A) nucleus
B) axon
C) dendrite
D) cell body
E) terminal
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Contraction of the uterus during childbirth is stimulated by
A) prolactin.
B) luteinizing hormone (LH) .
C) oxytocin.
D) glucagon.
E) parathyroid hormone (PTH) .
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The exophthalmos seen in Graves disease results from hypersecretion of the
A) thyroid gland.
B) parathyroid glands.
C) posterior pituitary.
D) adrenal cortex.
E) pancreas.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is mismatched?
A) diencephalon-thalamus
B) brain stem-medulla oblongata
C) cerebral cortex-occipital lobe
D) cerebellum-midbrain
E) frontal lobe-prefrontal area
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of neuron is completely contained within the CNS?
A) sensory neuron
B) motor neuron
C) autonomic neuron
D) interneuron
E) sympathetic neuron
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gigantism can result from excessive secretion from the
A) posterior pituitary.
B) anterior pituitary.
C) adrenal medulla.
D) adrenal cortex.
E) pancreas.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A spinal nerve contains
A) axons of sensory neurons only.
B) myelinated axons only.
C) axons of motor neurons only.
D) dendrites only.
E) both sensory and motor axons.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an individual's pancreatic islets have been destroyed, the result will be
A) Cushing syndrome.
B) Graves disease.
C) type 2 diabetes mellitus.
D) Addison disease.
E) type 1 diabetes mellitus.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gaps in the myelin sheath are termed
A) nodes of Ranvier.
B) interaxons.
C) ganglia.
D) nuclei.
E) synapses.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient's pons has been affected by a rapidly growing tumor. Of the choices listed below, which is the most likely result?
A) loss of the normal breathing rhythm
B) hearing loss
C) inability to understand speech
D) inability to regulate blood pressure
E) inability to experience emotions
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are relaxing, having a snack and watching TV, when suddenly the entire house begins to shake violently. The activity of your _____ quickly decreases, while that of your _____ increases.
A) somatic nervous system; autonomic nervous system
B) autonomic nervous system; somatic nervous system
C) sympathetic division; parasympathetic division
D) sympathetic division; somatic nervous system
E) parasympathetic division; sympathetic division
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The arrow shows the direction of the nerve impulse in a neuron. Part X would represent a(n) ________. 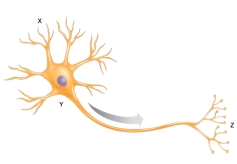
A) axon
B) dendrite
C) cell body
D) myelin sheath
E) axon terminal
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The arrow shows the direction of the nerve impulse in a neuron. Where is the neurotransmitter released from the neuron? 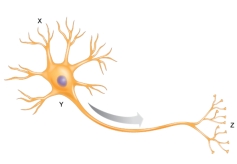
A) axon
B) dendrite
C) cell body
D) myelin sheath
E) axon terminal
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long, myelinated nerve fibers are called _____ in the PNS and _____ in the CNS.
A) tracts; nuclei
B) nerves; ganglia
C) ganglia; nuclei
D) nerves; tracts
E) ganglia; tracts
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spinal cord's gray matter is located
A) on the outside, surrounding a central core of white matter.
B) on the inside, surrounding the central canal.
C) on both the inside and the outside.
D) neither inside nor outside-the spinal cord is entirely white matter.
E) scattered among a collection of ganglia.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Only the glands of the endocrine system
A) uses chemical signals to bring about changes in target organs.
B) works to regulate the activities of other body systems.
C) uses the bloodstream to convey signals throughout the body.
D) helps to maintain homeostasis.
E) brings about rapid responses by target organs.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nerve impulse travels down a myelinated axon by
A) repolarization.
B) saltatory conduction.
C) simple diffusion.
D) integration.
E) summation.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these works by inhibiting dopamine reuptake into synapses?
A) cocaine
B) THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
C) heroin
D) marijuana
E) all drugs of abuse
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a neuron receives both excitatory and inhibitory signals, will an action potential be generated?
A) No, because any inhibitory signals will cancel out the excitatory signals.
B) Yes, but the action potential will be much smaller than if only excitatory signals were received.
C) It depends; if more excitatory than inhibitory signals are received, then an action potential may result.
D) Yes, because excitatory signals always stimulate an action potential.
E) It depends; if more inhibitory than excitatory signals are received, then the neuron will be free to produce an action potential.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ inhibits osteoclasts, and _____ stimulates them.
A) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) ; calcitonin
B) Growth hormone (GH) ; calcitonin
C) Epinephrine; norepinephrine
D) Calcitonin; parathyroid hormone (PTH)
E) Glucagon; growth hormone (GH)
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 52
Related Exams