A) Any evolution at any scale is considered microevolution.
B) Large scale changes over a long period of time.
C) Small scale changes over a long period of time.
D) Small scale changes over a short period of time.
E) Changes of any scale within microorganisms.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure shown here, flower color of a population is distributed in a bell-shaped normal curve. If the pink flower color increases in frequency in the population, this would illustrate
A) stabilizing selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effects of genetic drift are more significant in
A) large populations.
B) small populations.
C) populations that mate randomly.
D) populations that are undergoing natural selection.
E) populations in which the frequency of mutations is high.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What might occur in moth populations if pollution from industry was cleaned up, and the color of tree bark returned to its natural color?
A) Dark moths would continue to be the predominant phenotype.
B) Birds would now see the dark moths easier than the lighter color moths.
C) Dark- and light-colored moths would survive in equal numbers.
D) Both dark and light color moths would be preyed upon equally by birds.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the survivors of an original population survived due to specific phenotypes that they possessed, then this event is an example of
A) natural selection.
B) genetic drift.
C) founder effect.
D) industrial melanism.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure shown here, the bell-shaped curve representing the population illustrates that
A) most individuals are white, few individuals are pink.
B) most individuals are white, few individuals are yellow.
C) most individuals are yellow, few individuals are pink.
D) most individuals are pink, few individuals are yellow or white.
E) most individuals are yellow and white, few individuals are pink.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the typical mutation rate within a cell?
A) 1/100,000
B) 1/1000
C) 1/10,000
D) 1/100
E) 1/10
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
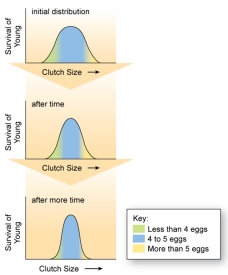 The figure shown here represents stabilizing selection. What happens when an individual is produced that possesses a trait far away from the mean value?
The figure shown here represents stabilizing selection. What happens when an individual is produced that possesses a trait far away from the mean value?
A) That extreme individual will likely not survive and reproduce.
B) That extreme individual will be more likely to survive and reproduce.
C) That extreme individual will have neither an advantage nor a disadvantage than other individuals.
D) All phenotypes have equal likelihood of surviving and reproducing.
E) The average phenotype is less likely to survive and reproduce.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what type of environment is being heterozygous in regards to the sickle cell trait an advantage?
A) An environment that has malaria.
B) An environment that is malaria free.
C) Environment that is exposed to a large amount of sunlight year round.
D) Environments that are degraded.
E) Cold and rainy environments favor the heterozygote.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Dominance causes an allele to become more common.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In random mating,
A) individuals choose the most attractive mate.
B) there is no influence on mate choice.
C) breeding occurs between two different species.
D) breeding occurs between two different subspecies.
E) fertile offspring are not produced.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Microevolution is not influenced by which of the following?
A) mutation
B) random mating
C) gene flow
D) natural selection
E) genetic drift
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Hardy-Weinberg formula, what does q2 represent?
A) frequency of the dominant allele
B) frequency of the recessive allele
C) frequency of the heterozygotes
D) frequency of the homozygous dominants
E) frequency of the homozygous recessives
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the average leg size of a reptile continually got smaller through generations, this would be an example of
A) disruptive selection.
B) stabilizing selection.
C) directional selection.
D) genetic drift.
E) bottleneck effect.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the genotype of an individual that is lives in protection from both sickle cell disease and malaria?
A) HbAHbA
B) HbAHbS
C) HbSHbS
D) HbS Hbs
E) HbA Hba
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If p2 = 0.04, what is the frequency of homozygous recessives in the population?
A) 0.04
B) 0.2
C) 0.32
D) 0.64
E) 0.8
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A female peacock chooses a male as a mate based on his showy plumage and courtship dance. This is an example of
A) random mating.
B) assortative mating.
C) sexual selection.
D) gene flow.
E) natural selection.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in their reliance on mutations for generating genetic variation?
A) Prokaryotes are smaller in size than eukaryotes.
B) Prokaryotes sexually reproduce, eukaryotes do not.
C) Eukaryotes sexually reproduce, prokaryotes do not.
D) Eukaryotes possess a nucleus, prokaryotes do not.
E) Prokaryotes are single-celled, eukaryotes are multicellular.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely an example of a founder effect event?
A) A random small group of a bird population migrates to an island and then returns to breed.
B) A random large group of a bird population migrates to an island and then returns to breed.
C) A selected small group of a bird population migrates to an island and then returns to breed.
D) A random small group of a bird population migrates to an island and does not return to breed.
E) A random large group of a bird population migrates to an island and does not return to breed.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which Hardy-Weinberg condition is violated by sexual selection?
A) no mutations
B) no natural selection
C) random mating
D) no genetic drift
E) no gene flow
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 50
Related Exams