A) advertising
B) sales promotion
C) personal selling
D) public relations
E) advertising and public relations
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ford Motor Company provides support and incentives for its Ford and Lincoln dealers worldwide.Through a multilevel program,Ford provides incentives to reward dealers for meeting sales goals.Dealers receive an incentive when they are near a goal,another when they reach a goal,and a larger incentive if they exceed sales projections.All of these actions are intended to encourage dealers to __________ the Ford products through the channel to consumers.
A) dump
B) pull
C) unload
D) no haggle
E) push
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are forms of direct marketing except which?
A) catalogs
B) in-store free samples
C) telemarketing
D) television home shopping
E) direct mail
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Directing the promotional mix at ultimate consumers to encourage them to ask retailers for the product is referred to as
A) a push strategy.
B) an intense strategy.
C) an inertia strategy.
D) an exclusivity strategy.
E) a pull strategy.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Direct marketing currently accounts for about __________ percent of the total U.S.gross domestic product.
A) 9
B) 12
C) 15
D) 20
E) 25
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major weakness of _________________ as a form of promotion is that it requires expensive database management.
A) advertising
B) personal selling
C) sales promotion
D) publicity
E) direct marketing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The owner of a nail shop that operates in a local strip mall told her daughter,"Well,after budgeting for all of our expenses for next year,we still have about $7,500 remaining for emergencies.Let's budget 20 percent of that amount for advertising." What budgeting technique is the retailer most likely using?
A) all-you-can-afford budgeting
B) percentage of sales budgeting
C) competitive parity budgeting
D) objective and task budgeting
E) linear forecast budgeting
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which stage of the product life cycle does the marketer spend little money in the promotional mix?
A) decline
B) maturity
C) growth
D) introduction
E) reminder
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of having the receiver take a set of symbols,the message,and transform them into an idea during the communication process is referred to as
A) decoding.
B) encoding.
C) integrating.
D) back translation.
E) transformation.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a weakness of publicity?
A) Publicity has high absolute costs.
B) Publicity is difficult to receive good feedback.
C) Publicity is easily duplicated.
D) There is a lack of user control over publicity.
E) Publicity can easily lead to promotion wars.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Customers report many benefits of direct marketing,including which of these?
A) There is more privacy than in-store shopping.
B) There are fewer product returns.
C) Instant gratification is higher.
D) There are a greater number of additional incentives from sellers to retain customer loyalty.
E) Products are generally bundled with other products to offer buyers greater value.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 14-4
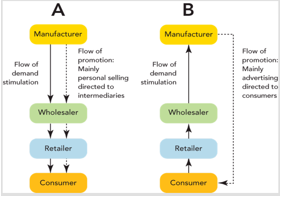 -Channel A in Figure 14-4 represents which type of promotional channel strategy?
-Channel A in Figure 14-4 represents which type of promotional channel strategy?
A) direct
B) indirect
C) push
D) pull
E) vertical
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All-you-can-afford budgeting refers to
A) allocating funds to a promotion as a percentage of past or anticipated sales, in terms of either dollars or units sold.
B) matching a competitor's absolute level of spending or the proportion per point of market share.
C) determining a firm's promotion objectives, outlining the tasks to accomplish these objectives, and determining the advertising cost of performing these tasks.
D) allocating funds to a promotion only after all other budget items are covered.
E) allocating funds to a promotion based on expected profits generated from it.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Advertising,sales promotion,and public relations are often said to use __________ because they are used with groups of prospective buyers.
A) cooperative selling
B) mass selling
C) customized selling
D) collection selling
E) paid selling
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marketers can communicate best with college students by
A) using cable TV ads since this demographic watches TV more than any other medium.
B) adding mobile media to their IMC campaigns.
C) placing ads on Sirius XM radio.
D) using "Twitter Jockeys."
E) discouraging media multitasking.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A prospective buyer goes through a sequence of stages including awareness,interest,evaluation,trial,and adoption,which are referred to as
A) the hierarchy of effects.
B) Maslow's hierarchy.
C) the purchase decision continuum.
D) the consumer-product cycle.
E) the consumer purchasing hierarchy.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After watching the 30-minute infomercial on Oxy-Clean,Sarah was certain the cleaning product would remove the grape juice stain from her white carpet.In terms of the communication process,Sarah was __________ the message from Oxy-Clean.
A) integrating
B) transforming
C) translating
D) decoding
E) encoding
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Managers often use the promotion-to-sales ratio on their marketing dashboards to assess how effective the integrated marketing communications program expenditures were at generating
A) sales.
B) customer satisfaction.
C) profits.
D) promotional sustainability.
E) CPM.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about advertising is most accurate?
A) Advertisers have limited control as to when and how often their advertisements will be placed.
B) A key advantage of advertising is its ability to use customized interactions.
C) Advertisers have very limited control over what it can say due to FCC regulations.
D) Advertising is the least costly form of promotion because ads go through significant pretesting.
E) Through advertising, a company can control what it says and, to some extent, to whom the message is sent.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"To remind" is the promotional objective of which stage of the product life cycle?
A) early growth
B) growth
C) accelerated development
D) maturity
E) introduction
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 289
Related Exams