A) supply curve for Z to the left.
B) supply curve for Z to the right.
C) demand curve for Z to the left.
D) demand curve for Z to the right.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things equal, if the price of a key resource used to produce product X falls, the
A) supply curve of product X will shift to the right.
B) demand curve of product X will shift to the right.
C) supply curve of product X will shift to the left.
D) supply curve of product X will not shift.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about price ceilings?
A) price ceilings create surpluses for goods but shortages for services.
B) Price ceilings cause goods to be rationed by some other means than legally determined market prices.
C) Ration coupons are the only way to ration goods when price ceilings are in place.
D) All of the other statements are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All markets involve the following elements, except
A) demand or buyers.
B) face-to-face negotiation.
C) prices of goods and services.
D) supply or sellers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following are explanations of the Law of Demand, except
A) expectations effect.
B) diminishing marginal utility.
C) income effect.
D) substitution effect.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A television station reports that the price of coffee has increased and the quantity traded in the market has decreased. This situation would be caused by a(n)
A) increase in demand.
B) increase in supply.
C) decrease in demand.
D) decrease in supply.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price of pork may increase as a result of
A) a decrease in the cost of feed for pigs.
B) decreased advertising of pork.
C) an increase in the cost of producing beef.
D) a subsidy to pork producers.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question based on the following supply and demand schedules in units per week for a product. 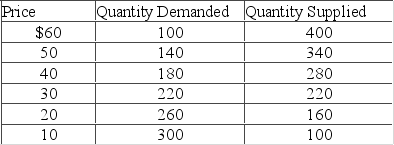 Refer to the above table. If demand increased by 100 units at each price level and the government set a price ceiling of $40, then there would be
Refer to the above table. If demand increased by 100 units at each price level and the government set a price ceiling of $40, then there would be
A) a shortage.
B) a surplus.
C) no shortage or surplus.
D) a decrease in supply.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the weekly demand for hamburger in a market where there are just three buyers.  If the price of hamburger falls from $5 to $3, then the weekly market quantity demanded will
If the price of hamburger falls from $5 to $3, then the weekly market quantity demanded will
A) increase from 24 to 52.
B) decrease from 52 to 24.
C) increase from 120 to 156.
D) increase from 29 to 55.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that at prices of $1, $2, $3, $4, and $5 for product Z, the corresponding quantities supplied are 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 units, respectively. Which of the following would increase the quantities supplied of Z to, say, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14 units at these prices?
A) improved technology for producing Z
B) an increase in the prices of the resources used to make Z
C) an increase in the excise tax on product Z
D) increases in the incomes of the buyers of Z
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If price is above the equilibrium level, competition among sellers to reduce the resulting
A) surplus will increase quantity demanded and decrease quantity supplied.
B) shortage will decrease quantity demanded and increase quantity supplied.
C) surplus will decrease quantity demanded and increase quantity supplied.
D) shortage will increase quantity demanded and decrease quantity supplied.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces its most wanted goods but uses outdated production methods, it is
A) achieving productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency.
B) not achieving productive efficiency.
C) achieving both productive and allocative efficiency.
D) engaged in roundabout production.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the graphs show a competitive market for the product stated in the question. 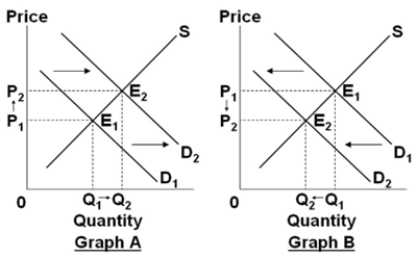
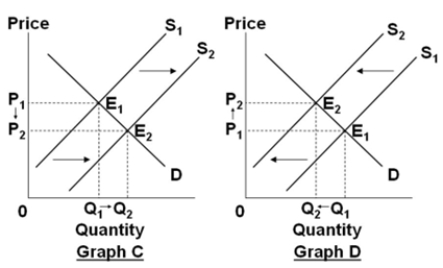 Select the graph above that best shows the change in the market for wheat, when the cost of fertilizer decreases.
Select the graph above that best shows the change in the market for wheat, when the cost of fertilizer decreases.
A) Graph A
B) Graph B
C) Graph C
D) Graph D
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X. Consumer expectations that the price of X will rise sharply in the future will
A) increase S, increase P, and increase Q.
B) increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
C) decrease S, increase P, and increase Q.
D) increase D, decrease P, and increase Q.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graphically, the market demand curve is
A) steeper than any individual demand curve that is part of it.
B) greater than the sum of the individual demand curves.
C) the horizontal sum of individual demand curves.
D) the vertical sum of individual demand curves.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in consumer incomes will cause a decrease in the demand for an inferior good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve shows the relationship between
A) money income and quantity demanded.
B) price and production costs.
C) price and quantity demanded.
D) consumer tastes and quantity demanded.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allocative efficiency involves determining
A) which output mix will result in the most rapid rate of economic growth.
B) which production possibilities curve reflects the lowest opportunity costs.
C) the mix of output that will maximize society's satisfaction.
D) the optimal rate of technological progress.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The location of the product supply curve depends on
A) production technology.
B) the number of buyers in the market.
C) the tastes of buyers.
D) the location of the demand curve.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Digital cameras and memory cards are
A) substitute goods.
B) complementary goods.
C) independent goods.
D) inferior goods.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 339
Related Exams