circular MRP.
D) feasible MRP.
E) closed loop MRP.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
The following is a list of components required to produce one unit of end item P:
P: 2 As, 3 Bs, 3 Cs
A: 5 Ms, 2 Rs
B: 1 D, 3 Ns
C: 1 T, 4 Ns
M: 1 N
Determine the number of Ns that will be needed to make 60 Ps in each of these cases:
(A) There are currently 10 Ps on hand.
(B) On-hand inventory consists of 15 Ps, 10 As, 20 Bs, 10 Cs, 100 Ns, 300 Ts, and 200 Ms.
The product structure tree is:
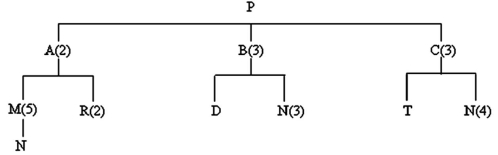
Correct Answer

verified
(A) [1 N per M × 5 Ms per A × 2 As per ...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is not an input in an MRP system?
A) planned-order schedules
B) bill of materials
C) master production schedule
D) inventory records
E) All are inputs.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
MRP, considering inventory position, bills of material, open purchase orders, and lead times guarantees a feasible production plan if the inputs to MRP are accurate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents an attempt to balance the benefits of stability against the benefits of responding to new information?
A) safety stock
B) safety time
C) bills of material
D) time fences
E) fixed-period lot sizing
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capacity requirements planning helps managers reconcile __________ with __________.
A) what is needed; what has been done
B) what is needed; what is possible
C) what has been done; who will be doing it
D) what needs to be done; where it will be done
E) what has been done; how much what needs to be done will cost
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Backflushing takes place:
A) when inventory records need updating.
B) after some bills of material have been found to be inaccurate.
C) after production has been completed.
D) when customer orders are being reconciled.
E) when previous periods' planned releases are converted to scheduled receipts.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not usually necessary in order to have an effective MRP system?
A) a computer and software
B) an accurate bill of materials
C) lot-for-lot ordering
D) an up-to-date master schedule
E) integrity of file data
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A visual depiction of the subassemblies and components that are needed to produce and/or assemble a product is called a(n) :
A) assembly time chart.
B) product structure tree.
C) MRP II.
D) pegging.
E) Gantt chart.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The MRP input stating which end items are to be produced, when they are needed, and what quantities are needed, is the:
A) master schedule.
B) bill of materials.
C) inventory records.
D) assembly time chart.
E) net requirements chart.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
MRP works best if the inventory items have dependent demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lot sizing methods does not attempt to balance ordering (or setup) and holding costs?
A) economic order quantity
B) economic run size
C) lot-for-lot
D) part-period
E) all of these
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comparing known and expected capacity requirements with projected capacity availability is the job of:
A) planned releases.
B) load reports.
C) lot sizing.
D) work loading.
E) time fencing.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The identification of parent items is called:
A) paternity.
B) pegging.
C) requirement I.D.
D) relationship tracking.
E) master scheduling.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 89
Related Exams