A) All are required to explain the utility-maximizing position of a consumer.
B) They are all empirically measurable.
C) They all help explain the upsloping supply curve.
D) They all help explain the downsloping demand curve.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fact that most medical care purchases are financed through insurance
A) has no effect on health care consumption because aggregate costs are the same regardless of payment method.
B) reduces the amount of health care consumed by raising the price of additional units of care.
C) has decreased health care costs and therefore reduced aggregate health care expenditures.
D) increases the amount of health care consumed by reducing the price of additional units of care.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that Tonya consumes only two products, pizza and potato chips, out of a given budget. Both are normal goods for Tonya. If the price of pizza decreases, then Tonya's consumption of pizza will
A) decrease due to the income effect.
B) decrease due to the substitution effect.
C) increase due to the income effect.
D) increase due to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Edith is buying products X and Y with her money income. Suppose her budget line shifts rightward (outward) . This might be the result of
A) the prices of X and Y increasing while her money income remains constant.
B) her money income decreasing while the prices of X and Y remain constant.
C) her money income increasing more than increases in the prices of X and Y.
D) none of these.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal utility can be
A) positive, but not negative.
B) positive or negative, but not zero.
C) positive, negative, or zero.
D) decreasing, but not negative.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following two schedules, which show the amounts of additional satisfaction (marginal utility) that a consumer would get from successive quantities of products J and K. 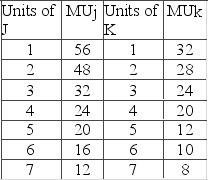 If the consumer's money income were cut from $52 to $28, and the prices of J and K remain at $8 and $4, respectively, she would maximize her satisfaction by purchasing
If the consumer's money income were cut from $52 to $28, and the prices of J and K remain at $8 and $4, respectively, she would maximize her satisfaction by purchasing
A) 3 units of J and 3 units of K.
B) 1 unit of J and 3 units of K.
C) 4 units of J and 1 unit of K.
D) 2 units of J and 3 units of K.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An indifference map implies that
A) money income is constant, but the prices of the two products vary directly with the quantities purchased.
B) the two products under consideration are perfectly substitutable for one another.
C) a consumer is better off to be at some point high on a given curve as opposed to a point low on the same curve.
D) curves farther from the origin yield higher levels of total utility.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of product X rises, then the resulting decline in the amount purchased will
A) necessarily increase the consumer's total utility from his total purchases.
B) increase the marginal utility of the last unit consumed of this good.
C) increase the total utility from purchases of this good.
D) reduce the marginal utility of the last unit consumed of this good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The substitution effect of a price decrease for a good causes an increase in the consumption of the good, regardless of whether the good is normal or inferior.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a topographic map, each line represents a particular elevation above sea level, and in an indifference map, each line represents a particular level of
A) total utility.
B) marginal utility.
C) income.
D) demand.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution
A) may increase or decrease on a given indifference curve, depending on whether the substitution or the income effect is dominant.
B) increases as one moves southeast along an indifference curve.
C) is constant at all points on the budget line.
D) declines as one moves southeast along an indifference curve.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A consumer maximizes total utility when she or he purchases the combination of the two products at which her or his budget line is tangent to an indifference curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In deciding what to buy, the consumer will choose the good with the
A) highest marginal utility.
B) lowest price.
C) highest marginal utility-to-price ratio.
D) lowest marginal utility-to-price ratio.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A consumer is in equilibrium and is spending income in such a way that the marginal utility of product X is 40 units and that of Y is 16 units. If the unit price of X is $5, then the price of Y must be
A) $1 per unit.
B) $2 per unit.
C) $3 per unit.
D) $4 per unit.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When total utility reaches a maximum, then marginal utility is
A) increasing.
B) decreasing.
C) at a minimum.
D) equal to zero.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following total utility data for products L and M. Assume that the prices of L and M are $3 and $4, respectively, and that the consumer's income is $18 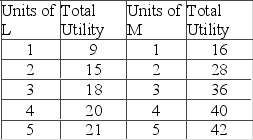 How many units of the two products will the rational consumer purchase?
How many units of the two products will the rational consumer purchase?
A) 3 of L and none of M
B) 4 of L and 2 of M
C) 3 of L and 5 of M
D) 2 of L and 3 of M
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows a consumer's utility schedule. 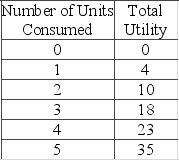 Based on the data, you can conclude that the consumer
Based on the data, you can conclude that the consumer
A) receives increasing marginal utility from consuming the first three units.
B) experiences diminishing marginal utility after consuming the first unit.
C) experiences diminishing marginal utility only after consuming the fourth unit.
D) will never consume just one unit of the product.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question based on the table below showing the marginal utility schedules for product X and product Y for a hypothetical consumer. The price of product X is $4, and the price of product Y is $2. The income of the consumer is $20.
 If the consumer buys product X or product Y one unit at a time, which of the following will the consumer's first two purchases be?
If the consumer buys product X or product Y one unit at a time, which of the following will the consumer's first two purchases be?
A) a first unit of X followed by a first unit of Y
B) a first unit of X followed by a second unit of X
C) a first unit of Y followed by a first unit of X
D) a first unit of Y followed by a second unit of Y
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram. If the budget line shifts from ab to ac, the 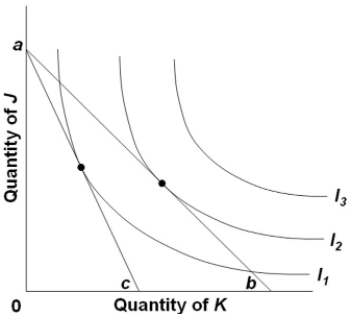
A) consumer's level of total utility will increase.
B) consumer will purchase more of both J and K.
C) consumer will purchase less of both J and K.
D) consumer will purchase more of J and less of K.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In moving along a given budget line,
A) the prices of both products and money income are assumed to be constant.
B) each point on the line will be equally satisfactory to consumers.
C) money income varies, but the prices of the two goods are constant.
D) the prices of both products are assumed to vary, but money income is constant.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 256
Related Exams