A) 442 buckets
B) 764 buckets
C) 1,050 buckets
D) 3,150 buckets
E) 4,200 buckets
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The vertical axis of a demand curve graph represents
A) market growth rate.
B) relative market share.
C) price per unit.
D) potential profit in dollars.
E) quantity demanded.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Quantity discounts refers to
A) price reductions in unit costs for placing a larger order.
B) price reductions for placing long-term pre-scheduled orders.
C) price reductions to encourage retailers to stock inventory earlier than their normal demand would require.
D) BOGOs.
E) reductions in unit costs for taking merchandise that will soon be replaced by new and improved versions of the original product.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
RadioShack,an electronics retail chain,couldn't compete with the prices offered by other retailers.The company enacted price-matching programs and promoted large discounts on its merchandise to raise cash and hopefully stave off bankruptcy.The best pricing objective at this point for RadioShack most likely was
A) profit.
B) market share.
C) unit volume.
D) survival.
E) social responsibility.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The key to setting a final price for a product is finding an approximate price level to use as a reasonable starting point.Which of the following is one of four common approaches to selecting an approximate price level?
A) cost-oriented
B) cause-oriented
C) revenue-oriented
D) stakeholder-oriented
E) distribution-oriented
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about consumer demand as a pricing constraint is most accurate?
A) The number of potential buyers for the product class has little effect on the price a seller can charge.
B) The number of potential buyers for the product affects the price a seller can charge, but only if the product is using a push strategy in the channel.
C) The number of potential buyers for the product affects the price a seller can charge, but only if the product is a necessity item.
D) The number of potential buyers for the brand affects the price a seller can charge in the growth stage of a product life cycle, but not in the introductory stage.
E) The number of potential buyers generally affects the price a seller can charge.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major grocery chain pays its baggers a regular hourly wage.The baggers not only pack the groceries,but they also will take customers' groceries to their car,regardless of the weather.The baggers are not permitted to accept tips,even if they are offered.The consumer will experience this shopping experience as
A) pricing enhancement.
B) societal pricing.
C) revenue sharing.
D) value-pricing.
E) cost-plus pricing.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a __________ pricing strategy,a price setter stresses the __________ side of the pricing problem.
A) demand-oriented; cost
B) supply-oriented; target ROI
C) competition-oriented; marketing channel
D) cost-oriented; cost
E) profit-oriented; revenue
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a competition-oriented approach to pricing?
A) skimming pricing
B) target pricing
C) customary pricing
D) target return-on-sales pricing
E) standard markup pricing
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To increase value,marketers may __________,decrease price,or do both.
A) decrease benefits
B) increase benefits
C) increase price
D) increase advertising
E) do nothing and let the perceived value of the item increase as it matures in the life cycle
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What pricing strategy did the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) use to pay Lockheed Martin for the Orion lunar spacecraft?
A) cost-plus-percentage-of-cost pricing
B) experience curve pricing
C) standard markup pricing
D) yield management pricing
E) cost-plus-fixed-fee pricing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-6a 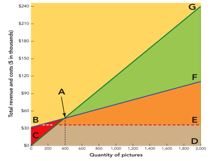 -In the break-even chart in Figure 11-6a,the rectangular area EBCD represents the firm's
-In the break-even chart in Figure 11-6a,the rectangular area EBCD represents the firm's
A) fixed costs.
B) break-even point.
C) variable costs.
D) profit.
E) total revenue.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The use of special fees and surcharges is driven by consumers' zeal for low prices and
A) the ease of making price comparisons on the Internet.
B) value, the idea of getting more for their money.
C) the need for extra accessories.
D) avoiding state sales taxes from Internet purchases.
E) a dislike of price haggling or negotiating.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In one of its least favorite actions,Amazon.com was caught manipulating its prices.Avid DVD buyers,buying in quantity for resale,found that the online retailer was offering different customers different prices for the same DVD,and complained vociferously.Company officials admitted that the company was trying to see how much it could charge for an item before buyers balked.Amazon was caught attempting
A) horizontal price-fixing.
B) price discrimination.
C) resale price maintenance.
D) predatory pricing.
E) bait and switch pricing.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The manufacturer of a new kind of fat-free ice cream that has the consistency and taste of regular ice cream is thinking of using a penetration pricing strategy for its new product.Which of the following conditions would argue against using a penetration pricing strategy for the tasty dessert treat?
A) The ice cream market is highly conservative.
B) Economies of scale in production would be substantial.
C) Retailers are not willing to carry new brands of ice cream in the already overcrowded category.
D) Once the initial price is set, it is nearly impossible to lower the price without alienating early buyers.
E) The ice cream market exhibits inelastic demand over a fairly broad range of prices.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reference value is developed by the consumer through
A) considering the amount of time and energy a consumer puts into the purchase process.
B) judging similar items used by the consumer's peers.
C) performing a careful break-even analysis.
D) comparing the costs and benefits of substitute items.
E) examining the true difference between customers' "needs" and "wants."
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are demand factors except
A) the price of similar products.
B) consumer tastes.
C) consumer income.
D) the availability of similar products.
E) the number of distribution outlets carrying the product.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-3b 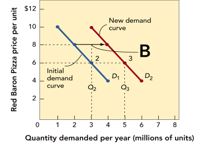 -Figure 11-3b shows that when the quantity demanded for Red Baron frozen cheese pizzas moves from 2 to 3 million units from the demand curve D1 to the demand curve D2,the profit
-Figure 11-3b shows that when the quantity demanded for Red Baron frozen cheese pizzas moves from 2 to 3 million units from the demand curve D1 to the demand curve D2,the profit
A) impacts cannot be determined. Figure 11-3b does not indicate what happens to profit when the quantity demanded changes.
B) increases from $2 to $3 per unit.
C) stays the same per unit.
D) increases from $6 to $8 per unit.
E) decreases from $8 to $6 per unit.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The total expense incurred by a firm in producing and marketing a product,which equals the sum of fixed cost and variable cost,is referred to as
A) overhead cost.
B) total cost.
C) unit cost.
D) average cost.
E) marginal cost.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You can buy a General Electric dishwasher for $399 or you can buy a similar Bosch brand dishwasher for $989.Since Bosch uses its pricing strategy to project a high-quality product image,it is most likely using __________ pricing.
A) yield management
B) standard markup
C) prestige
D) penetration
E) cost-plus-fixed-fee
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 374
Related Exams