A) a downward-sloping demand curve for products
B) the presence of strong diseconomies of scale
C) the presence of different groups of buyers with different price elasticity of demand
D) the absence of a scope for reselling a product
E) the presence of some amount of market power with a producer
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9.1
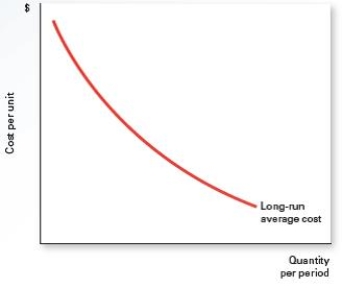 -Refer to Exhibit 9.1,which shows the long-run average cost of a firm.The downward-sloping long-run average cost curve indicates that this firm can supply market demand _____
-Refer to Exhibit 9.1,which shows the long-run average cost of a firm.The downward-sloping long-run average cost curve indicates that this firm can supply market demand _____
A) at a lower average cost per unit than two or more firms each producing a smaller amount of output.
B) at a lower average cost per unit than two or more firms each producing a larger amount of output.
C) at a higher average cost per unit than two or more firms each producing a larger amount of output.
D) at a higher average cost per unit than two or more firms each producing a smaller amount of output.
E) at the same average cost per unit as two or more firms each producing a larger amount of output.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Offering discounts to senior citizens is an example of a monopolist _____
A) decreasing profit.
B) sorting customers by age.
C) separating customers in time.
D) meeting minimum legal requirements.
E) being fair to all groups.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A natural monopoly forms when _____
A) small firms merge to form larger firms.
B) one firm has control over the entire supply of a basic input required to produce the product.
C) one firm's monopoly position is created and enforced by the government.
D) one firm receives patent protection for certain basic production processes.
E) the long-run average cost incurred by a firm declines as the firm expands output.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 9.4 -Refer to Table 9.4,which shows the demand schedule for a monopolist.Marginal revenue associated with the sale of the fourth unit of output is _____
A) $10.
B) $30.
C) $60.
D) $240.
E) $210.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a single firm supplies all the ceramic windlasses in the United States.The demand curve that the firm faces is _____
A) elastic everywhere.
B) unit elastic everywhere.
C) inelastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
D) perfectly inelastic everywhere.
E) elastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist that does not practice price discrimination is operating at an output level where price equals average total cost,we can conclude that _____
A) its economic profit is $0.
B) it is not maximizing profit.
C) it should go out of business in the long run.
D) it is not earning a normal profit.
E) it should shut down in the short run.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for both perfect competition and monopoly?
A) Firms produce a differentiated product.
B) Firms cannot earn economic profit in the long run.
C) Individual firms have no ability to control the price of their output and must accept the market price.
D) Firms go out of business in the long run if total revenue cannot cover total cost.
E) Firms usually earn economic profit in the long run.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is a key difference between a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolist that does not practice price discrimination?
A) The marginal cost curve is U-shaped for a perfectly competitive firm but not for a monopolist.
B) Price is equal to average revenue for a perfectly competitive firm in equilibrium but not for a monopolist.
C) Price is equal to marginal revenue for a perfectly competitive firm in equilibrium but not for a monopolist.
D) The average revenue curve is the demand curve for a perfectly competitive firm but not for a monopolist.
E) A monopolist aims to maximize profits, while a perfectly competitive firm tries to maximize total revenue.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following prevents potential competitors from entering a monopolized market?
A) legal restrictions
B) diseconomies of scale
C) product differentiation
D) stable market demand
E) an abundant supply of resources
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why would a monopolist sort customers by age or separate customers in time?
A) to prevent those who pay the lower price from reselling the product to those paying the higher price
B) to indicate that the firm is a price maker and has market power
C) to make sure there are at least two groups of consumers for the product
D) to ensure that the firm can charge each group a different price for essentially the same product
E) to meet legal requirements
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9.2
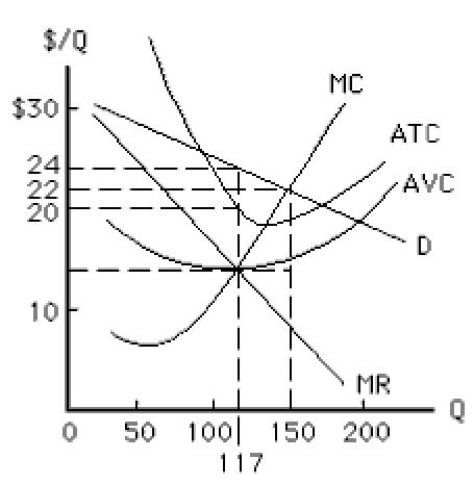 -Refer to Exhibit 9.2.A non-discriminating,profit-maximizing monopolist will earn a profit of _____ per unit of output.
-Refer to Exhibit 9.2.A non-discriminating,profit-maximizing monopolist will earn a profit of _____ per unit of output.
A) $10
B) $5
C) $4
D) $0
E) $15
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can be concluded about a monopolist whose marginal revenue is zero for a particular output level?
A) The economic profit earned by the monopolist by producing that output level is zero.
B) Total revenue earned by the monopolist is at its maximum at that output level.
C) Total revenue earned by the monopolist increases at an increasing rate as output increases beyond that output level.
D) Total revenue earned by the monopolist increases at a decreasing rate as output increases beyond that output level.
E) Average revenue earned by the firm for that output level is less than marginal revenue for that output level.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gilligan runs the only dry-cleaning business on a desert isle.If the cost of cleaning fluid falls,he can increase profit by _____
A) accepting fewer dry-cleaning orders.
B) charging the highest price he can.
C) using less cleaning fluid.
D) lowering his price.
E) charging a price that is equal to marginal cost.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist practices price discrimination by _____
A) charging different buyers different prices for different products.
B) charging different buyers different prices for the same product.
C) selling at a price below average total cost.
D) selling at a price below marginal cost.
E) selling at a price above marginal revenue.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9.7
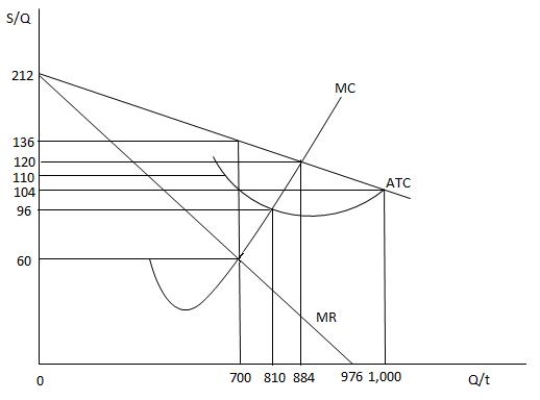 -Refer to Exhibit 9.7,which shows the cost and revenue curves for a monopolist.If the monopolist chooses to produce 1,000 units and does not discriminate among its customers,its total profit will be _____
-Refer to Exhibit 9.7,which shows the cost and revenue curves for a monopolist.If the monopolist chooses to produce 1,000 units and does not discriminate among its customers,its total profit will be _____
A) $0.
B) $104,000.
C) $212,000.
D) maximized.
E) negative.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9.2
 -Refer to Exhibit 9.2,which shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopolist.At the profit-maximizing output level for the monopolist,_____
-Refer to Exhibit 9.2,which shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopolist.At the profit-maximizing output level for the monopolist,_____
A) marginal revenue is zero.
B) marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) marginal cost is less than marginal revenue.
D) marginal cost is equal to average total cost.
E) price is equal to marginal cost.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of the profit earned by a monopolist?
A) Profit is maximized where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
B) Normal profit is ensured where price is equal to average total cost.
C) Normal profit is ensured where marginal cost exceeds average revenue.
D) Profit is maximized along the inelastic portion of the demand curve.
E) Economic profit is made where average variable cost equals marginal revenue.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a natural monopoly?
A) De Beers Consolidated Mines
B) pandas from China
C) professional sports leagues
D) Starbucks
E) Alcoa in the 1900s
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monopolists can earn positive economic profits in the long run because they are more productively efficient than perfectly competitive firms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 197
Related Exams