A) integrating the service component of the marketing mix with efforts to influence consumer demand.
B) when the service provider is available but there is no demand.
C) charging different prices during different times of the day or during different days of the week to reflect variations in demand for the service.
D) the practice of changing prices for services in real time in response to supply and demand conditions.
E) the operating cost per hour per employee or technology subtracted from the revenue generated by each full-time employee equivalent.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A marketing strategy that alters a product's characteristic,such as its quality,performance,or appearance,to increase its value and sales to customers is referred to as
A) market modification.
B) product modification.
C) product repositioning.
D) market-product synergy.
E) product management.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Several factors explain why a consumer would be reluctant to adopt a new product.For example,a consumer might be reluctant to adopt a new product because of a value barrier,which occurs when
A) there are physical, economic, or social risks.
B) there are cultural differences.
C) the financial commitment is too great.
D) there is no incentive to change.
E) the product is not consistent with existing habits.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine that Eveready has developed solar rechargeable batteries that cost only slightly more to produce than the rechargeable batteries currently available.These solar batteries can be recharged by sunlight up to five times,after which they must be discarded.Unfortunately,the production process cannot be patented,so competitors could enter the market within a year.Which of the following would be the least sound marketing program decision?
A) Select a skimming pricing strategy to position the product as "premium."
B) Seek widespread distribution to gain a foothold in what might be a potentially huge market.
C) Limit production capacity until you are certain consumers will actually want the product.
D) Avoid a connection to the Eveready brand until the product has proven itself.
E) Use multiple brand names to discourage other competitors from entering the market.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A risk with __________ is that too many uses for one brand name can dilute the meaning of a brand for consumers.
A) brand extensions
B) product line extensions
C) co-branding
D) private branding
E) mixed branding
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following quotes from a new-product adopter would signal the need for a firm to counteract a psychological barrier?
A) "But I feel self-conscious wearing this."
B) "What if I can't make the monthly payments?"
C) "I don't want to try this if it means I have to swallow it with milk."
D) "Big deal, the only difference is the shape of the package."
E) "Sure I'll try it; why not!"
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What agency registers the trademarks of a firm?
A) U.S. Chamber of Commerce Trademark and Servicemark Office
B) U.S. Department of Commerce Trademark Registry
C) United Nations Global Trademark Clearinghouse
D) U.S. Federal Trade Commission-Trademark Division
E) U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The __________ stage of the product life cycle occurs when a product is launched to its intended target market.
A) concept
B) introduction
C) growth
D) maturity
E) decline
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interactive television with video-on-demand capabilities changes how people watch television and how consumers access the Internet.This technology requires significant customer education for most people.What type of product life cycle curve would be associated with this product?
A) generalized
B) high-learning
C) low-learning
D) fashion
E) fad
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A branding strategy that involves giving each product a distinct name when each brand is intended for a different market segment is referred to as
A) product differentiation branding.
B) multibranding.
C) mixed branding.
D) segmentation branding.
E) multiproduct branding.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Apple introduced the Apple II personal computer in 1977,industry analysts predicted that very few would be sold.However,a short time after the product was made available,consumers who were young,highly educated,adventuresome,and well-informed began buying them.While those buyers were relatively few in number,marketers such as IBM and Compaq were encouraged because other,less adventuresome consumers,like businesspeople,would likely adopt personal computers later.Based on the diffusion of innovation concept,those first buyers of personal computers were
A) early adopters.
B) early majority.
C) innovators.
D) product leaders.
E) diffusion leaders.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the diffusion of innovation concept,consumers who are venturesome,higher educated,and use multiple information sources in their adoption of products are called
A) innovators.
B) early adopters.
C) the early majority.
D) the late majority.
E) laggards.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the introduction stage of the product life cycle,the place (distribution) element of the marketing mix is highly involved with
A) increasing inventory levels at warehouses and distribution centers to meet potential demand.
B) gaining as many retail distribution outlets as possible, even though many will be reluctant to carry the new product.
C) using an intermodal logistics system to get the products through the marketing channel as quickly as possible.
D) building storage warehouses and distribution centers to establish an efficient infrastructure for the new product.
E) obtaining contracts with independent sales agents and brokers instead of using the firm's sales force.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marketing for a product in the introduction stage of its product life cycle should focus primarily on gaining awareness and which other marketing objective?
A) stress differentiation
B) stimulate trial
C) foster brand loyalty
D) gain as much distribution as possible
E) target a marketing niche
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When consumers think of Harley-Davidson,the image is of a masculine nonconformist.With Vespa motor scooters,the image is of a brainy environmentalist.Both Vespa and Harley-Davidson
A) have brand personalities.
B) avoid brand subcultures.
C) are logotypes.
D) use co-branding.
E) use product personification.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a characteristic of the growth stage of the product life cycle?
A) Advertising emphasis switches to selective demand.
B) A growing proportion of trial purchases come from brand loyal users.
C) Product features remain unchanged.
D) Profit margins increase as sales increase.
E) The product is sold in a narrowly selected number of retail outlets.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-5 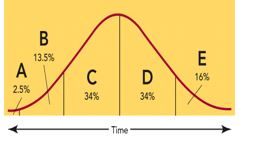 -The consumers represented by D in Figure 10-5 are called
-The consumers represented by D in Figure 10-5 are called
A) innovators.
B) late majority.
C) early majority.
D) early adopters.
E) laggards.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
IKEA sells a portable workbench called the Fahrtfull.The product has many positive features,and in German or Swedish markets,the name describes the product's features well (fahrt meaning travel) .This brand name in the United States,however,may not be as effective due to
A) disappointment when the product fails to perform as the brand name implies.
B) the poor attempt at humor, which makes consumers question product quality.
C) governmental restrictions on brand names that read or sound like bodily functions.
D) its unfavorable phonetic and semantic associations in English.
E) difficulty in showing "fahrtfull" in German and Swedish advertising.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
7Up is a lemon-lime carbonated soft drink that has been very successful in the United States.Dr.Pepper/Seven Up,Inc.,the maker of 7Up,uses a family branding strategy to market 7Up worldwide.In China,sales have suffered since the brand name means "death through drinking." Which criterion for picking a good band name did Dr.Pepper/Seven Up,Inc.violate when it chose to use a family branding strategy to market 7Up in China?
A) The name should have favorable phonetic and semantic associations in other languages.
B) The name should be simple.
C) The name should have no governmental restrictions.
D) The name should suggest the product's benefits.
E) The name should not be difficult to spell or pronounce.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Integrating the service component of the marketing mix with efforts to influence consumer demand is referred to as
A) customer experience management.
B) internal marketing.
C) product management.
D) capacity management.
E) seven Ps of services marketing.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 375
Related Exams