A) imposing greater penalties for those who are caught and convicted.
B) using more sophisticated security systems.
C) enhancing the legitimate earnings of potential criminals.
D) cutting out the middlemen ("fences") by selling stolen goods via Internet auction sites.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Children who dislike Brussels sprouts exemplify the notion that the marginal utility of Brussels sprouts is
A) zero.
B) negative.
C) positive, but decreasing.
D) less than the total utility.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The income effect of a price increase for a normal good causes an increase in the consumption of the good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Last Word) Theft and burglary
A) can be viewed as attempts to maximize utility, given certain marginal costs and marginal benefits.
B) are examples of irrational behavior.
C) are applications of the law of increasing opportunity cost.
D) are less economically rational than crimes of passion and violence.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best explains why most people don't consume units of goods to the point that their marginal utility falls to zero?
A) If marginal utility is falling, then total utility is falling.
B) Consumers face budget constraints that limit how much they can purchase.
C) Governments tend to limit how much of a good a person is allowed to consume.
D) The price of a good tends to rise as an individual attempts to purchase more.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following defines marginal utility?
A) the change in total utility divided by the price of a product
B) the maximum amount of satisfaction from consuming a product
C) the total satisfaction derived from a certain amount of the product
D) the additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit of a product
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The utility from a specific product is
A) determined by a consumer's income.
B) determined by the price of the product.
C) a measure of one's preference or taste for it.
D) constant as one consumes more units of it.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an assumption of the theory of consumer behavior described in this chapter?
A) The consumer has to make purchasing decisions within a given budget constraint.
B) The consumer experiences diminishing marginal utility from consuming goods.
C) The consumer's tastes and preferences continually change within the period studied.
D) The consumer aims to get maximum total utility out of a given budget.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume initially that the price of X (the quantity of which is measured on the horizontal axis) is $9 and the price of Y (the quantity of which is measured on the vertical axis) is $4. If the price of X now declines to $6, the budget line will
A) be unaffected.
B) shift outward on the vertical axis.
C) shift inward on the horizontal axis.
D) shift outward on the horizontal axis.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium points shown in the diagram, along with the price change that produced the shift of the budget line from ab to ac, 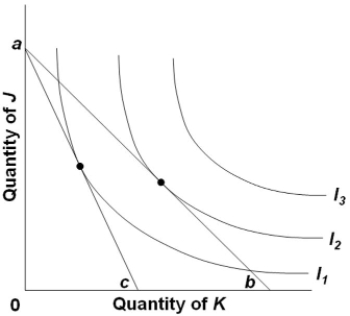
A) are consistent with a downsloping demand curve for product K.
B) imply that the consumer's money income has declined, but his or her real income has increased.
C) imply consumer irrationality since the dearer product is being substituted for the cheaper product.
D) suggest that K is an inferior good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Susie buys two goods: rounds of golf and massages. Suppose that the price of a round of golf is $20 and the price of a massage is $30. In a typical week, Susie will play two rounds of golf, getting 20 utils of satisfaction from the second round. She normally buys three massages each week, with the third giving her 30 utils of satisfaction. If she were to buy a fourth massage in a week, it would give her 20 utils of satisfaction. If the price of massages is reduced to $15, which of the following outcomes might we expect to occur?
A) Susie would leave her consumption choices unchanged because of diminishing marginal utility in the consumption of massages.
B) Susie would buy more massages and fewer rounds of golf, as predicted by the income effect.
C) Susie would buy more massages and more rounds of golf, as predicted by the substitution effect.
D) Susie would buy more massages and fewer rounds of golf, as predicted by the substitution effect.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that product Alpha and product Beta are both priced at $1 per unit and that Ellie has $20 to spend on Alpha and Beta. She buys 8 units of Alpha and 12 units of Beta. The marginal utility of Alpha is 40 and the marginal utility of Beta is 20. This indicates that
A) Ellie should make no change in consumption.
B) given another dollar, Ellie should buy an additional unit of Beta.
C) in order to maximize utility, Ellie should buy more of Beta and less of Alpha.
D) in order to maximize utility, Ellie should buy more of Alpha and less of Beta.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the price of product Y (the quantity of which is on the vertical axis) is $15 and the price of product X (the quantity of which is on the horizontal axis) is $3. Also assume that money income is $60. The absolute value of the slope of the resulting budget line is
A) 5.
B) 1/5.
C) 4.
D) 20.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer currently spends a given budget on two goods, X and Y, in such quantities that the marginal utility of X is 10 and the marginal utility of Y is 8. The unit priceof X is $5 and the unit price of Y is $2. The utility-maximizing rule suggests that this consumer should
A) increase consumption of product X and decrease consumption of product Y.
B) increase consumption of product X and increase consumption of product Y.
C) increase consumption of product Y and decrease consumption of product X.
D) stick with the current consumption mix because it yields maximum utility.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) There is no firm mathematical relationship between marginal utility and total utility.
B) Total utility is equal to the change in marginal utility from consuming an additional unit of a product.
C) If marginal utility is diminishing and is a positive amount, total utility will increase.
D) If marginal utility is diminishing, total utility must also be diminishing.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to economists, gift registries, returning gifts for cash refunds, and "recycling gifts"
A) are inefficient because the time spent in these activities is never worth the benefit recipients receive from doing them.
B) are equally efficient because the recipient gets exactly what he wants.
C) are more efficient than if givers simply gave cash gifts.
D) increase the efficiency of gift-giving because they allow the recipient to consume goods that provide greater utility and transfer away those goods that are less satisfying.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) When marginal utility is decreasing, an increase in the quantity consumed will decrease total utility.
B) When marginal utility is positive, an increase in the quantity consumed will decrease total utility.
C) When marginal utility is positive, an increase in the quantity consumed will increase total utility.
D) When marginal utility is zero, an increase in the quantity consumed will make total utility zero.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Graphically, the consumer maximizes total utility where the budget line is tangent to an indifference curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram, where xy is the relevant budget line and I1, I2, and I3 are indifference curves. At point K, 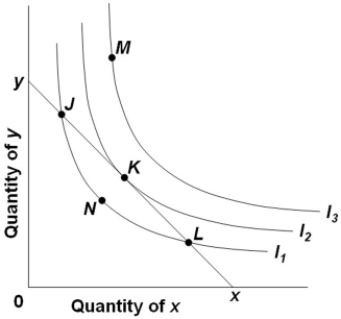
A) MUx = MUy.
B) MRS = Px/Py.
C) MRS = Py/Px.
D) Px exceeds Py.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of a product falls for a normal good, the
A) income and substitution effects will encourage consumers to purchase more of the product.
B) income and substitution effects will encourage consumers to purchase less of the product.
C) substitution effect will encourage consumers to purchase less of the product, and the income effect will encourage them to purchase more.
D) substitution effect will encourage consumers to purchase more of the product, and the income effect will encourage them to purchase less.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 256
Related Exams